Jalees Nehvi
360° Volumetric Portrait Avatar
Dec 08, 2023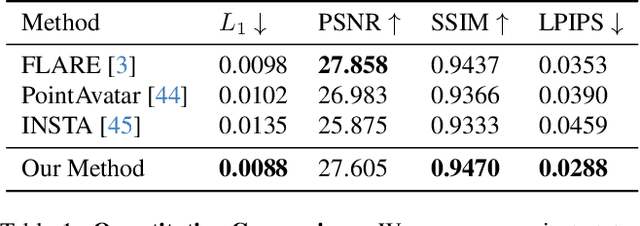
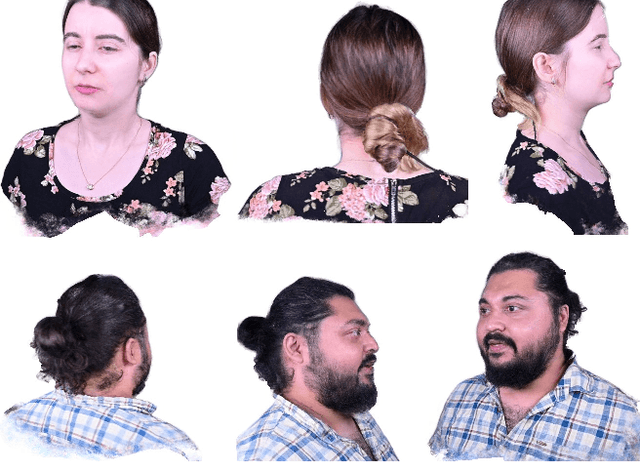
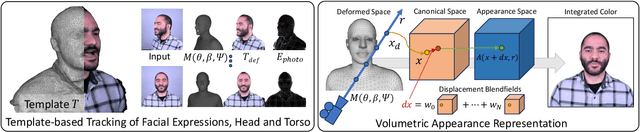
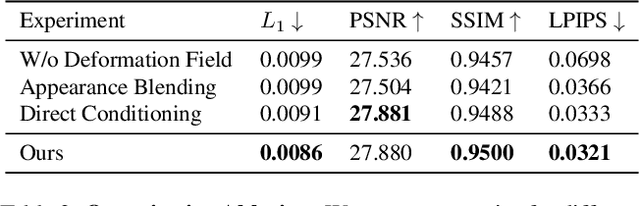

Abstract:We propose 360{\deg} Volumetric Portrait (3VP) Avatar, a novel method for reconstructing 360{\deg} photo-realistic portrait avatars of human subjects solely based on monocular video inputs. State-of-the-art monocular avatar reconstruction methods rely on stable facial performance capturing. However, the common usage of 3DMM-based facial tracking has its limits; side-views can hardly be captured and it fails, especially, for back-views, as required inputs like facial landmarks or human parsing masks are missing. This results in incomplete avatar reconstructions that only cover the frontal hemisphere. In contrast to this, we propose a template-based tracking of the torso, head and facial expressions which allows us to cover the appearance of a human subject from all sides. Thus, given a sequence of a subject that is rotating in front of a single camera, we train a neural volumetric representation based on neural radiance fields. A key challenge to construct this representation is the modeling of appearance changes, especially, in the mouth region (i.e., lips and teeth). We, therefore, propose a deformation-field-based blend basis which allows us to interpolate between different appearance states. We evaluate our approach on captured real-world data and compare against state-of-the-art monocular reconstruction methods. In contrast to those, our method is the first monocular technique that reconstructs an entire 360{\deg} avatar.
Differentiable Event Stream Simulator for Non-Rigid 3D Tracking
Apr 30, 2021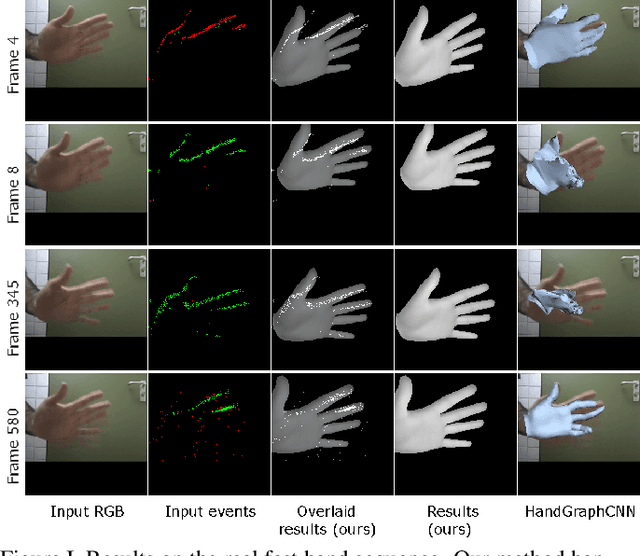
Abstract:This paper introduces the first differentiable simulator of event streams, i.e., streams of asynchronous brightness change signals recorded by event cameras. Our differentiable simulator enables non-rigid 3D tracking of deformable objects (such as human hands, isometric surfaces and general watertight meshes) from event streams by leveraging an analysis-by-synthesis principle. So far, event-based tracking and reconstruction of non-rigid objects in 3D, like hands and body, has been either tackled using explicit event trajectories or large-scale datasets. In contrast, our method does not require any such processing or data, and can be readily applied to incoming event streams. We show the effectiveness of our approach for various types of non-rigid objects and compare to existing methods for non-rigid 3D tracking. In our experiments, the proposed energy-based formulations outperform competing RGB-based methods in terms of 3D errors. The source code and the new data are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge