Inbar Gat
ShapeUP: Scalable Image-Conditioned 3D Editing
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D foundation models have enabled the generation of high-fidelity assets, yet precise 3D manipulation remains a significant challenge. Existing 3D editing frameworks often face a difficult trade-off between visual controllability, geometric consistency, and scalability. Specifically, optimization-based methods are prohibitively slow, multi-view 2D propagation techniques suffer from visual drift, and training-free latent manipulation methods are inherently bound by frozen priors and cannot directly benefit from scaling. In this work, we present ShapeUP, a scalable, image-conditioned 3D editing framework that formulates editing as a supervised latent-to-latent translation within a native 3D representation. This formulation allows ShapeUP to build on a pretrained 3D foundation model, leveraging its strong generative prior while adapting it to editing through supervised training. In practice, ShapeUP is trained on triplets consisting of a source 3D shape, an edited 2D image, and the corresponding edited 3D shape, and learns a direct mapping using a 3D Diffusion Transformer (DiT). This image-as-prompt approach enables fine-grained visual control over both local and global edits and achieves implicit, mask-free localization, while maintaining strict structural consistency with the original asset. Our extensive evaluations demonstrate that ShapeUP consistently outperforms current trained and training-free baselines in both identity preservation and edit fidelity, offering a robust and scalable paradigm for native 3D content creation.
AnyTop: Character Animation Diffusion with Any Topology
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Generating motion for arbitrary skeletons is a longstanding challenge in computer graphics, remaining largely unexplored due to the scarcity of diverse datasets and the irregular nature of the data. In this work, we introduce AnyTop, a diffusion model that generates motions for diverse characters with distinct motion dynamics, using only their skeletal structure as input. Our work features a transformer-based denoising network, tailored for arbitrary skeleton learning, integrating topology information into the traditional attention mechanism. Additionally, by incorporating textual joint descriptions into the latent feature representation, AnyTop learns semantic correspondences between joints across diverse skeletons. Our evaluation demonstrates that AnyTop generalizes well, even with as few as three training examples per topology, and can produce motions for unseen skeletons as well. Furthermore, our model's latent space is highly informative, enabling downstream tasks such as joint correspondence, temporal segmentation and motion editing. Our webpage, https://anytop2025.github.io/Anytop-page, includes links to videos and code.
Monkey See, Monkey Do: Harnessing Self-attention in Motion Diffusion for Zero-shot Motion Transfer
Jun 10, 2024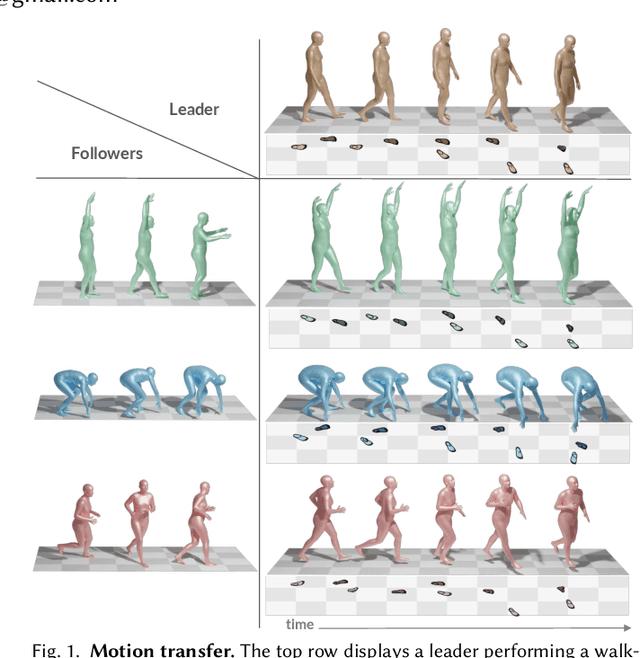
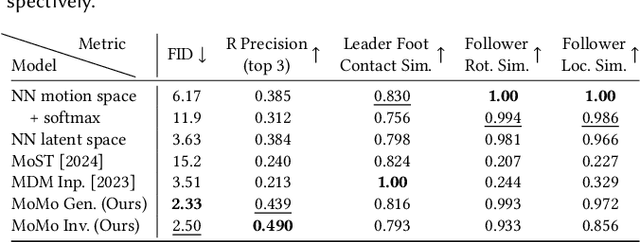
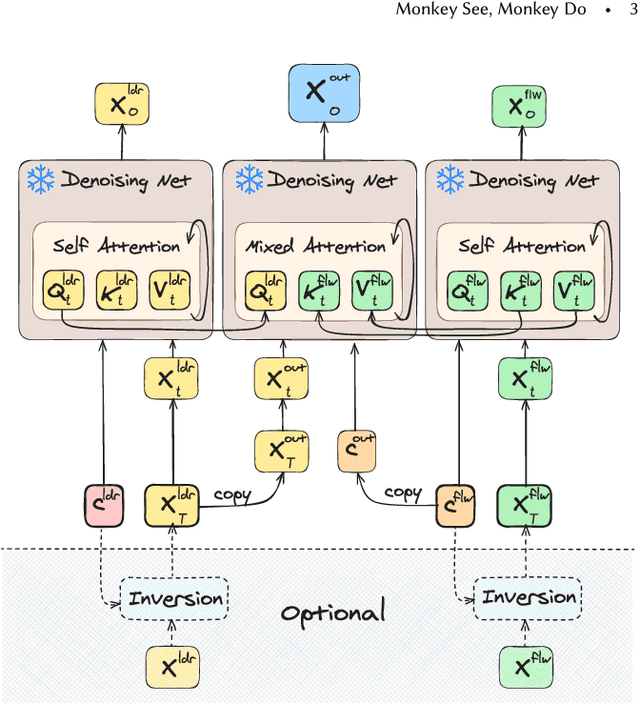
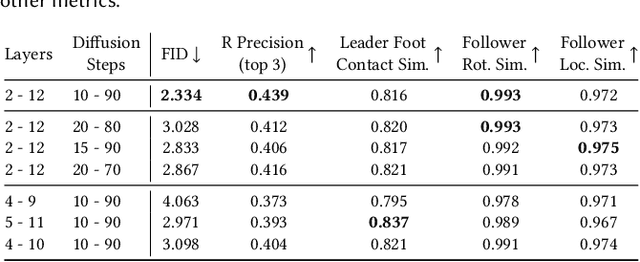
Abstract:Given the remarkable results of motion synthesis with diffusion models, a natural question arises: how can we effectively leverage these models for motion editing? Existing diffusion-based motion editing methods overlook the profound potential of the prior embedded within the weights of pre-trained models, which enables manipulating the latent feature space; hence, they primarily center on handling the motion space. In this work, we explore the attention mechanism of pre-trained motion diffusion models. We uncover the roles and interactions of attention elements in capturing and representing intricate human motion patterns, and carefully integrate these elements to transfer a leader motion to a follower one while maintaining the nuanced characteristics of the follower, resulting in zero-shot motion transfer. Editing features associated with selected motions allows us to confront a challenge observed in prior motion diffusion approaches, which use general directives (e.g., text, music) for editing, ultimately failing to convey subtle nuances effectively. Our work is inspired by how a monkey closely imitates what it sees while maintaining its unique motion patterns; hence we call it Monkey See, Monkey Do, and dub it MoMo. Employing our technique enables accomplishing tasks such as synthesizing out-of-distribution motions, style transfer, and spatial editing. Furthermore, diffusion inversion is seldom employed for motions; as a result, editing efforts focus on generated motions, limiting the editability of real ones. MoMo harnesses motion inversion, extending its application to both real and generated motions. Experimental results show the advantage of our approach over the current art. In particular, unlike methods tailored for specific applications through training, our approach is applied at inference time, requiring no training. Our webpage is at https://monkeyseedocg.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge