Jan Weinreich
Reflections from the 2024 Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry
Nov 20, 2024
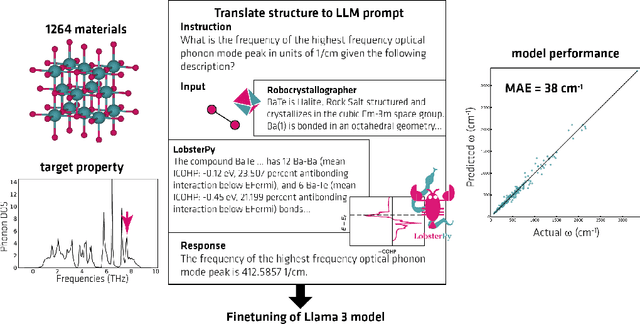
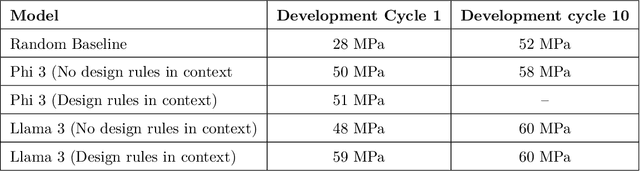
Abstract:Here, we present the outcomes from the second Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry, which engaged participants across global hybrid locations, resulting in 34 team submissions. The submissions spanned seven key application areas and demonstrated the diverse utility of LLMs for applications in (1) molecular and material property prediction; (2) molecular and material design; (3) automation and novel interfaces; (4) scientific communication and education; (5) research data management and automation; (6) hypothesis generation and evaluation; and (7) knowledge extraction and reasoning from scientific literature. Each team submission is presented in a summary table with links to the code and as brief papers in the appendix. Beyond team results, we discuss the hackathon event and its hybrid format, which included physical hubs in Toronto, Montreal, San Francisco, Berlin, Lausanne, and Tokyo, alongside a global online hub to enable local and virtual collaboration. Overall, the event highlighted significant improvements in LLM capabilities since the previous year's hackathon, suggesting continued expansion of LLMs for applications in materials science and chemistry research. These outcomes demonstrate the dual utility of LLMs as both multipurpose models for diverse machine learning tasks and platforms for rapid prototyping custom applications in scientific research.
Integer linear programming for unsupervised training set selection in molecular machine learning
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Integer linear programming (ILP) is an elegant approach to solve linear optimization problems, naturally described using integer decision variables. Within the context of physics-inspired machine learning applied to chemistry, we demonstrate the relevance of an ILP formulation to select molecular training sets for predictions of size-extensive properties. We show that our algorithm outperforms existing unsupervised training set selection approaches, especially when predicting properties of molecules larger than those present in the training set. We argue that the reason for the improved performance is due to the selection that is based on the notion of local similarity (i.e., per-atom) and a unique ILP approach that finds optimal solutions efficiently. Altogether, this work provides a practical algorithm to improve the performance of physics-inspired machine learning models and offers insights into the conceptual differences with existing training set selection approaches.
Encrypted machine learning of molecular quantum properties
Dec 22, 2022Abstract:Large machine learning models with improved predictions have become widely available in the chemical sciences. Unfortunately, these models do not protect the privacy necessary within commercial settings, prohibiting the use of potentially extremely valuable data by others. Encrypting the prediction process can solve this problem by double-blind model evaluation and prohibits the extraction of training or query data. However, contemporary ML models based on fully homomorphic encryption or federated learning are either too expensive for practical use or have to trade higher speed for weaker security. We have implemented secure and computationally feasible encrypted machine learning models using oblivious transfer enabling and secure predictions of molecular quantum properties across chemical compound space. However, we find that encrypted predictions using kernel ridge regression models are a million times more expensive than without encryption. This demonstrates a dire need for a compact machine learning model architecture, including molecular representation and kernel matrix size, that minimizes model evaluation costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge