Ibrahim Khebour
TRACE: Real-Time Multimodal Common Ground Tracking in Situated Collaborative Dialogues
Mar 12, 2025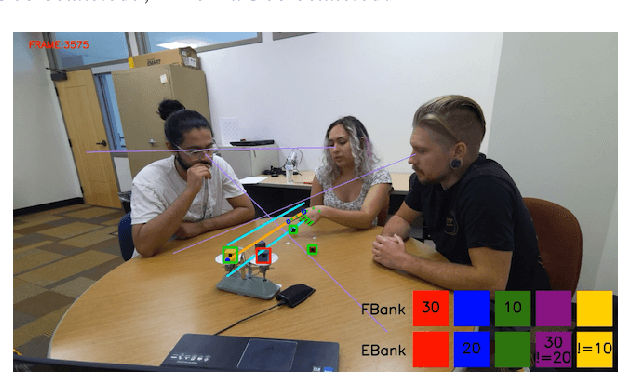

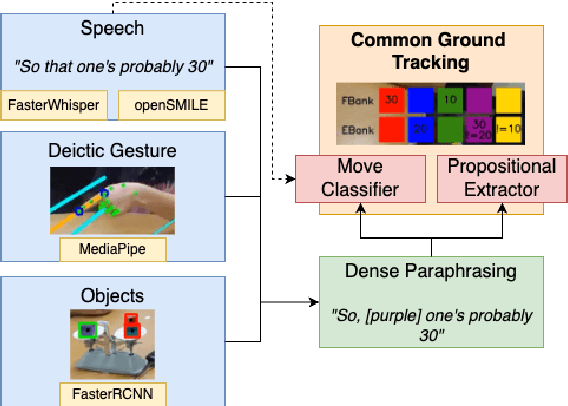
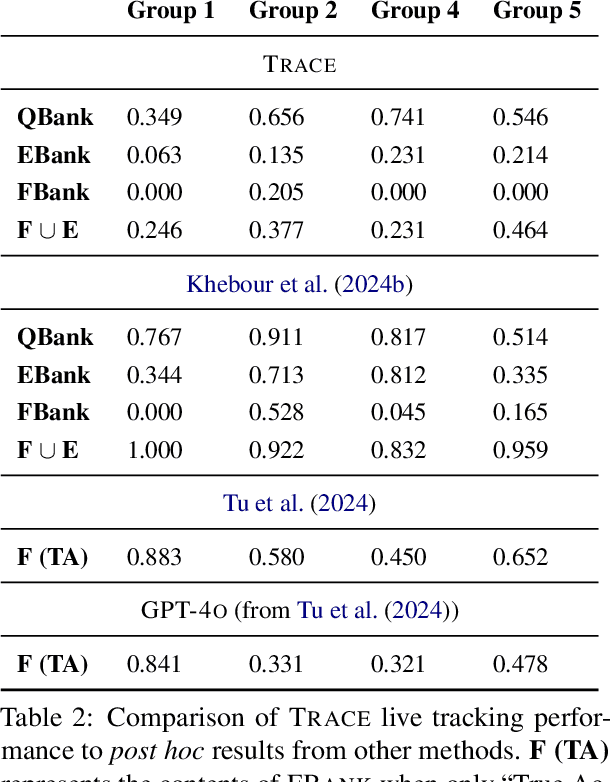
Abstract:We present TRACE, a novel system for live *common ground* tracking in situated collaborative tasks. With a focus on fast, real-time performance, TRACE tracks the speech, actions, gestures, and visual attention of participants, uses these multimodal inputs to determine the set of task-relevant propositions that have been raised as the dialogue progresses, and tracks the group's epistemic position and beliefs toward them as the task unfolds. Amid increased interest in AI systems that can mediate collaborations, TRACE represents an important step forward for agents that can engage with multiparty, multimodal discourse.
Speech Is Not Enough: Interpreting Nonverbal Indicators of Common Knowledge and Engagement
Dec 08, 2024

Abstract:Our goal is to develop an AI Partner that can provide support for group problem solving and social dynamics. In multi-party working group environments, multimodal analytics is crucial for identifying non-verbal interactions of group members. In conjunction with their verbal participation, this creates an holistic understanding of collaboration and engagement that provides necessary context for the AI Partner. In this demo, we illustrate our present capabilities at detecting and tracking nonverbal behavior in student task-oriented interactions in the classroom, and the implications for tracking common ground and engagement.
Common Ground Tracking in Multimodal Dialogue
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:Within Dialogue Modeling research in AI and NLP, considerable attention has been spent on ``dialogue state tracking'' (DST), which is the ability to update the representations of the speaker's needs at each turn in the dialogue by taking into account the past dialogue moves and history. Less studied but just as important to dialogue modeling, however, is ``common ground tracking'' (CGT), which identifies the shared belief space held by all of the participants in a task-oriented dialogue: the task-relevant propositions all participants accept as true. In this paper we present a method for automatically identifying the current set of shared beliefs and ``questions under discussion'' (QUDs) of a group with a shared goal. We annotate a dataset of multimodal interactions in a shared physical space with speech transcriptions, prosodic features, gestures, actions, and facets of collaboration, and operationalize these features for use in a deep neural model to predict moves toward construction of common ground. Model outputs cascade into a set of formal closure rules derived from situated evidence and belief axioms and update operations. We empirically assess the contribution of each feature type toward successful construction of common ground relative to ground truth, establishing a benchmark in this novel, challenging task.
How Good is Automatic Segmentation as a Multimodal Discourse Annotation Aid?
May 27, 2023


Abstract:Collaborative problem solving (CPS) in teams is tightly coupled with the creation of shared meaning between participants in a situated, collaborative task. In this work, we assess the quality of different utterance segmentation techniques as an aid in annotating CPS. We (1) manually transcribe utterances in a dataset of triads collaboratively solving a problem involving dialogue and physical object manipulation, (2) annotate collaborative moves according to these gold-standard transcripts, and then (3) apply these annotations to utterances that have been automatically segmented using toolkits from Google and OpenAI's Whisper. We show that the oracle utterances have minimal correspondence to automatically segmented speech, and that automatically segmented speech using different segmentation methods is also inconsistent. We also show that annotating automatically segmented speech has distinct implications compared with annotating oracle utterances--since most annotation schemes are designed for oracle cases, when annotating automatically-segmented utterances, annotators must invoke other information to make arbitrary judgments which other annotators may not replicate. We conclude with a discussion of how future annotation specs can account for these needs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge