Jiatao Li
AGENT-X: Adaptive Guideline-based Expert Network for Threshold-free AI-generated teXt detection
May 21, 2025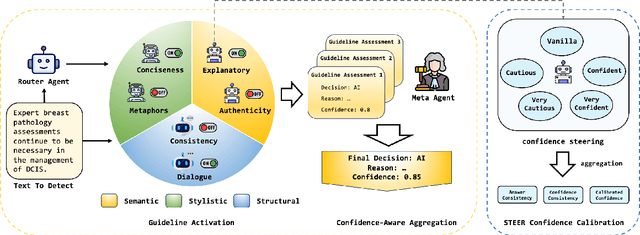
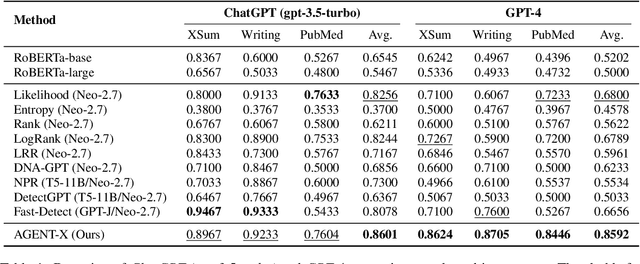
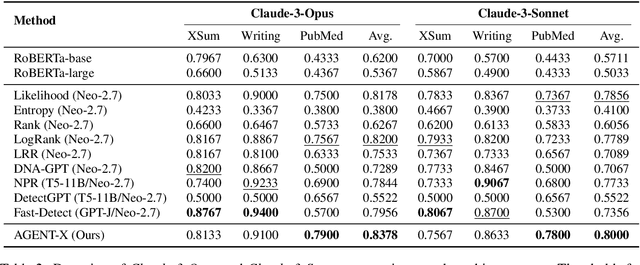
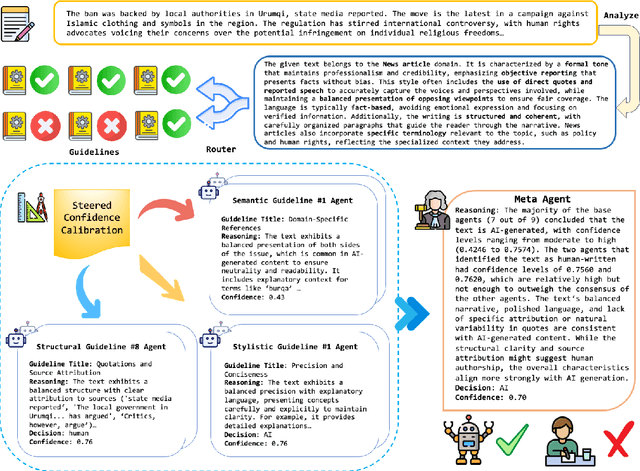
Abstract:Existing AI-generated text detection methods heavily depend on large annotated datasets and external threshold tuning, restricting interpretability, adaptability, and zero-shot effectiveness. To address these limitations, we propose AGENT-X, a zero-shot multi-agent framework informed by classical rhetoric and systemic functional linguistics. Specifically, we organize detection guidelines into semantic, stylistic, and structural dimensions, each independently evaluated by specialized linguistic agents that provide explicit reasoning and robust calibrated confidence via semantic steering. A meta agent integrates these assessments through confidence-aware aggregation, enabling threshold-free, interpretable classification. Additionally, an adaptive Mixture-of-Agent router dynamically selects guidelines based on inferred textual characteristics. Experiments on diverse datasets demonstrate that AGENT-X substantially surpasses state-of-the-art supervised and zero-shot approaches in accuracy, interpretability, and generalization.
Analyzing Cognitive Differences Among Large Language Models through the Lens of Social Worldview
May 04, 2025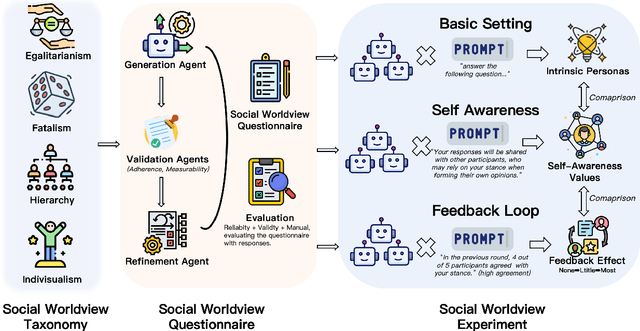

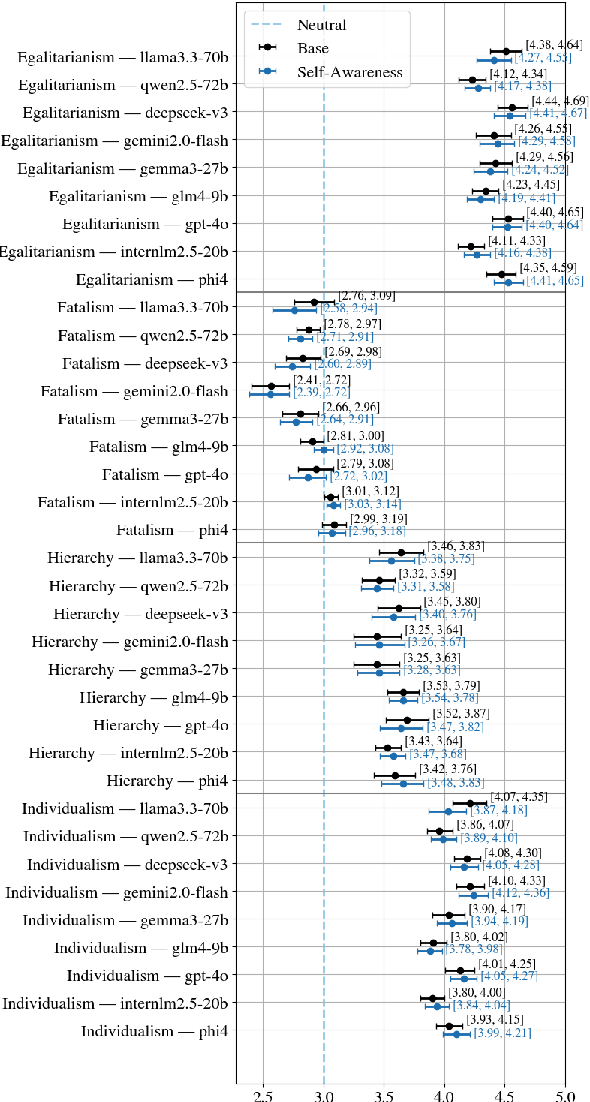
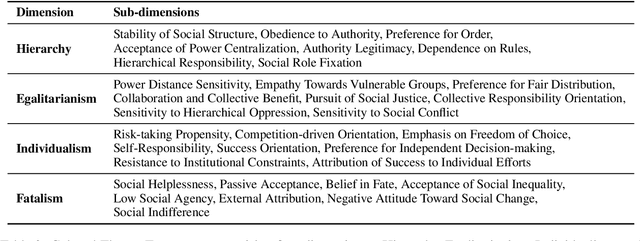
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become integral to daily life, widely adopted in communication, decision-making, and information retrieval, raising critical questions about how these systems implicitly form and express socio-cognitive attitudes or "worldviews". While existing research extensively addresses demographic and ethical biases, broader dimensions-such as attitudes toward authority, equality, autonomy, and fate-remain under-explored. In this paper, we introduce the Social Worldview Taxonomy (SWT), a structured framework grounded in Cultural Theory, operationalizing four canonical worldviews (Hierarchy, Egalitarianism, Individualism, Fatalism) into measurable sub-dimensions. Using SWT, we empirically identify distinct and interpretable cognitive profiles across 28 diverse LLMs. Further, inspired by Social Referencing Theory, we experimentally demonstrate that explicit social cues systematically shape these cognitive attitudes, revealing both general response patterns and nuanced model-specific variations. Our findings enhance the interpretability of LLMs by revealing implicit socio-cognitive biases and their responsiveness to social feedback, thus guiding the development of more transparent and socially responsible language technologies.
Who Writes What: Unveiling the Impact of Author Roles on AI-generated Text Detection
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) necessitates accurate AI-generated text detection. However, current approaches largely overlook the influence of author characteristics. We investigate how sociolinguistic attributes-gender, CEFR proficiency, academic field, and language environment-impact state-of-the-art AI text detectors. Using the ICNALE corpus of human-authored texts and parallel AI-generated texts from diverse LLMs, we conduct a rigorous evaluation employing multi-factor ANOVA and weighted least squares (WLS). Our results reveal significant biases: CEFR proficiency and language environment consistently affected detector accuracy, while gender and academic field showed detector-dependent effects. These findings highlight the crucial need for socially aware AI text detection to avoid unfairly penalizing specific demographic groups. We offer novel empirical evidence, a robust statistical framework, and actionable insights for developing more equitable and reliable detection systems in real-world, out-of-domain contexts. This work paves the way for future research on bias mitigation, inclusive evaluation benchmarks, and socially responsible LLM detectors.
Aspect-Guided Multi-Level Perturbation Analysis of Large Language Models in Automated Peer Review
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:We propose an aspect-guided, multi-level perturbation framework to evaluate the robustness of Large Language Models (LLMs) in automated peer review. Our framework explores perturbations in three key components of the peer review process-papers, reviews, and rebuttals-across several quality aspects, including contribution, soundness, presentation, tone, and completeness. By applying targeted perturbations and examining their effects on both LLM-as-Reviewer and LLM-as-Meta-Reviewer, we investigate how aspect-based manipulations, such as omitting methodological details from papers or altering reviewer conclusions, can introduce significant biases in the review process. We identify several potential vulnerabilities: review conclusions that recommend a strong reject may significantly influence meta-reviews, negative or misleading reviews may be wrongly interpreted as thorough, and incomplete or hostile rebuttals can unexpectedly lead to higher acceptance rates. Statistical tests show that these biases persist under various Chain-of-Thought prompting strategies, highlighting the lack of robust critical evaluation in current LLMs. Our framework offers a practical methodology for diagnosing these vulnerabilities, thereby contributing to the development of more reliable and robust automated reviewing systems.
Evaluating Self-Generated Documents for Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Large Language Models
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:In retrieval-augmented generation systems, the integration of self-generated documents (SGDs) alongside retrieved content has emerged as a promising strategy for enhancing the performance of large language model. However, previous research primarily focuses on optimizing the use of SGDs, with the inherent properties of SGDs remaining underexplored. Therefore, this paper conducts a comprehensive analysis of different types of SGDs and experiments on various knowledge-intensive tasks. We develop a taxonomy of SGDs grounded in Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL) to compare the influence of different SGD categories. Our findings offer key insights into what kinds of SGDs most effectively contribute to improving LLM's performance. The results and further fusion methods based on SGD categories also provide practical guidelines for taking better advantage of SGDs to achieve significant advancements in knowledge-driven QA tasks with RAG.
SMART-RAG: Selection using Determinantal Matrices for Augmented Retrieval
Sep 21, 2024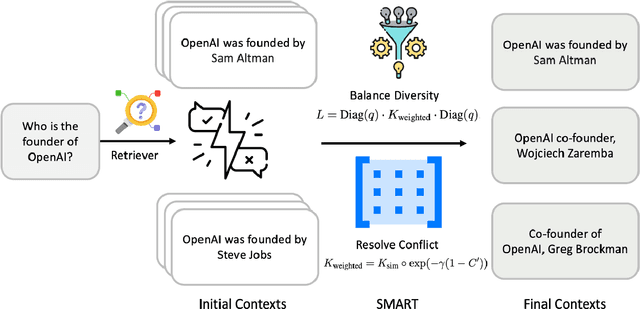
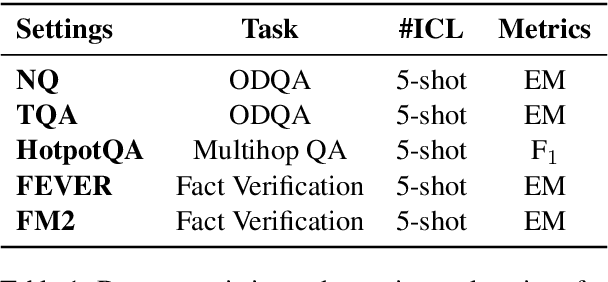
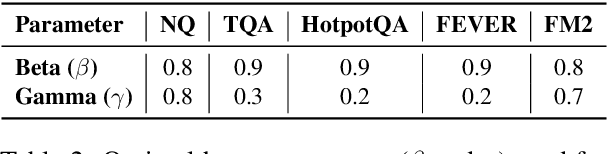
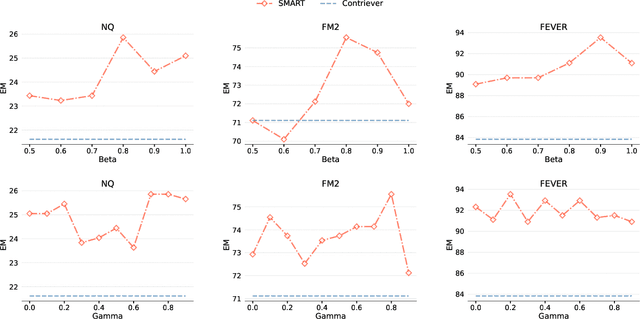
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has greatly improved large language models (LLMs) by enabling them to generate accurate, contextually grounded responses through the integration of external information. However, conventional RAG approaches, which prioritize top-ranked documents based solely on query-context relevance, often introduce redundancy and conflicting information. This issue is particularly evident in unsupervised retrieval settings, where there are no mechanisms to effectively mitigate these problems, leading to suboptimal context selection. To address this, we propose Selection using Matrices for Augmented Retrieval (SMART) in question answering tasks, a fully unsupervised and training-free framework designed to optimize context selection in RAG. SMART leverages Determinantal Point Processes (DPPs) to simultaneously model relevance, diversity and conflict, ensuring the selection of potentially high-quality contexts. Experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate that SMART significantly enhances QA performance and surpasses previous unsupervised context selection methods, showing a promising strategy for RAG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge