Jianing Ding
Coordinated Navigation Control of Cross-Domain Unmanned Systems via Guiding Vector Fields
Dec 18, 2023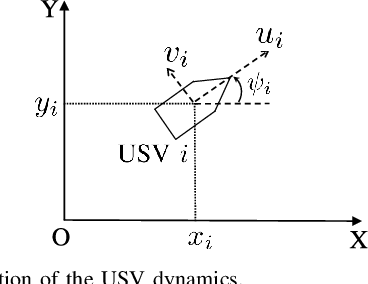
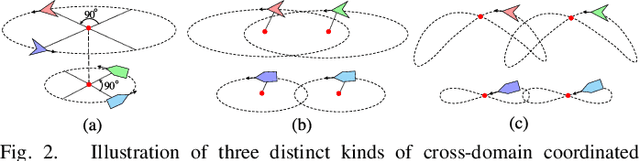
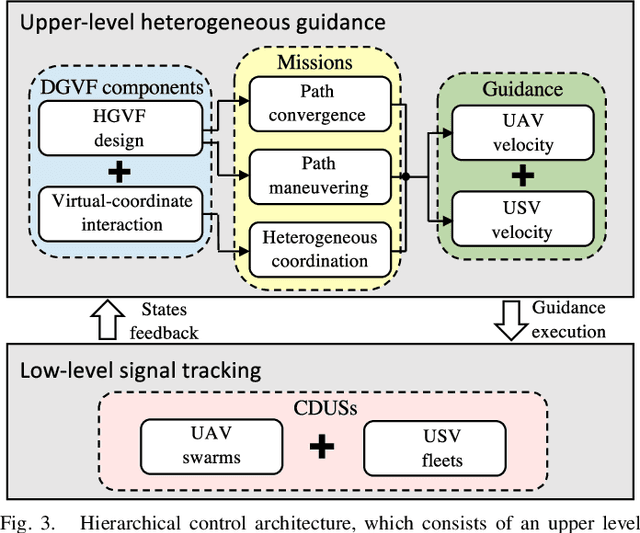
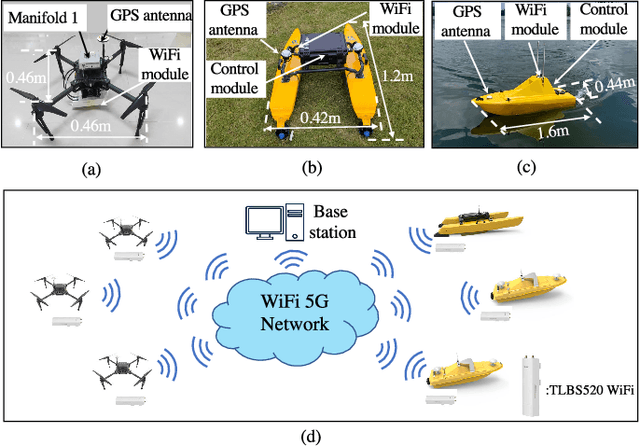
Abstract:This paper proposes a distributed guiding-vector-field (DGVF) controller for cross-domain unmanned systems (CDUSs) consisting of heterogeneous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned surface vehicles (USVs), to achieve coordinated navigation whereas maneuvering along their prescribed paths. In particular, the DGVF controller provides a hierarchical architecture of an upper-level heterogeneous guidance velocity controller and a lower-level signal tracking regulator. Therein, the upper-level controller is to govern multiple heterogeneous USVs and UAVs to approach and maneuver along the prescribed paths and coordinate the formation simultaneously, whereas the low-level regulator is to track the corresponding desired guidance signals provided by the upper-level module. Significantly, the heterogeneous coordination among neighboring UAVs and USVs is achieved merely by the lightweight communication of a scalar (i.e., the additional virtual coordinate), which substantially decreases the communication and computational costs. Sufficient conditions assuring asymptotical convergence of the closed-loop system are derived in presence of the exponentially vanishing tracking errors. Finally, real-lake experiments are conducted on a self-established cross-domain heterogeneous platform consisting of three M-100 UAVs, two HUSTER-16 USVs, a HUSTER-12C USV, and a WiFi 5G wireless communication station to verify the effectiveness of the present DGVF controller.
* 14 pages
Spontaneous-Ordering Platoon Control for Multirobot Path Navigation Using Guiding Vector Fields
Nov 02, 2023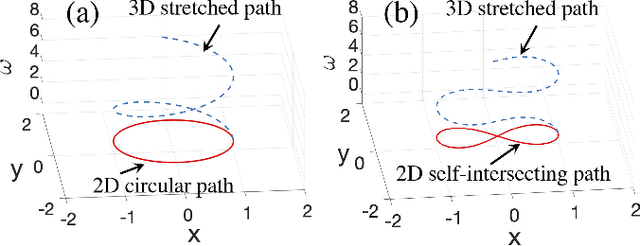
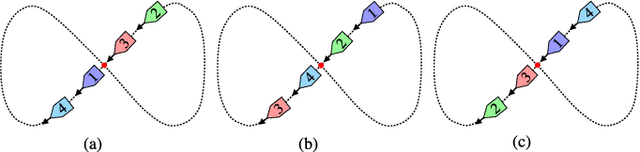
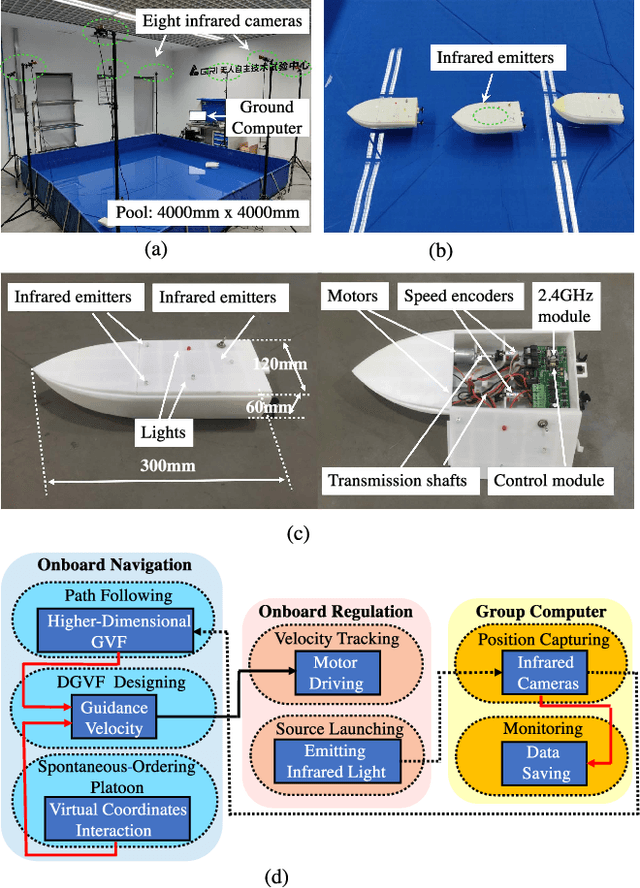
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a distributed guiding-vector-field (DGVF) algorithm for a team of robots to form a spontaneous-ordering platoon moving along a predefined desired path in the n-dimensional Euclidean space. Particularly, by adding a path parameter as an additional virtual coordinate to each robot, the DGVF algorithm can eliminate the singular points where the vector fields vanish, and govern robots to approach a closed and even self-intersecting desired path. Then, the interactions among neighboring robots and a virtual target robot through their virtual coordinates enable the realization of the desired platoon; in particular, relative parametric displacements can be achieved with arbitrary ordering sequences. Rigorous analysis is provided to guarantee the global convergence to the spontaneous-ordering platoon on the common desired path from any initial positions. 2D experiments using three HUSTER-0.3 unmanned surface vessels (USVs) are conducted to validate the practical effectiveness of the proposed DGVF algorithm, and 3D numerical simulations are presented to demonstrate its effectiveness and robustness when tackling higher-dimensional multi-robot path-navigation missions and some robots breakdown.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge