Jason I. Hong
MM-SCALE: Grounded Multimodal Moral Reasoning via Scalar Judgment and Listwise Alignment
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) continue to struggle to make morally salient judgments in multimodal and socially ambiguous contexts. Prior works typically rely on binary or pairwise supervision, which often fail to capture the continuous and pluralistic nature of human moral reasoning. We present MM-SCALE (Multimodal Moral Scale), a large-scale dataset for aligning VLMs with human moral preferences through 5-point scalar ratings and explicit modality grounding. Each image-scenario pair is annotated with moral acceptability scores and grounded reasoning labels by humans using an interface we tailored for data collection, enabling listwise preference optimization over ranked scenario sets. By moving from discrete to scalar supervision, our framework provides richer alignment signals and finer calibration of multimodal moral reasoning. Experiments show that VLMs fine-tuned on MM-SCALE achieve higher ranking fidelity and more stable safety calibration than those trained with binary signals.
Understanding Frontline Workers' and Unhoused Individuals' Perspectives on AI Used in Homeless Services
Mar 17, 2023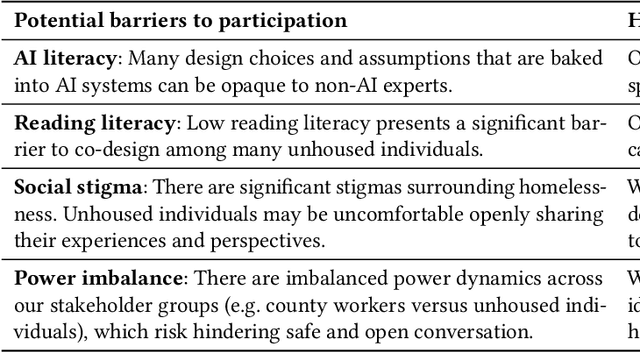
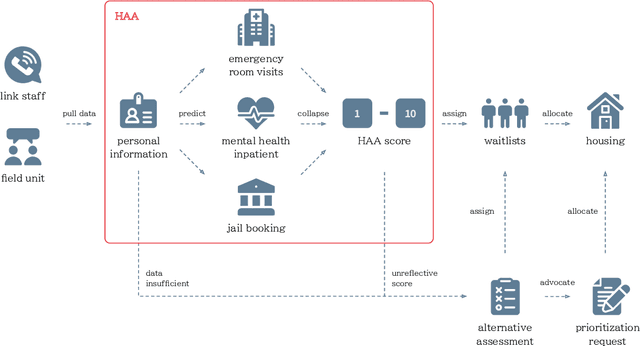
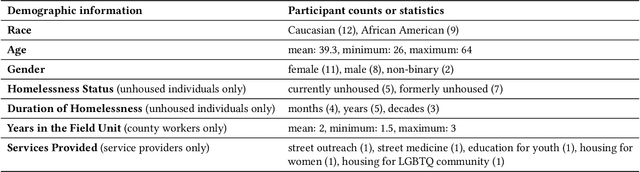

Abstract:Recent years have seen growing adoption of AI-based decision-support systems (ADS) in homeless services, yet we know little about stakeholder desires and concerns surrounding their use. In this work, we aim to understand impacted stakeholders' perspectives on a deployed ADS that prioritizes scarce housing resources. We employed AI lifecycle comicboarding, an adapted version of the comicboarding method, to elicit stakeholder feedback and design ideas across various components of an AI system's design. We elicited feedback from county workers who operate the ADS daily, service providers whose work is directly impacted by the ADS, and unhoused individuals in the region. Our participants shared concerns and design suggestions around the AI system's overall objective, specific model design choices, dataset selection, and use in deployment. Our findings demonstrate that stakeholders, even without AI knowledge, can provide specific and critical feedback on an AI system's design and deployment, if empowered to do so.
Improving Human-AI Collaboration With Descriptions of AI Behavior
Jan 06, 2023
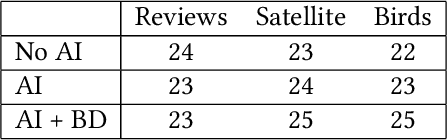
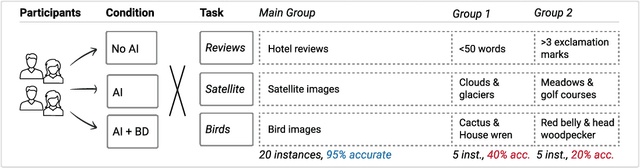
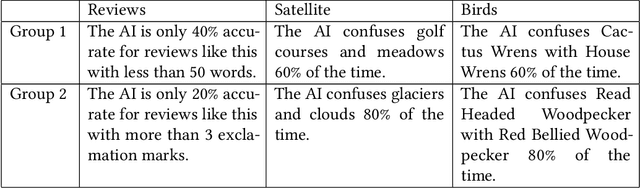
Abstract:People work with AI systems to improve their decision making, but often under- or over-rely on AI predictions and perform worse than they would have unassisted. To help people appropriately rely on AI aids, we propose showing them behavior descriptions, details of how AI systems perform on subgroups of instances. We tested the efficacy of behavior descriptions through user studies with 225 participants in three distinct domains: fake review detection, satellite image classification, and bird classification. We found that behavior descriptions can increase human-AI accuracy through two mechanisms: helping people identify AI failures and increasing people's reliance on the AI when it is more accurate. These findings highlight the importance of people's mental models in human-AI collaboration and show that informing people of high-level AI behaviors can significantly improve AI-assisted decision making.
* 21 pages
Discovering and Validating AI Errors With Crowdsourced Failure Reports
Sep 23, 2021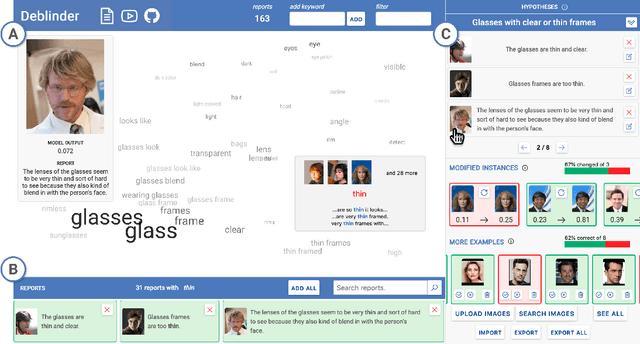
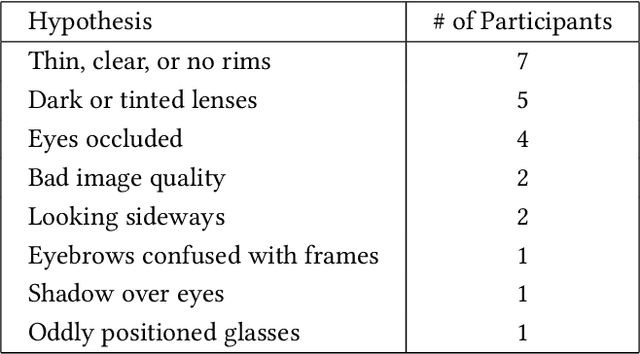
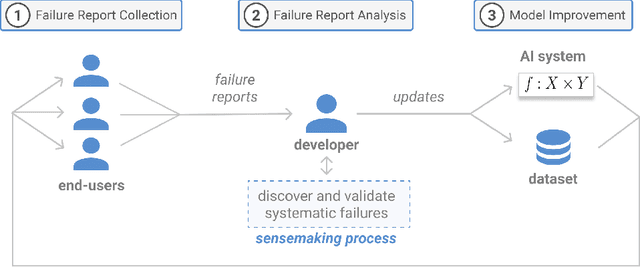

Abstract:AI systems can fail to learn important behaviors, leading to real-world issues like safety concerns and biases. Discovering these systematic failures often requires significant developer attention, from hypothesizing potential edge cases to collecting evidence and validating patterns. To scale and streamline this process, we introduce crowdsourced failure reports, end-user descriptions of how or why a model failed, and show how developers can use them to detect AI errors. We also design and implement Deblinder, a visual analytics system for synthesizing failure reports that developers can use to discover and validate systematic failures. In semi-structured interviews and think-aloud studies with 10 AI practitioners, we explore the affordances of the Deblinder system and the applicability of failure reports in real-world settings. Lastly, we show how collecting additional data from the groups identified by developers can improve model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge