Jacob Hoffman
CoAM: Corpus of All-Type Multiword Expressions
Dec 24, 2024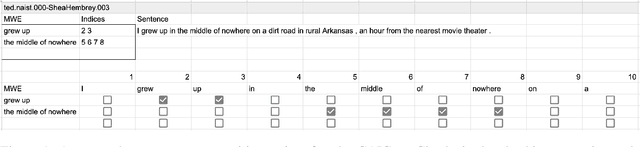
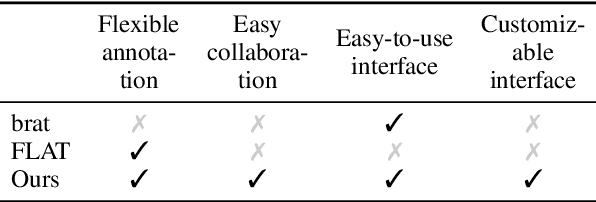
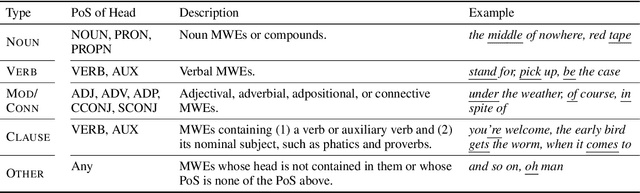

Abstract:Multiword expressions (MWEs) refer to idiomatic sequences of multiple words. MWE identification, i.e., detecting MWEs in text, can play a key role in downstream tasks such as machine translation. Existing datasets for MWE identification are inconsistently annotated, limited to a single type of MWE, or limited in size. To enable reliable and comprehensive evaluation, we created CoAM: Corpus of All-Type Multiword Expressions, a dataset of 1.3K sentences constructed through a multi-step process to enhance data quality consisting of human annotation, human review, and automated consistency checking. MWEs in CoAM are tagged with MWE types, such as Noun and Verb, to enable fine-grained error analysis. Annotations for CoAM were collected using a new interface created with our interface generator, which allows easy and flexible annotation of MWEs in any form, including discontinuous ones. Through experiments using CoAM, we find that a fine-tuned large language model outperforms the current state-of-the-art approach for MWE identification. Furthermore, analysis using our MWE type tagged data reveals that Verb MWEs are easier than Noun MWEs to identify across approaches.
MWE as WSD: Solving Multiword Expression Identification with Word Sense Disambiguation
Mar 12, 2023Abstract:Recent work in word sense disambiguation (WSD) utilizes encodings of the sense gloss (definition text), in addition to the input words and context, to improve performance. In this work we demonstrate that this approach can be adapted for use in multiword expression (MWE) identification by training a Bi-encoder model which uses gloss and context information to filter MWE candidates produced from a simple rule-based extraction pipeline. We achieve state-of-the-art results in MWE identification on the DiMSUM dataset, and competitive results on the PARSEME 1.1 English dataset using this method. Our model also retains most of its ability to perform WSD, demonstrating that a single model can successfully be applied to both of these tasks. Additionally, we experiment with applying Poly-encoder models to MWE identification and WSD, introducing a modified Poly-encoder architecture which outperforms the standard Poly-encoder on these tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge