Jamshidbek Mirzakhalov
Predicting Human Psychometric Properties Using Computational Language Models
May 12, 2022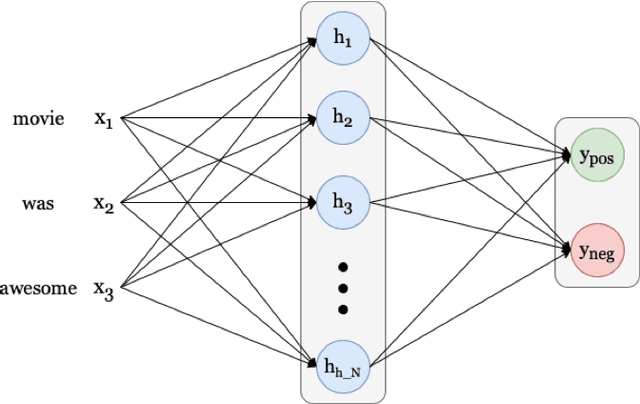
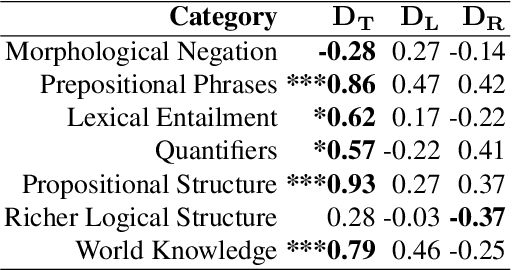
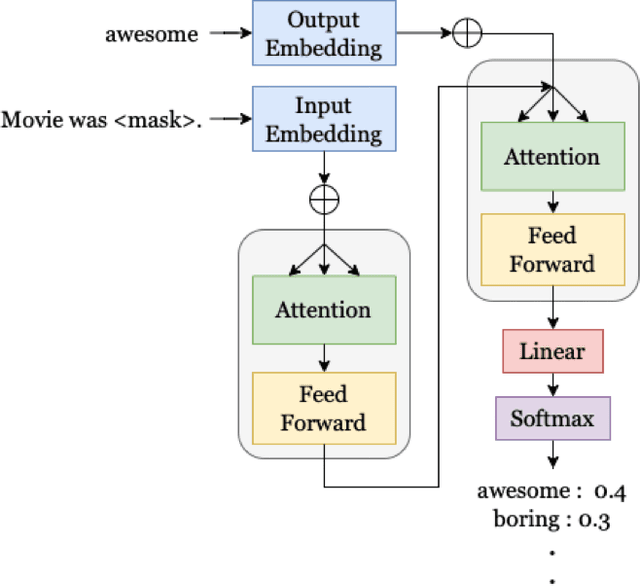
Abstract:Transformer-based language models (LMs) continue to achieve state-of-the-art performance on natural language processing (NLP) benchmarks, including tasks designed to mimic human-inspired "commonsense" competencies. To better understand the degree to which LMs can be said to have certain linguistic reasoning skills, researchers are beginning to adapt the tools and concepts from psychometrics. But to what extent can benefits flow in the other direction? In other words, can LMs be of use in predicting the psychometric properties of test items, when those items are given to human participants? If so, the benefit for psychometric practitioners is enormous, as it can reduce the need for multiple rounds of empirical testing. We gather responses from numerous human participants and LMs (transformer- and non-transformer-based) on a broad diagnostic test of linguistic competencies. We then use the human responses to calculate standard psychometric properties of the items in the diagnostic test, using the human responses and the LM responses separately. We then determine how well these two sets of predictions correlate. We find that transformer-based LMs predict the human psychometric data consistently well across most categories, suggesting that they can be used to gather human-like psychometric data without the need for extensive human trials.
Evaluating Multiway Multilingual NMT in the Turkic Languages
Sep 13, 2021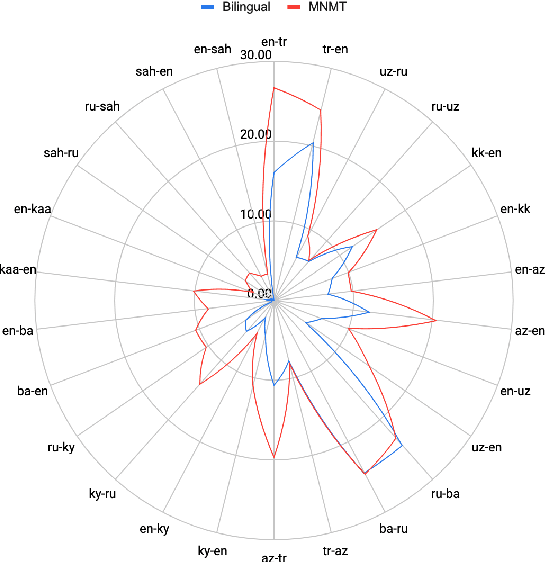
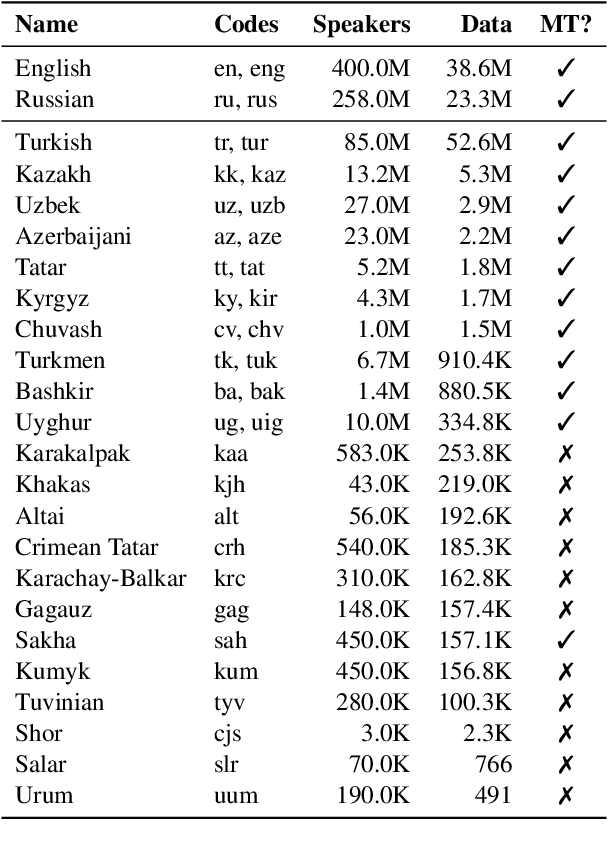
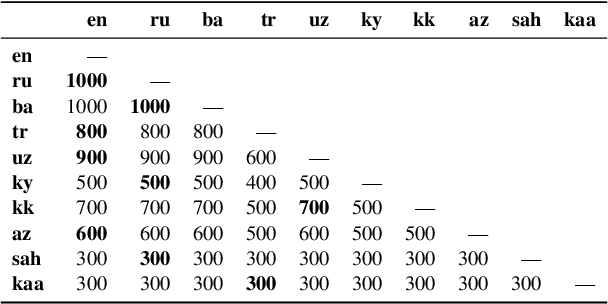
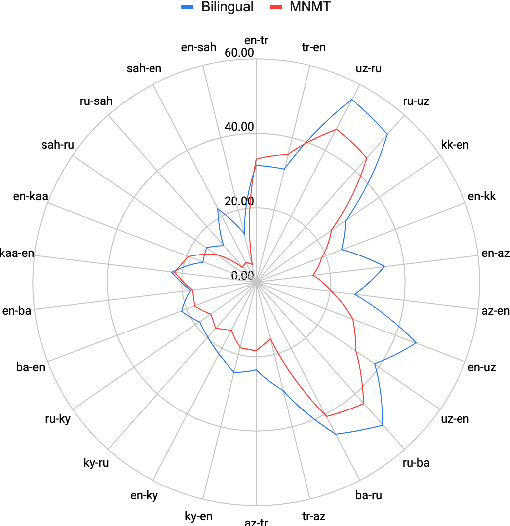
Abstract:Despite the increasing number of large and comprehensive machine translation (MT) systems, evaluation of these methods in various languages has been restrained by the lack of high-quality parallel corpora as well as engagement with the people that speak these languages. In this study, we present an evaluation of state-of-the-art approaches to training and evaluating MT systems in 22 languages from the Turkic language family, most of which being extremely under-explored. First, we adopt the TIL Corpus with a few key improvements to the training and the evaluation sets. Then, we train 26 bilingual baselines as well as a multi-way neural MT (MNMT) model using the corpus and perform an extensive analysis using automatic metrics as well as human evaluations. We find that the MNMT model outperforms almost all bilingual baselines in the out-of-domain test sets and finetuning the model on a downstream task of a single pair also results in a huge performance boost in both low- and high-resource scenarios. Our attentive analysis of evaluation criteria for MT models in Turkic languages also points to the necessity for further research in this direction. We release the corpus splits, test sets as well as models to the public.
A Large-Scale Study of Machine Translation in the Turkic Languages
Sep 09, 2021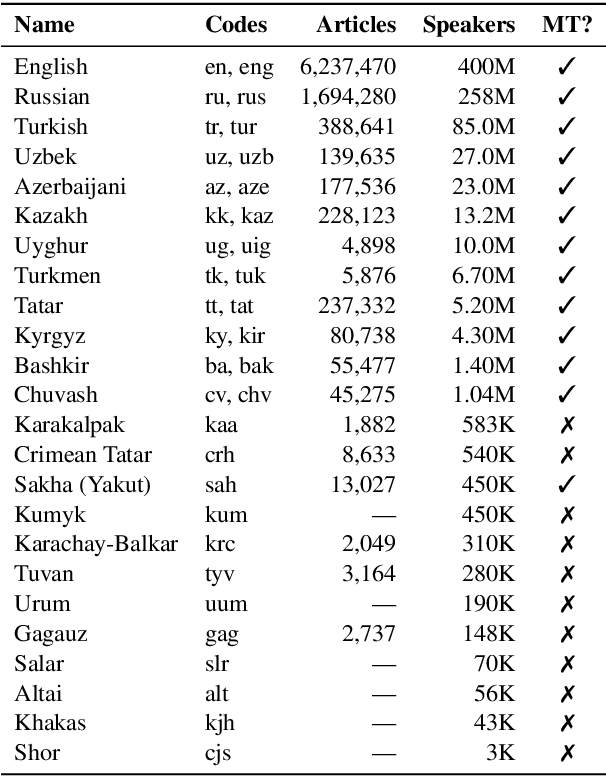
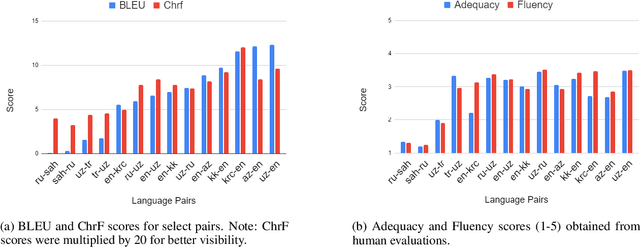
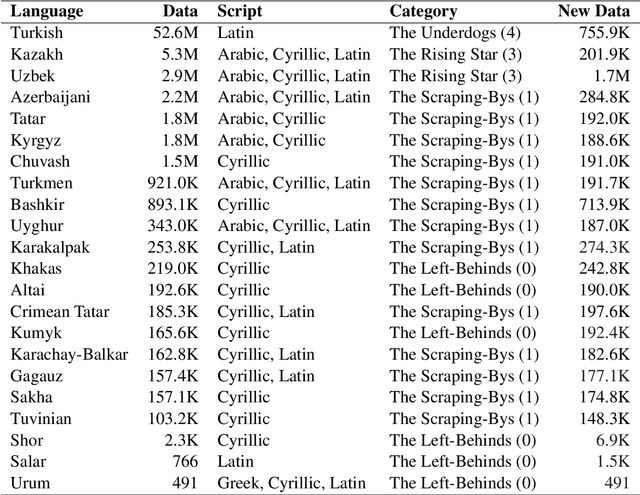
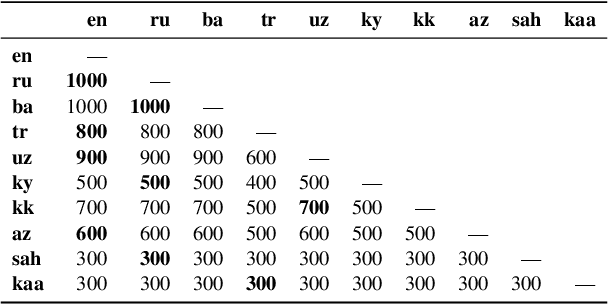
Abstract:Recent advances in neural machine translation (NMT) have pushed the quality of machine translation systems to the point where they are becoming widely adopted to build competitive systems. However, there is still a large number of languages that are yet to reap the benefits of NMT. In this paper, we provide the first large-scale case study of the practical application of MT in the Turkic language family in order to realize the gains of NMT for Turkic languages under high-resource to extremely low-resource scenarios. In addition to presenting an extensive analysis that identifies the bottlenecks towards building competitive systems to ameliorate data scarcity, our study has several key contributions, including, i) a large parallel corpus covering 22 Turkic languages consisting of common public datasets in combination with new datasets of approximately 2 million parallel sentences, ii) bilingual baselines for 26 language pairs, iii) novel high-quality test sets in three different translation domains and iv) human evaluation scores. All models, scripts, and data will be released to the public.
Can Transformer Language Models Predict Psychometric Properties?
Jun 12, 2021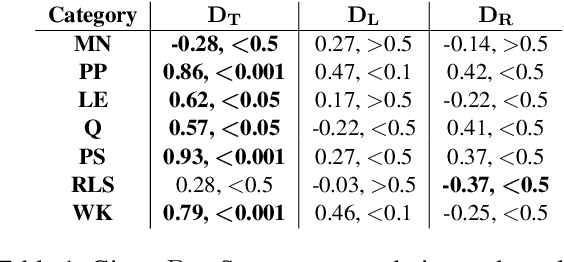
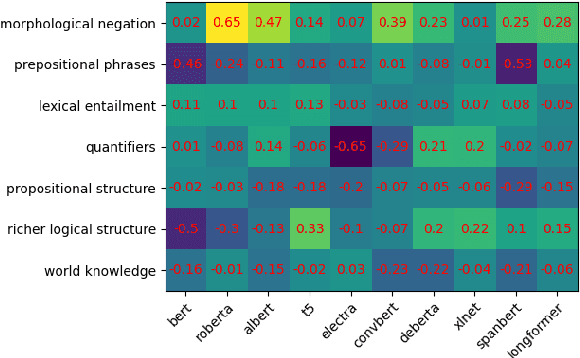
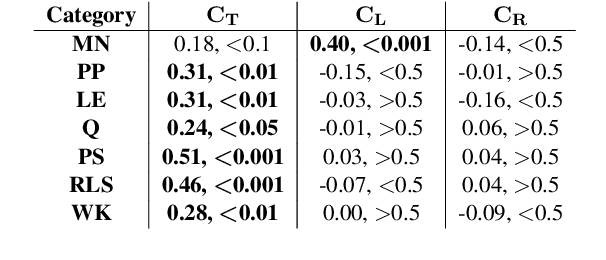
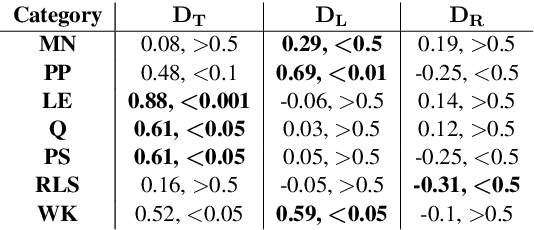
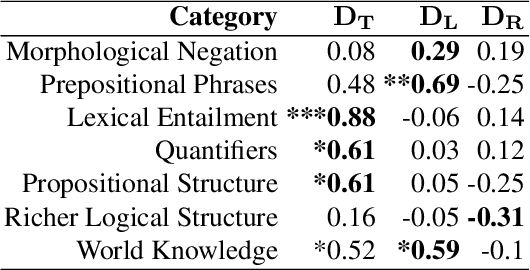
Abstract:Transformer-based language models (LMs) continue to advance state-of-the-art performance on NLP benchmark tasks, including tasks designed to mimic human-inspired "commonsense" competencies. To better understand the degree to which LMs can be said to have certain linguistic reasoning skills, researchers are beginning to adapt the tools and concepts of the field of psychometrics. But to what extent can the benefits flow in the other direction? I.e., can LMs be of use in predicting what the psychometric properties of test items will be when those items are given to human participants? We gather responses from numerous human participants and LMs (transformer and non-transformer-based) on a broad diagnostic test of linguistic competencies. We then use the responses to calculate standard psychometric properties of the items in the diagnostic test, using the human responses and the LM responses separately. We then determine how well these two sets of predictions match. We find cases in which transformer-based LMs predict psychometric properties consistently well in certain categories but consistently poorly in others, thus providing new insights into fundamental similarities and differences between human and LM reasoning.
Quality at a Glance: An Audit of Web-Crawled Multilingual Datasets
Mar 22, 2021
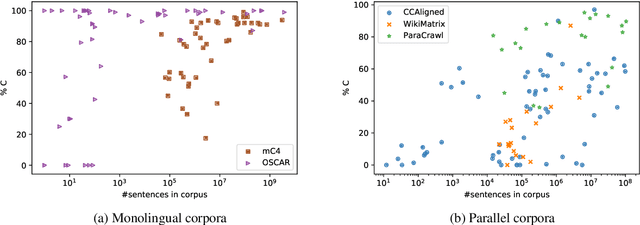
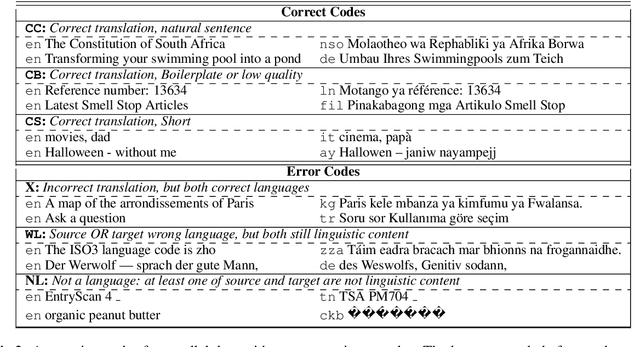
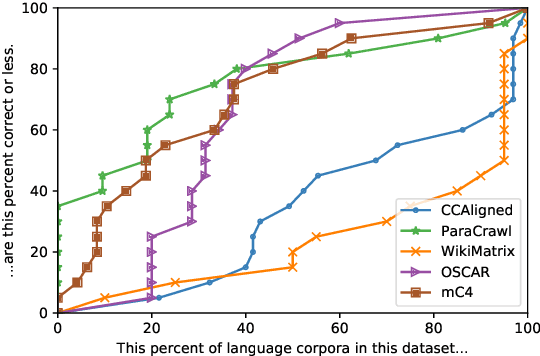
Abstract:With the success of large-scale pre-training and multilingual modeling in Natural Language Processing (NLP), recent years have seen a proliferation of large, web-mined text datasets covering hundreds of languages. However, to date there has been no systematic analysis of the quality of these publicly available datasets, or whether the datasets actually contain content in the languages they claim to represent. In this work, we manually audit the quality of 205 language-specific corpora released with five major public datasets (CCAligned, ParaCrawl, WikiMatrix, OSCAR, mC4), and audit the correctness of language codes in a sixth (JW300). We find that lower-resource corpora have systematic issues: at least 15 corpora are completely erroneous, and a significant fraction contains less than 50% sentences of acceptable quality. Similarly, we find 82 corpora that are mislabeled or use nonstandard/ambiguous language codes. We demonstrate that these issues are easy to detect even for non-speakers of the languages in question, and supplement the human judgements with automatic analyses. Inspired by our analysis, we recommend techniques to evaluate and improve multilingual corpora and discuss the risks that come with low-quality data releases.
Automating the Surveillance of Mosquito Vectors from Trapped Specimens Using Computer Vision Techniques
May 25, 2020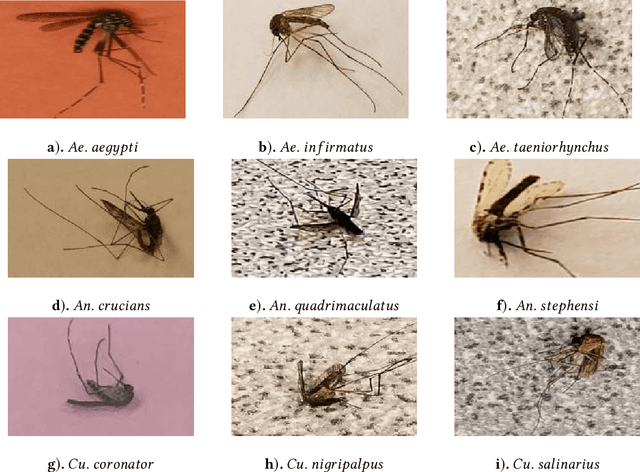
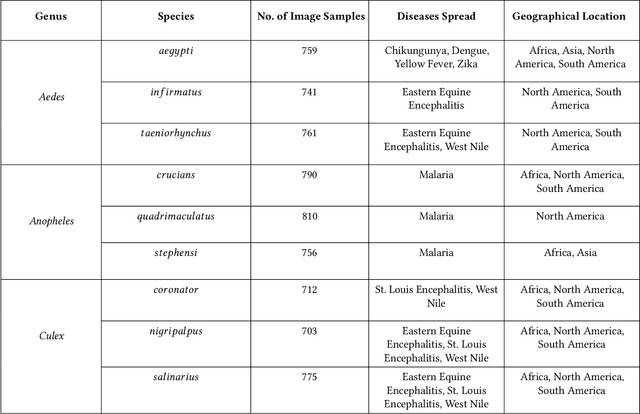
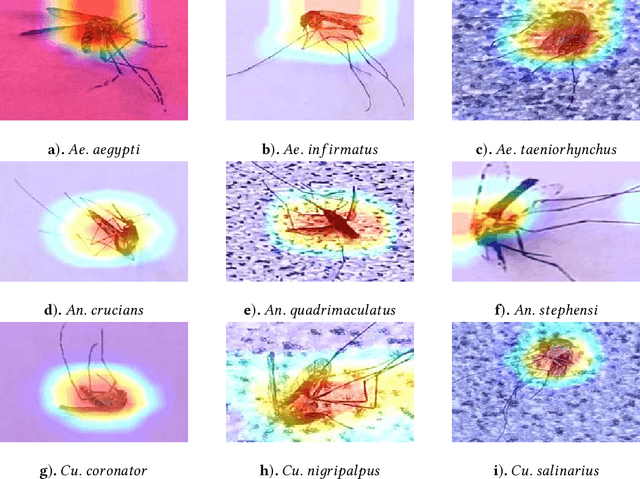
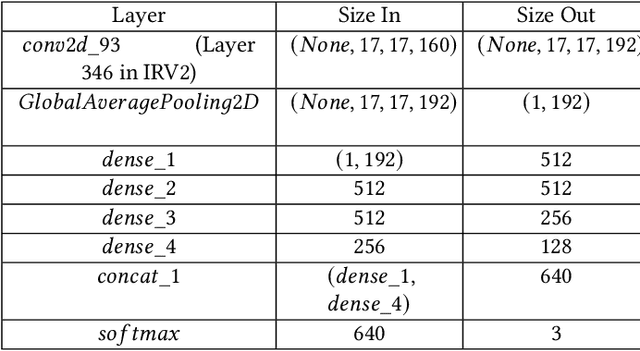
Abstract:Among all animals, mosquitoes are responsible for the most deaths worldwide. Interestingly, not all types of mosquitoes spread diseases, but rather, a select few alone are competent enough to do so. In the case of any disease outbreak, an important first step is surveillance of vectors (i.e., those mosquitoes capable of spreading diseases). To do this today, public health workers lay several mosquito traps in the area of interest. Hundreds of mosquitoes will get trapped. Naturally, among these hundreds, taxonomists have to identify only the vectors to gauge their density. This process today is manual, requires complex expertise/ training, and is based on visual inspection of each trapped specimen under a microscope. It is long, stressful and self-limiting. This paper presents an innovative solution to this problem. Our technique assumes the presence of an embedded camera (similar to those in smart-phones) that can take pictures of trapped mosquitoes. Our techniques proposed here will then process these images to automatically classify the genus and species type. Our CNN model based on Inception-ResNet V2 and Transfer Learning yielded an overall accuracy of 80% in classifying mosquitoes when trained on 25,867 images of 250 trapped mosquito vector specimens captured via many smart-phone cameras. In particular, the accuracy of our model in classifying Aedes aegypti and Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes (both of which are deadly vectors) is amongst the highest. We present important lessons learned and practical impact of our techniques towards the end of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge