Jeffrey Dominic
Data-Limited Tissue Segmentation using Inpainting-Based Self-Supervised Learning
Oct 14, 2022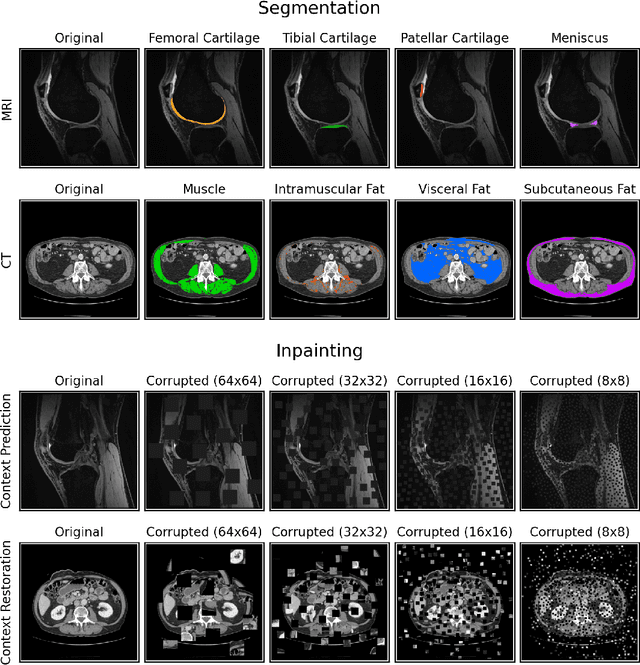
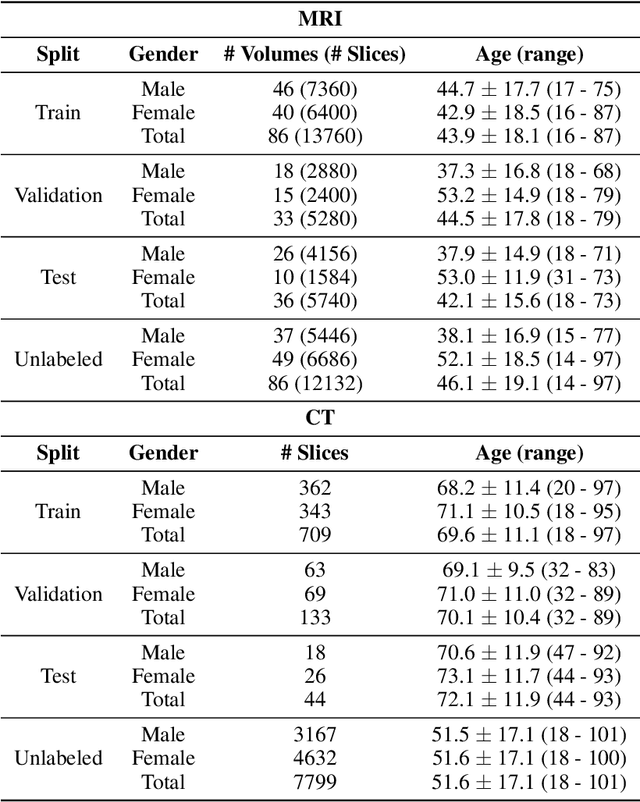
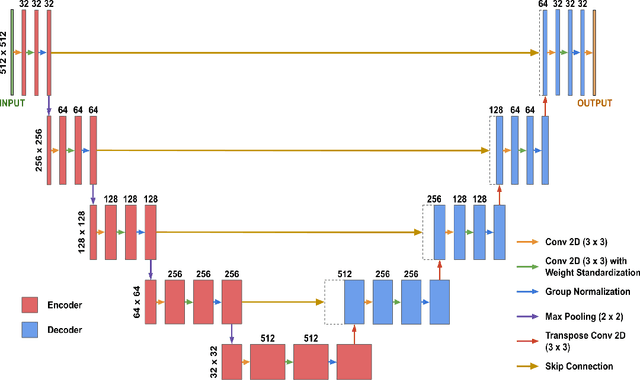
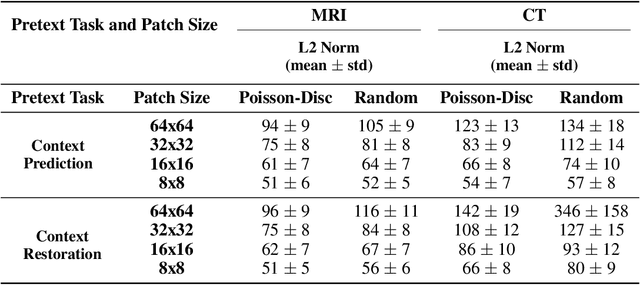
Abstract:Although supervised learning has enabled high performance for image segmentation, it requires a large amount of labeled training data, which can be difficult to obtain in the medical imaging field. Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods involving pretext tasks have shown promise in overcoming this requirement by first pretraining models using unlabeled data. In this work, we evaluate the efficacy of two SSL methods (inpainting-based pretext tasks of context prediction and context restoration) for CT and MRI image segmentation in label-limited scenarios, and investigate the effect of implementation design choices for SSL on downstream segmentation performance. We demonstrate that optimally trained and easy-to-implement inpainting-based SSL segmentation models can outperform classically supervised methods for MRI and CT tissue segmentation in label-limited scenarios, for both clinically-relevant metrics and the traditional Dice score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge