Jiayu Bai
Diving into Kronecker Adapters: Component Design Matters
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Kronecker adapters have emerged as a promising approach for fine-tuning large-scale models, enabling high-rank updates through tunable component structures. However, existing work largely treats the component structure as a fixed or heuristic design choice, leaving the dimensions and number of Kronecker components underexplored. In this paper, we identify component structure as a key factor governing the capacity of Kronecker adapters. We perform a fine-grained analysis of both the dimensions and number of Kronecker components. In particular, we show that the alignment between Kronecker adapters and full fine-tuning depends on component configurations. Guided by these insights, we propose Component Designed Kronecker Adapters (CDKA). We further provide parameter-budget-aware configuration guidelines and a tailored training stabilization strategy for practical deployment. Experiments across various natural language processing tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of CDKA. Code is available at https://github.com/rainstonee/CDKA.
SambaNova SN40L: Scaling the AI Memory Wall with Dataflow and Composition of Experts
May 13, 2024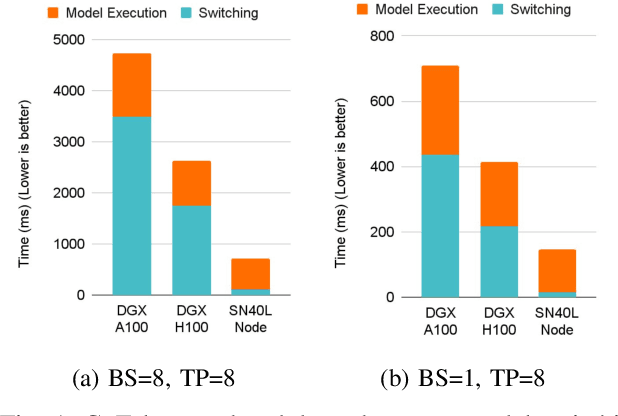
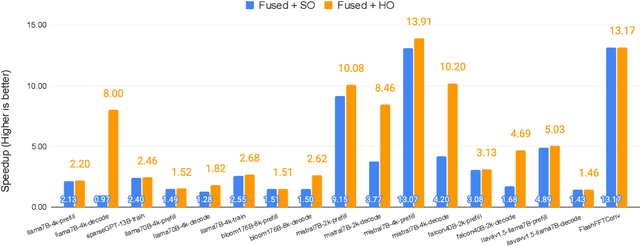
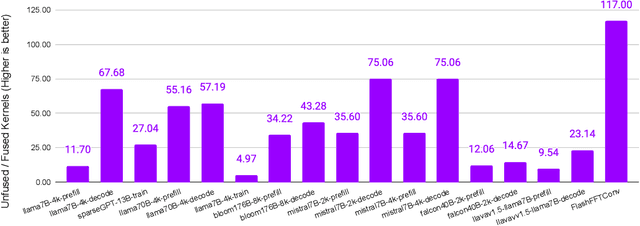
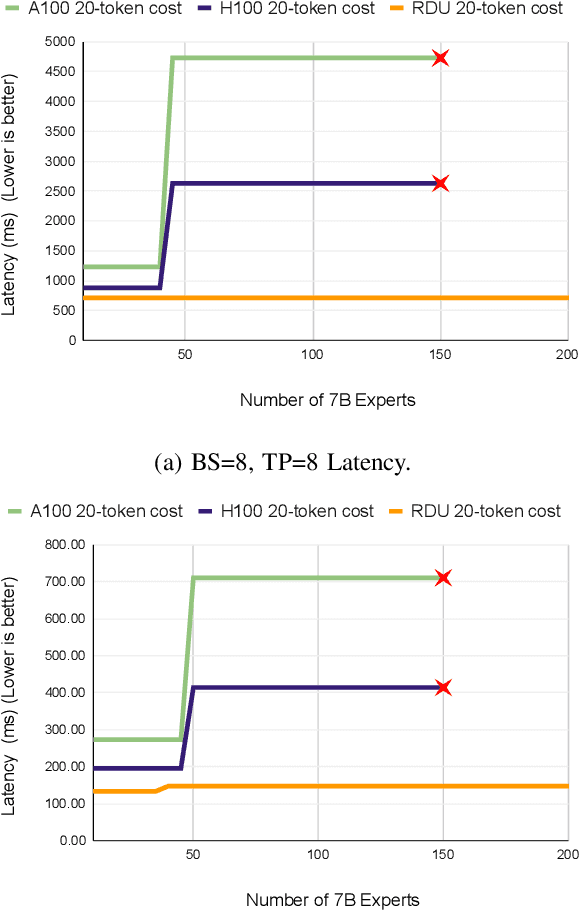
Abstract:Monolithic large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have paved the way for modern generative AI applications. Training, serving, and maintaining monolithic LLMs at scale, however, remains prohibitively expensive and challenging. The disproportionate increase in compute-to-memory ratio of modern AI accelerators have created a memory wall, necessitating new methods to deploy AI. Composition of Experts (CoE) is an alternative modular approach that lowers the cost and complexity of training and serving. However, this approach presents two key challenges when using conventional hardware: (1) without fused operations, smaller models have lower operational intensity, which makes high utilization more challenging to achieve; and (2) hosting a large number of models can be either prohibitively expensive or slow when dynamically switching between them. In this paper, we describe how combining CoE, streaming dataflow, and a three-tier memory system scales the AI memory wall. We describe Samba-CoE, a CoE system with 150 experts and a trillion total parameters. We deploy Samba-CoE on the SambaNova SN40L Reconfigurable Dataflow Unit (RDU) - a commercial dataflow accelerator architecture that has been co-designed for enterprise inference and training applications. The chip introduces a new three-tier memory system with on-chip distributed SRAM, on-package HBM, and off-package DDR DRAM. A dedicated inter-RDU network enables scaling up and out over multiple sockets. We demonstrate speedups ranging from 2x to 13x on various benchmarks running on eight RDU sockets compared with an unfused baseline. We show that for CoE inference deployments, the 8-socket RDU Node reduces machine footprint by up to 19x, speeds up model switching time by 15x to 31x, and achieves an overall speedup of 3.7x over a DGX H100 and 6.6x over a DGX A100.
Generating Game Levels of Diverse Behaviour Engagement
Jul 05, 2022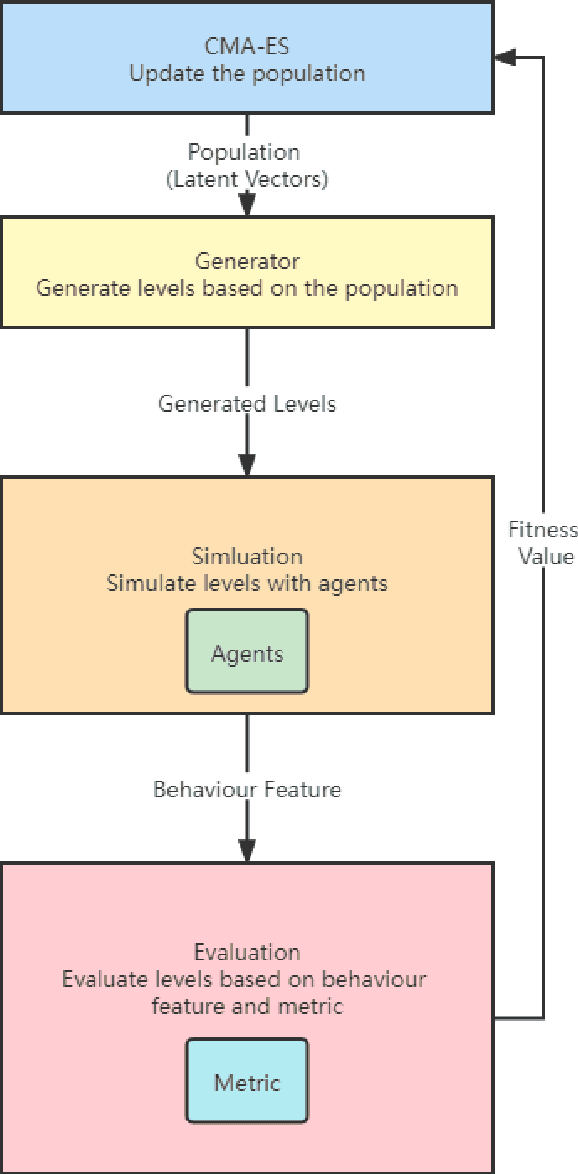

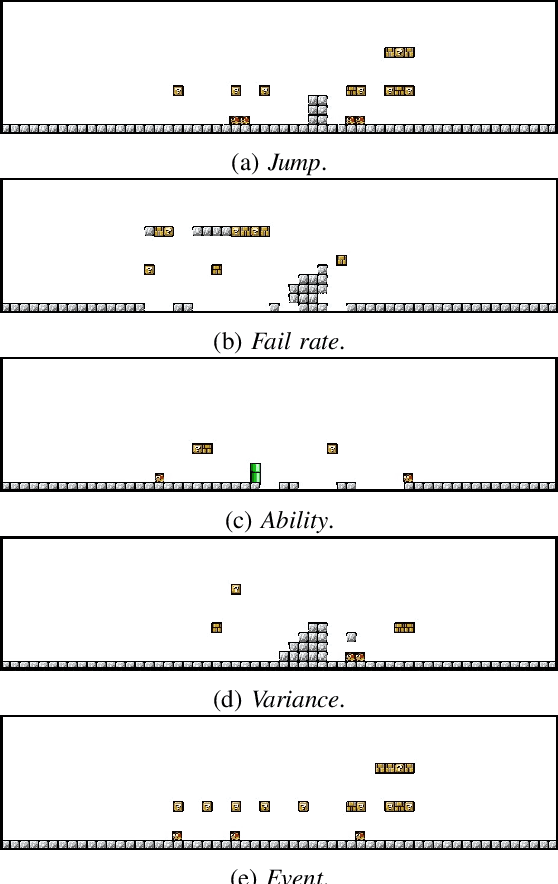
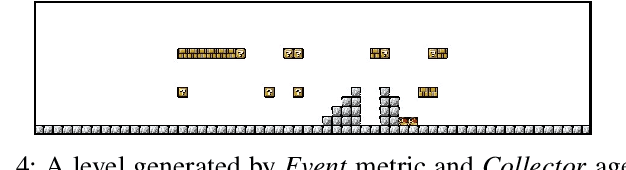
Abstract:Recent years, there has been growing interests in experience-driven procedural level generation. Various metrics have been formulated to model player experience and help generate personalised levels. In this work, we question whether experience metrics can adapt to agents with different personas. We start by reviewing existing metrics for evaluating game levels. Then, focusing on platformer games, we design a framework integrating various agents and evaluation metrics. Experimental studies on \emph{Super Mario Bros.} indicate that using the same evaluation metrics but agents with different personas can generate levels for particular persona. It implies that, for simple games, using a game-playing agent of specific player archetype as a level tester is probably all we need to generate levels of diverse behaviour engagement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge