Jalal Jalali
Shape Adaptive Reconfigurable Holographic Surfaces
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) have emerged as a key solution to dynamically adjust wireless propagation by tuning the reflection coefficients of large arrays of passive elements. Reconfigurable Holographic Surfaces (RHS) build on the same foundation as RIS but extend it by employing holographic principles for finer-grained wave manipulation | that is, applying higher spatial control over the reflected signals for more precise beam steering. In this paper, we investigate shape-adaptive RHS deployments in a multi-user network. Rather than treating each RHS as a uniform reflecting surface, we propose a selective element activation strategy that dynamically adapts the spatial arrangement of deployed RHS regions to a subset of predefined shapes. In particular, we formulate a system throughput maximization problem that optimizes the shape of the selected RHS elements, active beamforming at the access point (AP), and passive beamforming at the RHS to enhance coverage and mitigate signal blockage. The resulting problem is non-convex and becomes even more challenging to solve as the number of RHS and users increases; to tackle this, we introduce an alternating optimization (AO) approach that efficiently finds near-optimal solutions irrespective of the number or spatial configuration of RHS. Numerical results demonstrate that shape adaptation enables more efficient resource distribution, enhancing the effectiveness of multi-RHS deployments as the network scales.
Placement, Orientation, and Resource Allocation Optimization for Cell-Free OIRS-aided OWC Network
Jan 06, 2025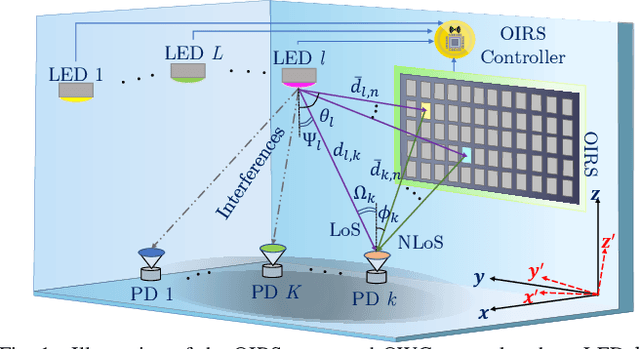
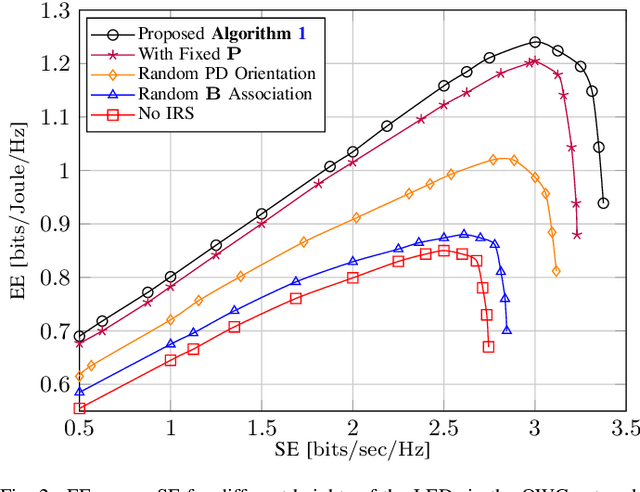
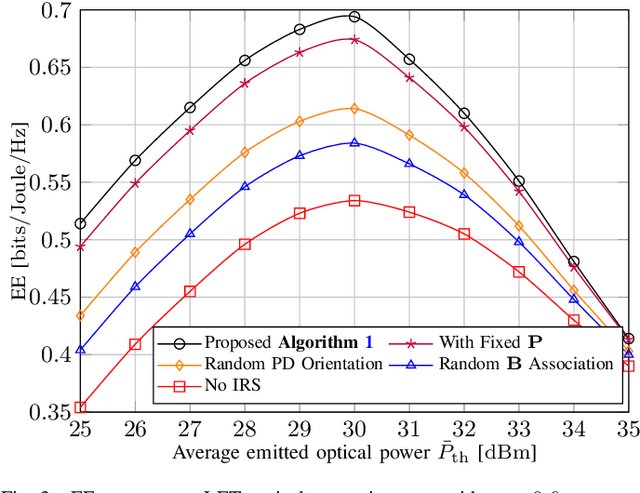
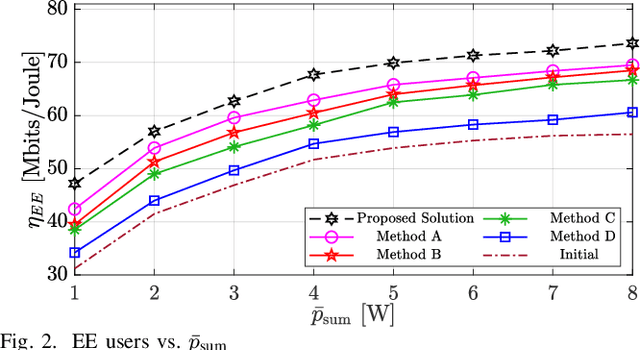
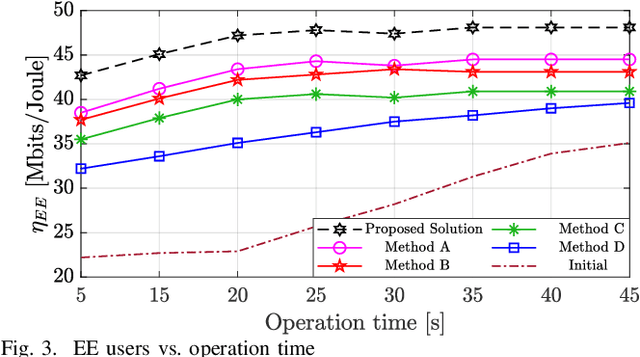
Abstract:The emergence of optical intelligent reflecting surface (OIRS) technologies marks a milestone in optical wireless communication (OWC) systems, enabling enhanced control over light propagation in indoor environments. This capability allows for the customization of channel conditions to achieve specific performance goals. This paper presents an enhancement in downlink cell-free OWC networks through the integration of OIRS. The key focus is on fine-tuning crucial parameters, including transmit power, receiver orientations, OIRS elements allocation, and strategic placement. In particular, a multi-objective optimization problem (MOOP) aimed at simultaneously improving the network's spectral efficiency (SE) and energy efficiency (EE) while adhering to the network's quality of service (QoS) constraints is formulated. The problem is solved by employing the $\epsilon$-constraint method to convert the MOOP into a single-objective optimization problem and solving it through successive convex approximation. Simulation results show the significant impact of OIRS on SE and EE, confirming its effectiveness in improving OWC network performance.
Miniature UAV Empowered Reconfigurable Energy Harvesting Holographic Surfaces in THz Cooperative Networks
Nov 27, 2024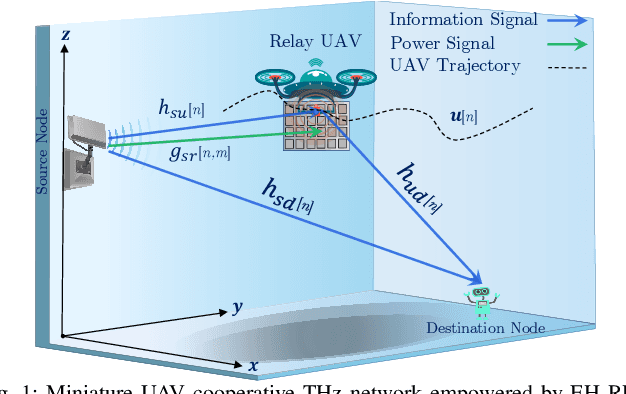
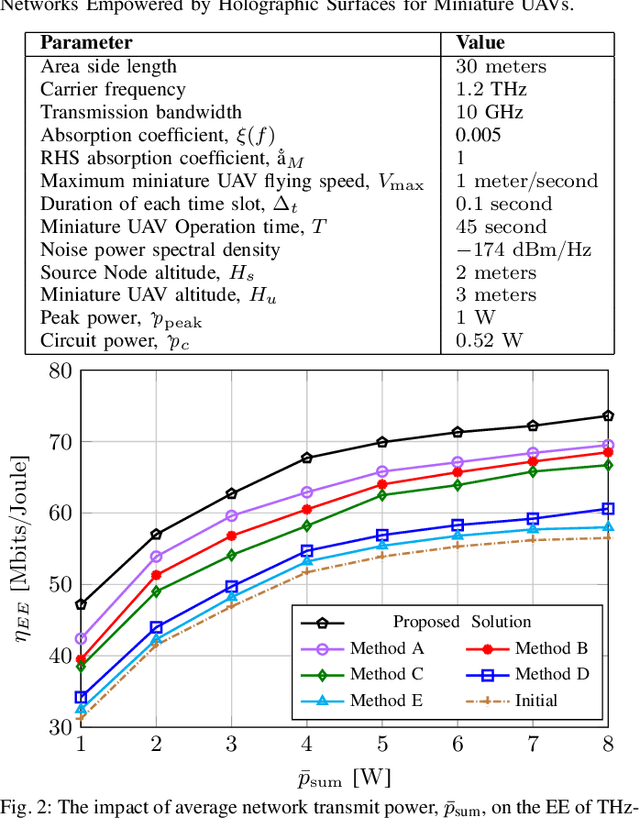
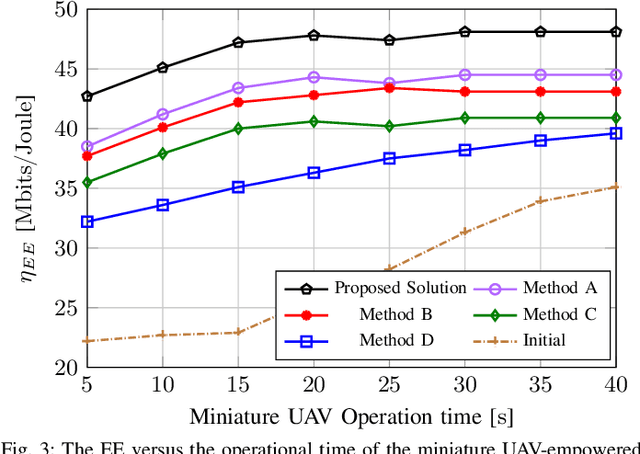
Abstract:This paper focuses on enhancing the energy efficiency (EE) of a cooperative network featuring a `miniature' unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that operates at terahertz (THz) frequencies, utilizing holographic surfaces to improve the network's performance. Unlike traditional reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) that are typically used as passive relays to adjust signal reflections, this work introduces a novel concept: Energy harvesting (EH) using reconfigurable holographic surfaces (RHS) mounted on the miniature UAV. In this system, a source node facilitates the simultaneous reception of information and energy signals by the UAV, with the harvested energy from the RHS being used by the UAV to transmit data to a specific destination. The EE optimization involves adjusting non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) power coefficients and the UAV's flight path, considering the peculiarities of the THz channel. The optimization problem is solved in two steps. Initially, the trajectory is refined using a successive convex approximation (SCA) method, followed by the adjustment of NOMA power coefficients through a quadratic transform technique. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated through simulations, showing superior results when compared to baseline methods.
Toward Energy Efficient Multiuser IRS-Assisted URLLC Systems: A Novel Rank Relaxation Method
Sep 26, 2023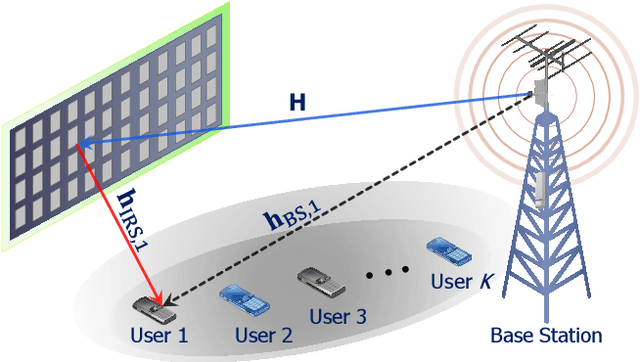
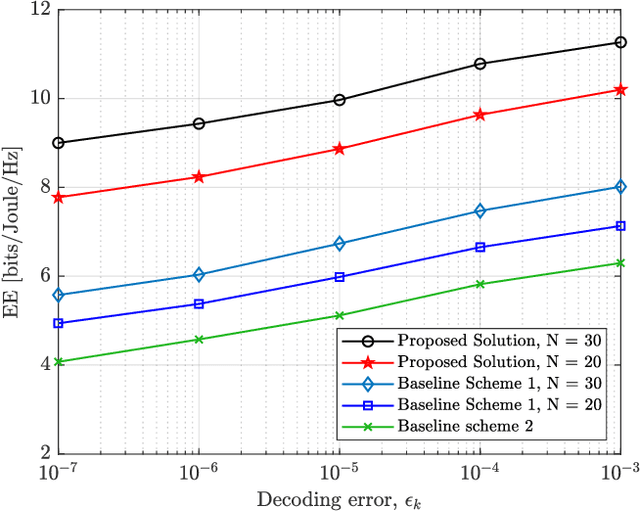
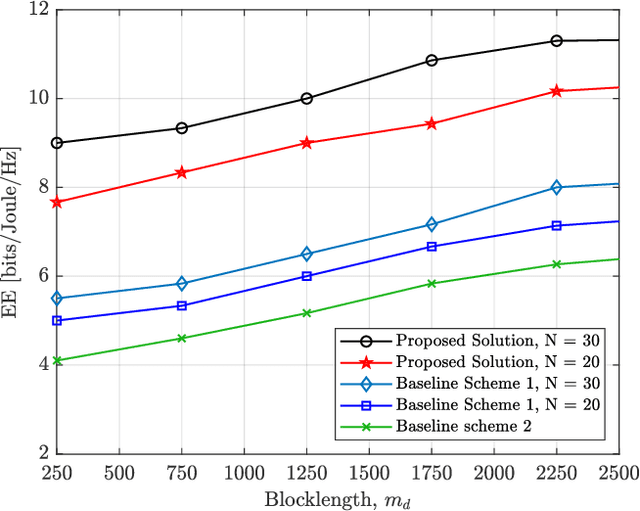
Abstract:This paper proposes an energy efficient resource allocation design algorithm for an intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted downlink ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) network. This setup features a multi-antenna base station (BS) transmitting data traffic to a group of URLLC users with short packet lengths. We maximize the total network's energy efficiency (EE) through the optimization of active beamformers at the BS and passive beamformers (a.k.a. phase shifts) at the IRS. The main non-convex problem is divided into two sub-problems. An alternating optimization (AO) approach is then used to solve the problem. Through the use of the successive convex approximation (SCA) with a novel iterative rank relaxation method, we construct a concave-convex objective function for each sub-problem. The first sub-problem is a fractional program that is solved using the Dinkelbach method and a penalty-based approach. The second sub-problem is then solved based on semi-definite programming (SDP) and the penalty-based approach. The iterative solution gradually approaches the rank-one for both the active beamforming and unit modulus IRS phase-shift sub-problems. Our results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed solution compared to existing benchmarks.
On the Energy Efficiency of THz-NOMA enhanced UAV Cooperative Network with SWIPT
Sep 25, 2023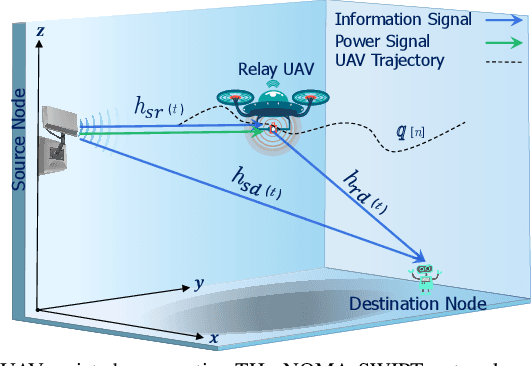
Abstract:This paper considers the energy efficiency (EE) maximization of a simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT)-assisted unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) cooperative network operating at TeraHertz (THz) frequencies. The source performs SWIPT enabling the UAV to receive both power and information while also transmitting the information to a designated destination node. Subsequently, the UAV utilizes the harvested energy to relay the data to the intended destination node effectively. Specifically, we maximize EE by optimizing the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) power allocation coefficients, SWIPT power splitting (PS) ratio, and UAV trajectory. The main problem is broken down into a two-stage optimization problem and solved using an alternating optimization approach. In the first stage, optimization of the PS ratio and trajectory is performed by employing successive convex approximation using a lower bound on the exponential factor in the THz channel model. In the second phase, the NOMA power coefficients are optimized using a quadratic transform approach. Numerical results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed resource allocation algorithm compared to the baselines where there is no trajectory optimization or no NOMA power or PS optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge