Jacob Hatef
DK
Scaling Large Language Model Training on Frontier with Low-Bandwidth Partitioning
Jan 08, 2025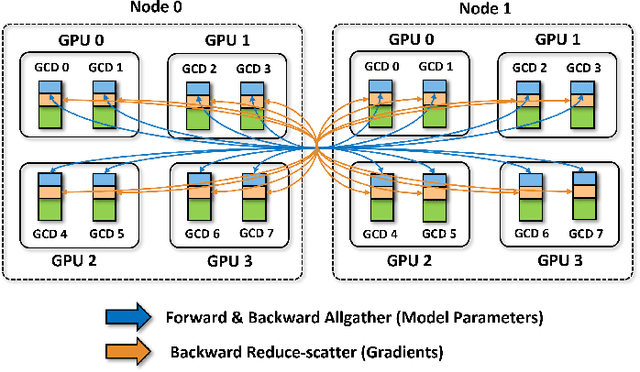
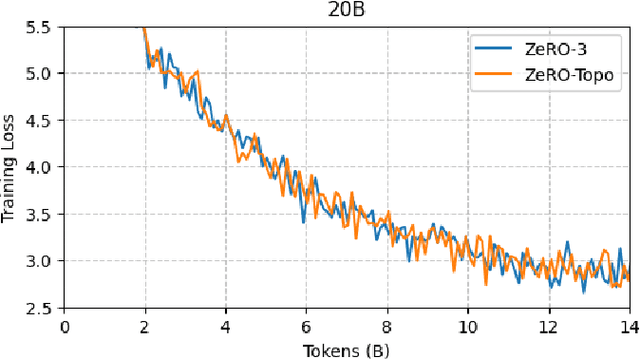
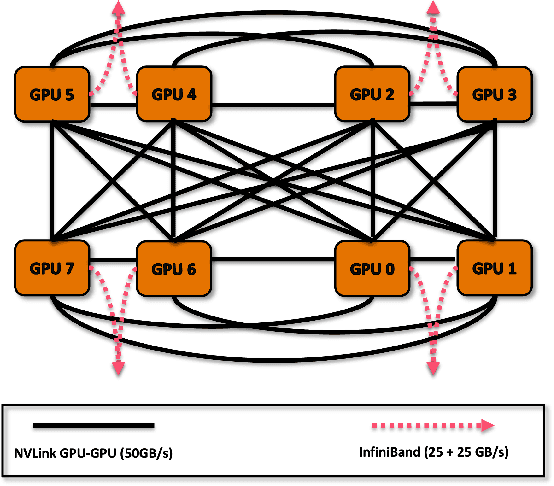
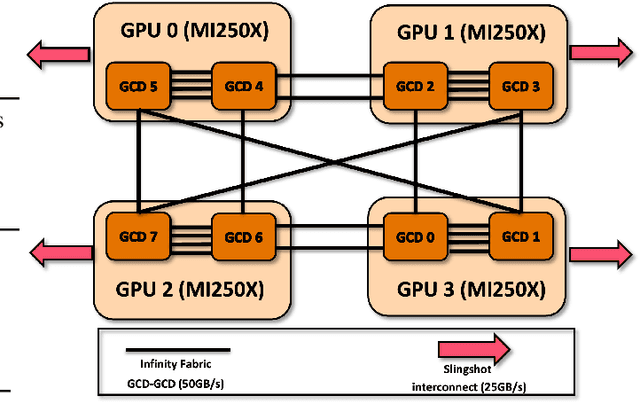
Abstract:Scaling up Large Language Model(LLM) training involves fitting a tremendous amount of training parameters across a limited number of workers. However, methods like ZeRO-3 that drastically reduce GPU memory pressure often incur heavy communication to ensure global synchronization and consistency. Established efforts such as ZeRO++ use secondary partitions to avoid inter-node communications, given that intra-node GPU-GPU transfer generally has more bandwidth and lower latency than inter-node connections. However, as more capable infrastructure like Frontier, equipped with AMD GPUs, emerged with impressive computing capability, there is a need for investigations on the hardware topology and to develop targeted strategies to improve training efficiency. In this work, we propose a collection of communication and optimization strategies for ZeRO++ to reduce communication costs and improve memory utilization. In this paper, we propose a 3-level hierarchical partitioning specifically for the current Top-1 supercomputing cluster, Frontier, which aims at leveraging various bandwidths across layers of communications (GCD-GCD, GPU-GPU, and inter-node) to reduce communication overhead. For a 20B GPT model, we observe a 1.71x increase in TFLOPS per GPU when compared with ZeRO++ up to 384 GCDs and a scaling efficiency of 0.94 for up to 384 GCDs. To the best of our knowledge, our work is also the first effort to efficiently optimize LLM workloads on Frontier AMD GPUs.
Demystifying the Communication Characteristics for Distributed Transformer Models
Aug 19, 2024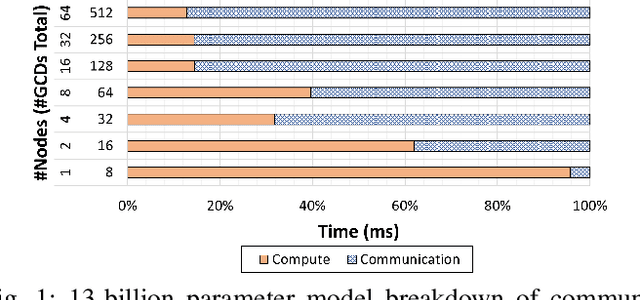
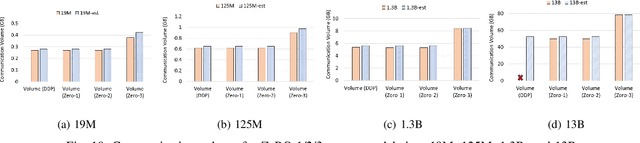
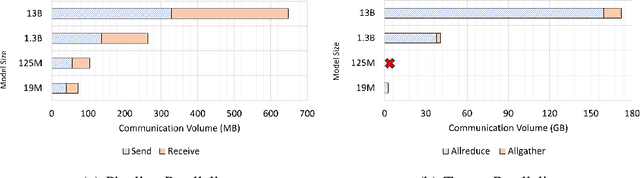
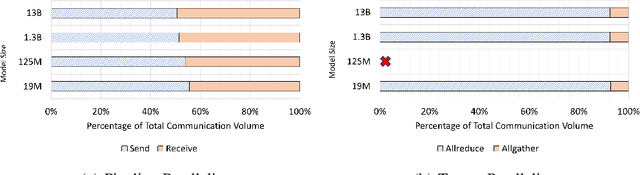
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models based on the transformer architecture have revolutionized many DL applications such as large language models (LLMs), vision transformers, audio generation, and time series prediction. Much of this progress has been fueled by distributed training, yet distributed communication remains a substantial bottleneck to training progress. This paper examines the communication behavior of transformer models - that is, how different parallelism schemes used in multi-node/multi-GPU DL Training communicate data in the context of transformers. We use GPT-based language models as a case study of the transformer architecture due to their ubiquity. We validate the empirical results obtained from our communication logs using analytical models. At a high level, our analysis reveals a need to optimize small message point-to-point communication further, correlations between sequence length, per-GPU throughput, model size, and optimizations used, and where to potentially guide further optimizations in framework and HPC middleware design and optimization.
The Case for Co-Designing Model Architectures with Hardware
Jan 30, 2024



Abstract:While GPUs are responsible for training the vast majority of state-of-the-art deep learning models, the implications of their architecture are often overlooked when designing new deep learning (DL) models. As a consequence, modifying a DL model to be more amenable to the target hardware can significantly improve the runtime performance of DL training and inference. In this paper, we provide a set of guidelines for users to maximize the runtime performance of their transformer models. These guidelines have been created by carefully considering the impact of various model hyperparameters controlling model shape on the efficiency of the underlying computation kernels executed on the GPU. We find the throughput of models with efficient model shapes is up to 39\% higher while preserving accuracy compared to models with a similar number of parameters but with unoptimized shapes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge