Ioannis Papavasileiou
University of Connecticut
Photonic Accelerators for Image Segmentation in Autonomous Driving and Defect Detection
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Photonic computing promises faster and more energy-efficient deep neural network (DNN) inference than traditional digital hardware. Advances in photonic computing can have profound impacts on applications such as autonomous driving and defect detection that depend on fast, accurate and energy efficient execution of image segmentation models. In this paper, we investigate image segmentation on photonic accelerators to explore: a) the types of image segmentation DNN architectures that are best suited for photonic accelerators, and b) the throughput and energy efficiency of executing the different image segmentation models on photonic accelerators, along with the trade-offs involved therein. Specifically, we demonstrate that certain segmentation models exhibit negligible loss in accuracy (compared to digital float32 models) when executed on photonic accelerators, and explore the empirical reasoning for their robustness. We also discuss techniques for recovering accuracy in the case of models that do not perform well. Further, we compare throughput (inferences-per-second) and energy consumption estimates for different image segmentation workloads on photonic accelerators. We discuss the challenges and potential optimizations that can help improve the application of photonic accelerators to such computer vision tasks.
Classification of Neurological Gait Disorders Using Multi-task Feature Learning
Feb 01, 2017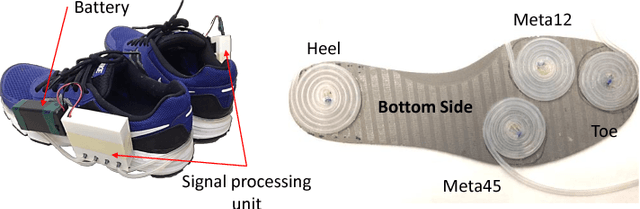
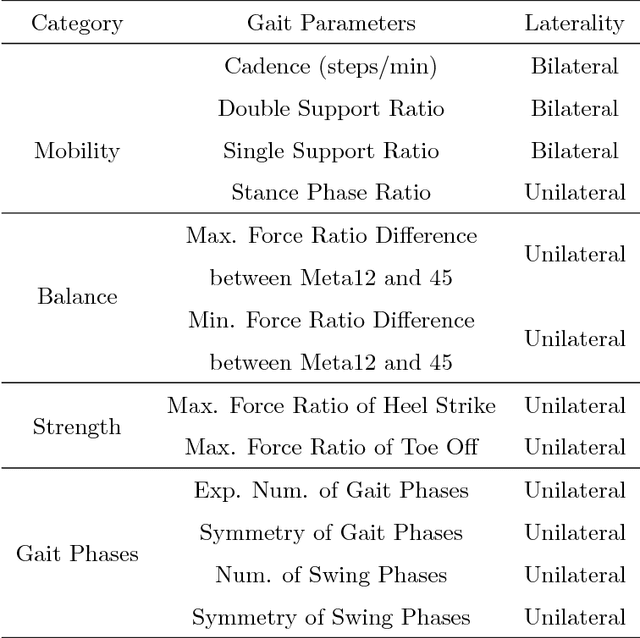
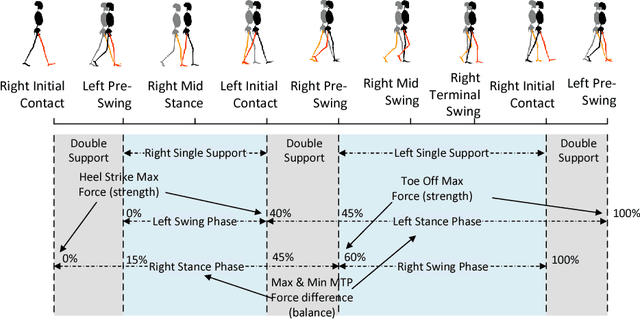
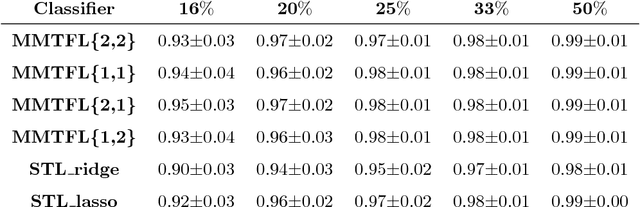
Abstract:As our population ages, neurological impairments and degeneration of the musculoskeletal system yield gait abnormalities, which can significantly reduce quality of life. Gait rehabilitative therapy has been widely adopted to help patients maximize community participation and living independence. To further improve the precision and efficiency of rehabilitative therapy, more objective methods need to be developed based on sensory data. In this paper, an algorithmic framework is proposed to provide classification of gait disorders caused by two common neurological diseases, stroke and Parkinson's Disease (PD), from ground contact force (GCF) data. An advanced machine learning method, multi-task feature learning (MTFL), is used to jointly train classification models of a subject's gait in three classes, post-stroke, PD and healthy gait. Gait parameters related to mobility, balance, strength and rhythm are used as features for the classification. Out of all the features used, the MTFL models capture the more important ones per disease, which will help provide better objective assessment and therapy progress tracking. To evaluate the proposed methodology we use data from a human participant study, which includes five PD patients, three post-stroke patients, and three healthy subjects. Despite the diversity of abnormalities, the evaluation shows that the proposed approach can successfully distinguish post-stroke and PD gait from healthy gait, as well as post-stroke from PD gait, with Area Under the Curve (AUC) score of at least 0.96. Moreover, the methodology helps select important gait features to better understand the key characteristics that distinguish abnormal gaits and design personalized treatment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge