Jeonghwan Choi
Completing Missing Annotation: Multi-Agent Debate for Accurate and Scalable Relevant Assessment for IR Benchmarks
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) evaluation remains challenging due to incomplete IR benchmark datasets that contain unlabeled relevant chunks. While LLMs and LLM-human hybrid strategies reduce costly human effort, they remain prone to LLM overconfidence and ineffective AI-to-human escalation. To address this, we propose DREAM, a multi-round debate-based relevance assessment framework with LLM agents, built on opposing initial stances and iterative reciprocal critique. Through our agreement-based debate, it yields more accurate labeling for certain cases and more reliable AI-to-human escalation for uncertain ones, achieving 95.2% labeling accuracy with only 3.5% human involvement. Using DREAM, we build BRIDGE, a refined benchmark that mitigates evaluation bias and enables fairer retriever comparison by uncovering 29,824 missing relevant chunks. We then re-benchmark IR systems and extend evaluation to RAG, showing that unaddressed holes not only distort retriever rankings but also drive retrieval-generation misalignment. The relevance assessment framework is available at https: //github.com/DISL-Lab/DREAM-ICLR-26; and the BRIDGE dataset is available at https://github.com/DISL-Lab/BRIDGE-Benchmark.
Learning to Verify Summary Facts with Fine-Grained LLM Feedback
Dec 14, 2024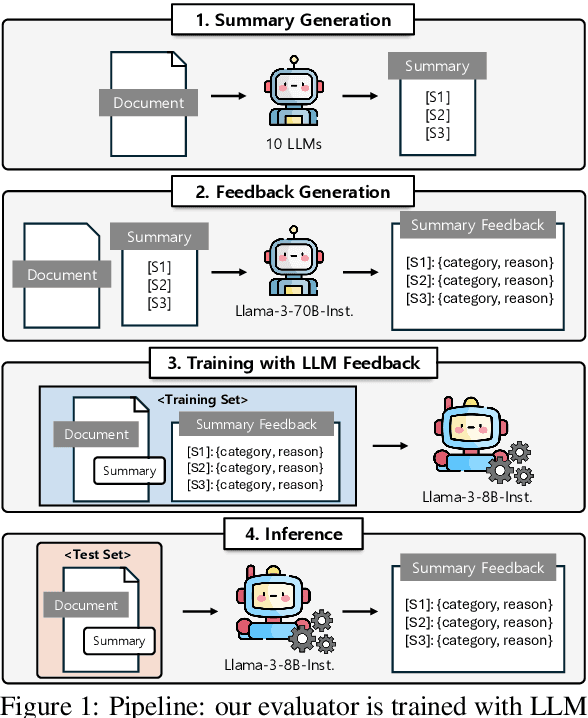
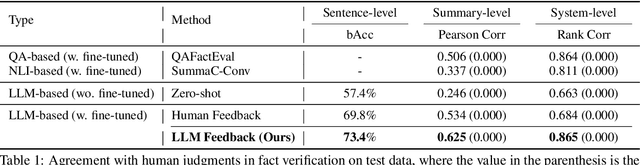
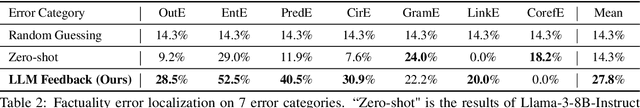

Abstract:Training automatic summary fact verifiers often faces the challenge of a lack of human-labeled data. In this paper, we explore alternative way of leveraging Large Language Model (LLM) generated feedback to address the inherent limitation of using human-labeled data. We introduce FineSumFact, a large-scale dataset containing fine-grained factual feedback on summaries. We employ 10 distinct LLMs for diverse summary generation and Llama-3-70B-Instruct for feedback. We utilize this dataset to fine-tune the lightweight open-source model Llama-3-8B-Instruct, optimizing resource efficiency while maintaining high performance. Our experimental results reveal that the model trained on extensive LLM-generated datasets surpasses that trained on smaller human-annotated datasets when evaluated using human-generated test sets. Fine-tuning fact verification models with LLM feedback can be more effective and cost-efficient than using human feedback. The dataset is available at https://github.com/DISL-Lab/FineSumFact.
DM: Dual-path Magnitude Network for General Speech Restoration
Sep 13, 2024


Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel general speech restoration model: the Dual-path Magnitude (DM) network, designed to address multiple distortions including noise, reverberation, and bandwidth degradation effectively. The DM network employs dual parallel magnitude decoders that share parameters: one uses a masking-based algorithm for distortion removal and the other employs a mapping-based approach for speech restoration. A novel aspect of the DM network is the integration of the magnitude spectrogram output from the masking decoder into the mapping decoder through a skip connection, enhancing the overall restoration capability. This integrated approach overcomes the inherent limitations observed in previous models, as detailed in a step-by-step analysis. The experimental results demonstrate that the DM network outperforms other baseline models in the comprehensive aspect of general speech restoration, achieving substantial restoration with fewer parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge