James Fulton
Unsupervised Change Detection of Extreme Events Using ML On-Board
Nov 04, 2021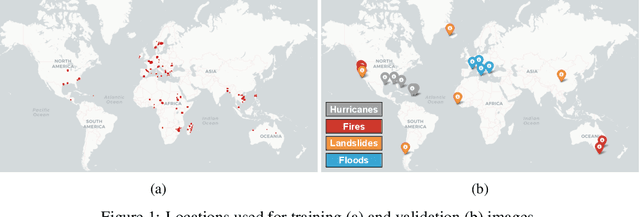
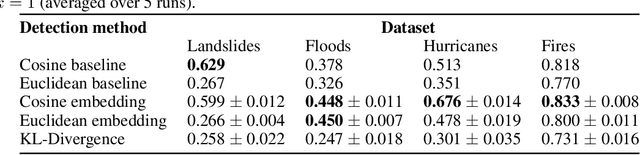
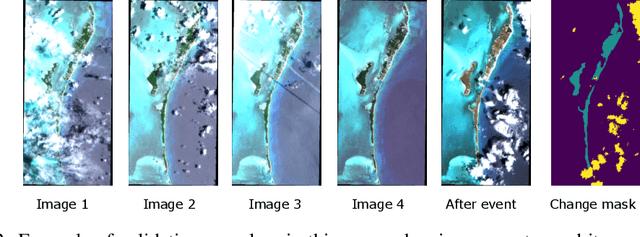
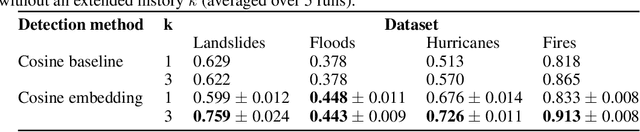
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce RaVAEn, a lightweight, unsupervised approach for change detection in satellite data based on Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) with the specific purpose of on-board deployment. Applications such as disaster management enormously benefit from the rapid availability of satellite observations. Traditionally, data analysis is performed on the ground after all data is transferred - downlinked - to a ground station. Constraint on the downlink capabilities therefore affects any downstream application. In contrast, RaVAEn pre-processes the sampled data directly on the satellite and flags changed areas to prioritise for downlink, shortening the response time. We verified the efficacy of our system on a dataset composed of time series of catastrophic events - which we plan to release alongside this publication - demonstrating that RaVAEn outperforms pixel-wise baselines. Finally we tested our approach on resource-limited hardware for assessing computational and memory limitations.
NightVision: Generating Nighttime Satellite Imagery from Infra-Red Observations
Dec 08, 2020
Abstract:The recent explosion in applications of machine learning to satellite imagery often rely on visible images and therefore suffer from a lack of data during the night. The gap can be filled by employing available infra-red observations to generate visible images. This work presents how deep learning can be applied successfully to create those images by using U-Net based architectures. The proposed methods show promising results, achieving a structural similarity index (SSIM) up to 86\% on an independent test set and providing visually convincing output images, generated from infra-red observations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge