Ioannis Alexiou
Reconstructing the Noise Manifold for Image Denoising
Mar 07, 2020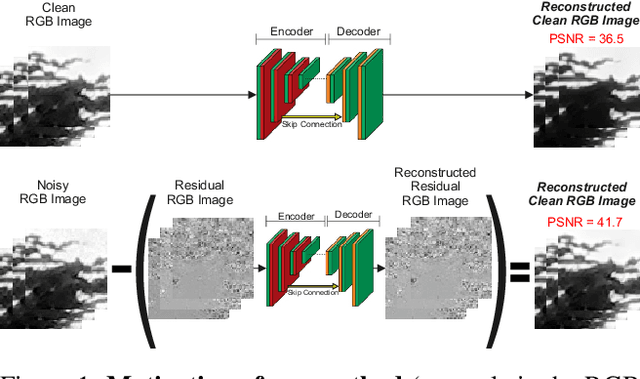
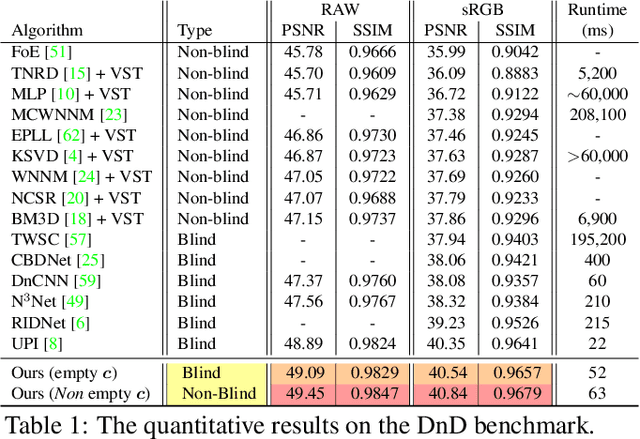
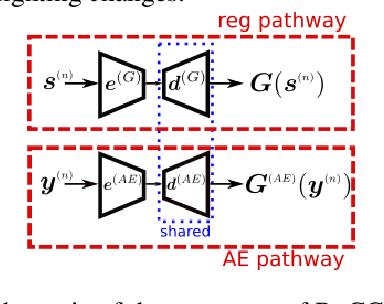
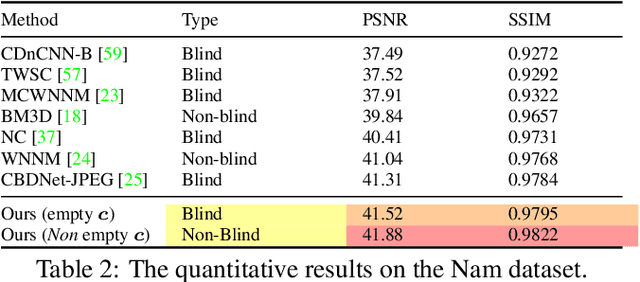
Abstract:Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been successfully used in many low-level vision problems like image denoising. Although the conditional image generation techniques have led to large improvements in this task, there has been little effort in providing conditional generative adversarial networks (cGAN)[42] with an explicit way of understanding the image noise for object-independent denoising reliable for real-world applications. The task of leveraging structures in the target space is unstable due to the complexity of patterns in natural scenes, so the presence of unnatural artifacts or over-smoothed image areas cannot be avoided. To fill the gap, in this work we introduce the idea of a cGAN which explicitly leverages structure in the image noise space. By learning directly a low dimensional manifold of the image noise, the generator promotes the removal from the noisy image only that information which spans this manifold. This idea brings many advantages while it can be appended at the end of any denoiser to significantly improve its performance. Based on our experiments, our model substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art architectures, resulting in denoised images with less oversmoothing and better detail.
Appearance-based indoor localization: A comparison of patch descriptor performance
Mar 11, 2015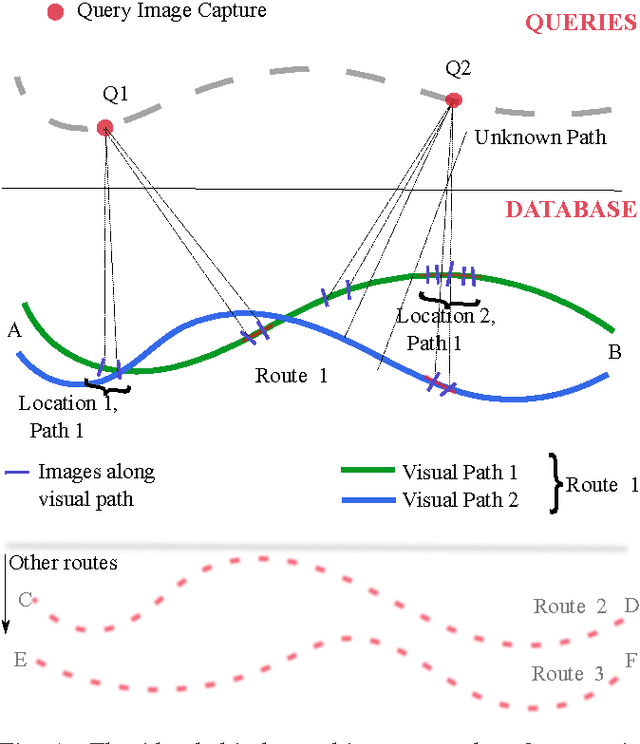

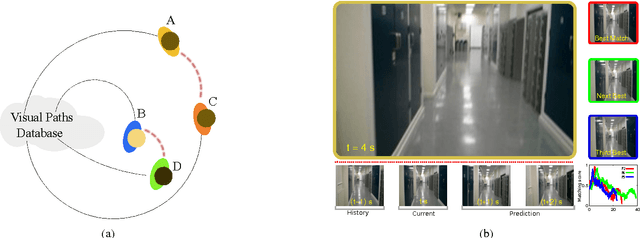
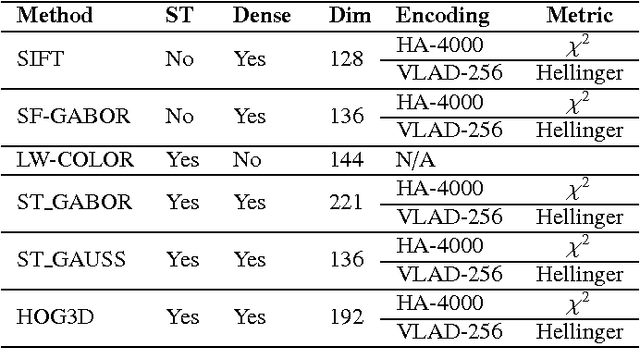
Abstract:Vision is one of the most important of the senses, and humans use it extensively during navigation. We evaluated different types of image and video frame descriptors that could be used to determine distinctive visual landmarks for localizing a person based on what is seen by a camera that they carry. To do this, we created a database containing over 3 km of video-sequences with ground-truth in the form of distance travelled along different corridors. Using this database, the accuracy of localization - both in terms of knowing which route a user is on - and in terms of position along a certain route, can be evaluated. For each type of descriptor, we also tested different techniques to encode visual structure and to search between journeys to estimate a user's position. The techniques include single-frame descriptors, those using sequences of frames, and both colour and achromatic descriptors. We found that single-frame indexing worked better within this particular dataset. This might be because the motion of the person holding the camera makes the video too dependent on individual steps and motions of one particular journey. Our results suggest that appearance-based information could be an additional source of navigational data indoors, augmenting that provided by, say, radio signal strength indicators (RSSIs). Such visual information could be collected by crowdsourcing low-resolution video feeds, allowing journeys made by different users to be associated with each other, and location to be inferred without requiring explicit mapping. This offers a complementary approach to methods based on simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge