Jean Le'Clerc Arrastia
University of Bremen, aisencia
Model Stitching and Visualization How GAN Generators can Invert Networks in Real-Time
Feb 04, 2023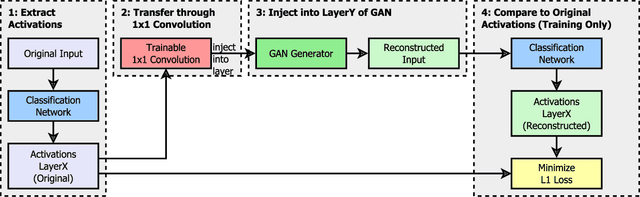
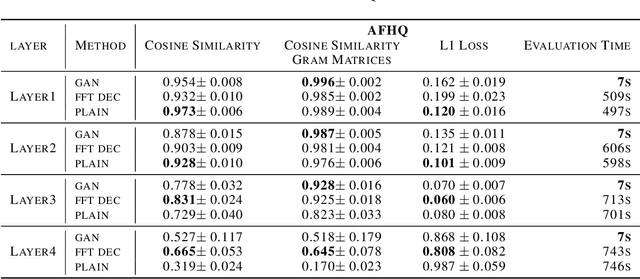
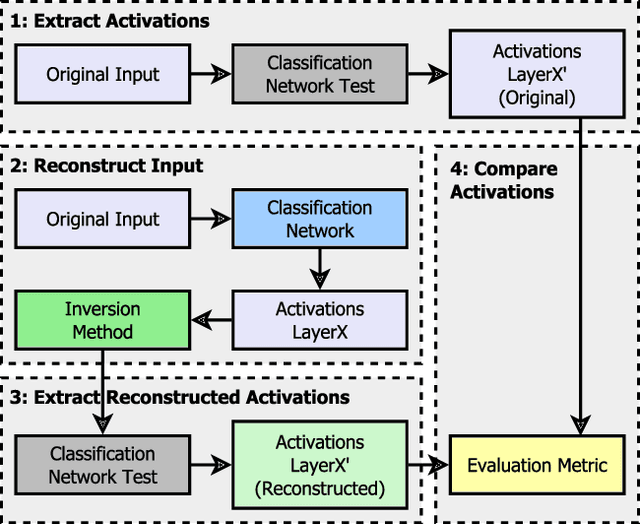
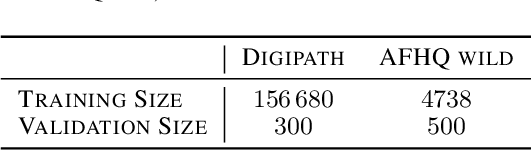
Abstract:Critical applications, such as in the medical field, require the rapid provision of additional information to interpret decisions made by deep learning methods. In this work, we propose a fast and accurate method to visualize activations of classification and semantic segmentation networks by stitching them with a GAN generator utilizing convolutions. We test our approach on images of animals from the AFHQ wild dataset and real-world digital pathology scans of stained tissue samples. Our method provides comparable results to established gradient descent methods on these datasets while running about two orders of magnitude faster.
Deeply supervised UNet for semantic segmentation to assist dermatopathological assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Mar 08, 2021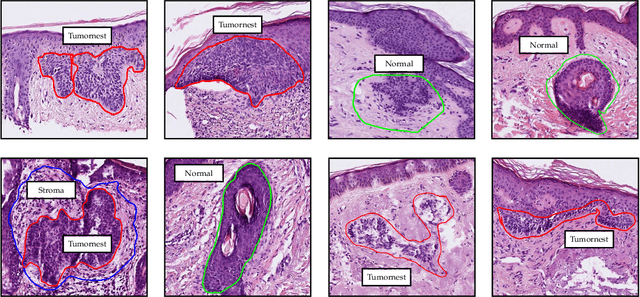
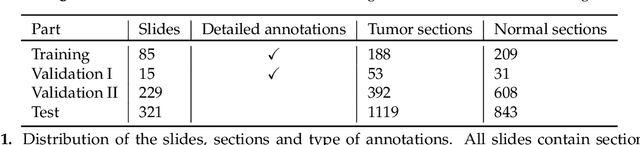
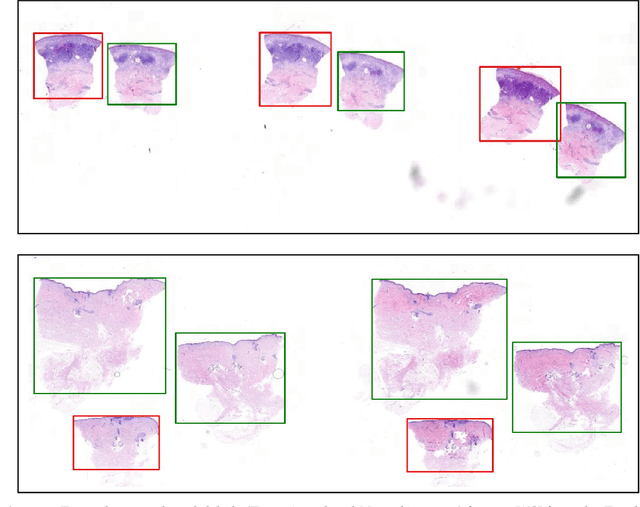
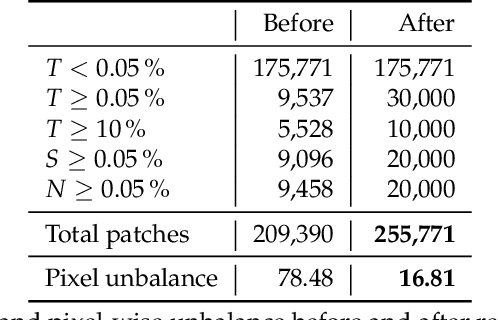
Abstract:Accurate and fast assessment of resection margins is an essential part of a dermatopathologist's clinical routine. In this work, we successfully develop a deep learning method to assist the pathologists by marking critical regions that have a high probability of exhibiting pathological features in Whole Slide Images (WSI). We focus on detecting Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) through semantic segmentation using several models based on the UNet architecture. The study includes 650 WSI with 3443 tissue sections in total. Two clinical dermatopathologists annotated the data, marking tumor tissues' exact location on 100 WSI. The rest of the data, with ground-truth section-wise labels, is used to further validate and test the models. We analyze two different encoders for the first part of the UNet network and two additional training strategies: a) deep supervision, b) linear combination of decoder outputs, and obtain some interpretations about what the network's decoder does in each case. The best model achieves over 96%, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity on the test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge