Jiangming Shi
Robust Pseudo-label Learning with Neighbor Relation for Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
May 09, 2024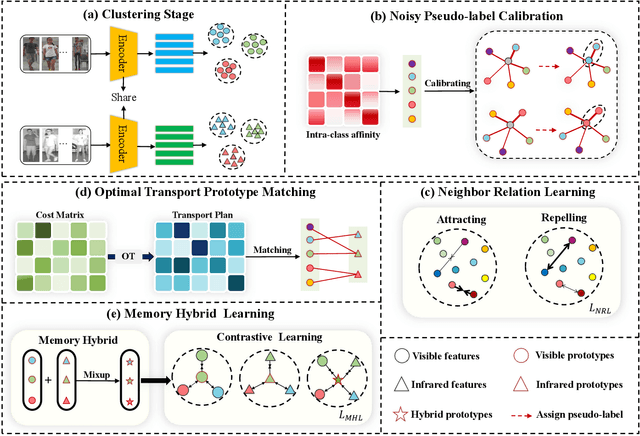
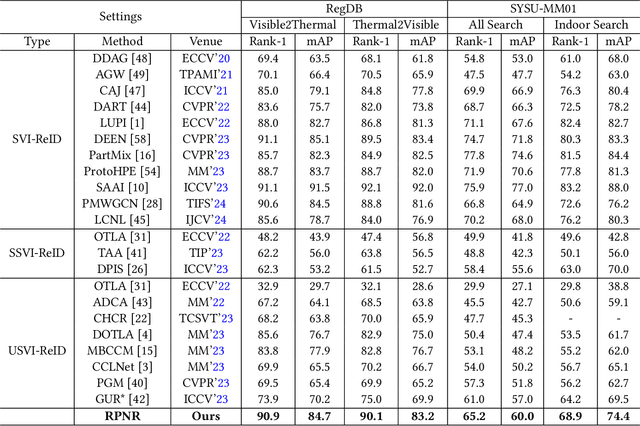
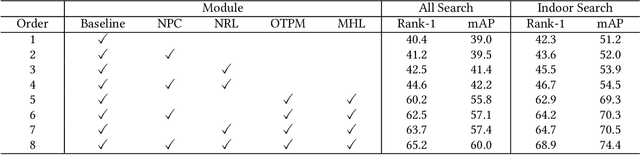

Abstract:Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification (USVI-ReID) presents a formidable challenge, which aims to match pedestrian images across visible and infrared modalities without any annotations. Recently, clustered pseudo-label methods have become predominant in USVI-ReID, although the inherent noise in pseudo-labels presents a significant obstacle. Most existing works primarily focus on shielding the model from the harmful effects of noise, neglecting to calibrate noisy pseudo-labels usually associated with hard samples, which will compromise the robustness of the model. To address this issue, we design a Robust Pseudo-label Learning with Neighbor Relation (RPNR) framework for USVI-ReID. To be specific, we first introduce a straightforward yet potent Noisy Pseudo-label Calibration module to correct noisy pseudo-labels. Due to the high intra-class variations, noisy pseudo-labels are difficult to calibrate completely. Therefore, we introduce a Neighbor Relation Learning module to reduce high intra-class variations by modeling potential interactions between all samples. Subsequently, we devise an Optimal Transport Prototype Matching module to establish reliable cross-modality correspondences. On that basis, we design a Memory Hybrid Learning module to jointly learn modality-specific and modality-invariant information. Comprehensive experiments conducted on two widely recognized benchmarks, SYSU-MM01 and RegDB, demonstrate that RPNR outperforms the current state-of-the-art GUR with an average Rank-1 improvement of 10.3%. The source codes will be released soon.
Progressive Contrastive Learning with Multi-Prototype for Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification
Feb 29, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification (USVI-ReID) aims to match specified people in infrared images to visible images without annotation, and vice versa. USVI-ReID is a challenging yet under-explored task. Most existing methods address the USVI-ReID problem using cluster-based contrastive learning, which simply employs the cluster center as a representation of a person. However, the cluster center primarily focuses on shared information, overlooking disparity. To address the problem, we propose a Progressive Contrastive Learning with Multi-Prototype (PCLMP) method for USVI-ReID. In brief, we first generate the hard prototype by selecting the sample with the maximum distance from the cluster center. This hard prototype is used in the contrastive loss to emphasize disparity. Additionally, instead of rigidly aligning query images to a specific prototype, we generate the dynamic prototype by randomly picking samples within a cluster. This dynamic prototype is used to retain the natural variety of features while reducing instability in the simultaneous learning of both common and disparate information. Finally, we introduce a progressive learning strategy to gradually shift the model's attention towards hard samples, avoiding cluster deterioration. Extensive experiments conducted on the publicly available SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. PCLMP outperforms the existing state-of-the-art method with an average mAP improvement of 3.9%. The source codes will be released.
Multi-Memory Matching for Unsupervised Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification (USL-VI-ReID) is a promising yet challenging retrieval task. The key challenges in USL-VI-ReID are to effectively generate pseudo-labels and establish pseudo-label correspondences across modalities without relying on any prior annotations. Recently, clustered pseudo-label methods have gained more attention in USL-VI-ReID. However, previous methods fell short of fully exploiting the individual nuances, as they simply utilized a single memory that represented an identity to establish cross-modality correspondences, resulting in ambiguous cross-modality correspondences. To address the problem, we propose a Multi-Memory Matching (MMM) framework for USL-VI-ReID. We first design a Cross-Modality Clustering (CMC) module to generate the pseudo-labels through clustering together both two modality samples. To associate cross-modality clustered pseudo-labels, we design a Multi-Memory Learning and Matching (MMLM) module, ensuring that optimization explicitly focuses on the nuances of individual perspectives and establishes reliable cross-modality correspondences. Finally, we design a Soft Cluster-level Alignment (SCA) module to narrow the modality gap while mitigating the effect of noise pseudo-labels through a soft many-to-many alignment strategy. Extensive experiments on the public SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets demonstrate the reliability of the established cross-modality correspondences and the effectiveness of our MMM. The source codes will be released.
CLIP-guided Federated Learning on Heterogeneous and Long-Tailed Data
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) provides a decentralized machine learning paradigm where a server collaborates with a group of clients to learn a global model without accessing the clients' data. User heterogeneity is a significant challenge for FL, which together with the class-distribution imbalance further enhances the difficulty of FL. Great progress has been made in large vision-language models, such as Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), which paves a new way for image classification and object recognition. Inspired by the success of CLIP on few-shot and zero-shot learning, we use CLIP to optimize the federated learning between server and client models under its vision-language supervision. It is promising to mitigate the user heterogeneity and class-distribution balance due to the powerful cross-modality representation and rich open-vocabulary prior knowledge. In this paper, we propose the CLIP-guided FL (CLIP2FL) method on heterogeneous and long-tailed data. In CLIP2FL, the knowledge of the off-the-shelf CLIP model is transferred to the client-server models, and a bridge is built between the client and server. Specifically, for client-side learning, knowledge distillation is conducted between client models and CLIP to improve the ability of client-side feature representation. For server-side learning, in order to mitigate the heterogeneity and class-distribution imbalance, we generate federated features to retrain the server model. A prototype contrastive learning with the supervision of the text encoder of CLIP is introduced to generate federated features depending on the client-side gradients, and they are used to retrain a balanced server classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge