Hussam Lawen
Solving ImageNet: a Unified Scheme for Training any Backbone to Top Results
Apr 07, 2022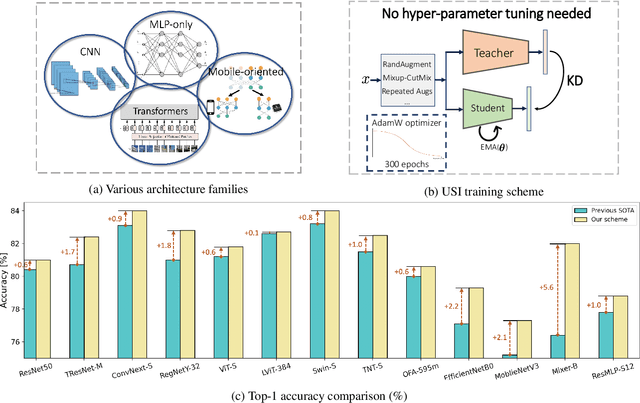
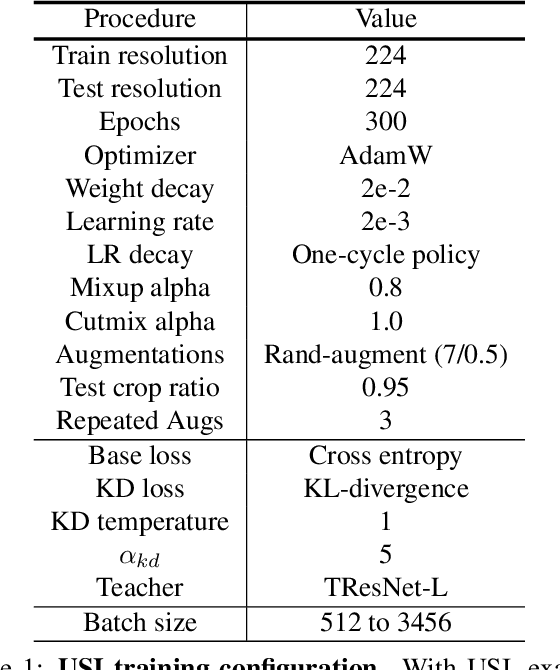
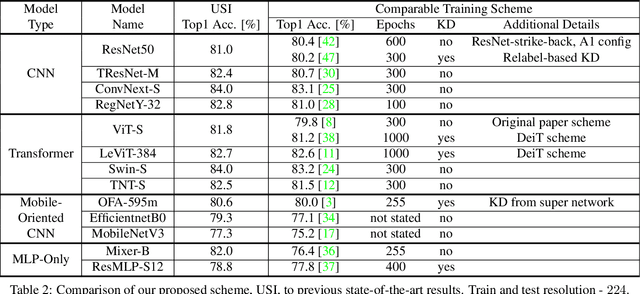
Abstract:ImageNet serves as the primary dataset for evaluating the quality of computer-vision models. The common practice today is training each architecture with a tailor-made scheme, designed and tuned by an expert. In this paper, we present a unified scheme for training any backbone on ImageNet. The scheme, named USI (Unified Scheme for ImageNet), is based on knowledge distillation and modern tricks. It requires no adjustments or hyper-parameters tuning between different models, and is efficient in terms of training times. We test USI on a wide variety of architectures, including CNNs, Transformers, Mobile-oriented and MLP-only. On all models tested, USI outperforms previous state-of-the-art results. Hence, we are able to transform training on ImageNet from an expert-oriented task to an automatic seamless routine. Since USI accepts any backbone and trains it to top results, it also enables to perform methodical comparisons, and identify the most efficient backbones along the speed-accuracy Pareto curve. Implementation is available at:https://github.com/Alibaba-MIIL/Solving_ImageNet
It's All in the Head: Representation Knowledge Distillation through Classifier Sharing
Jan 18, 2022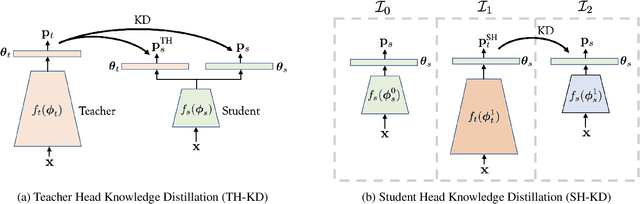
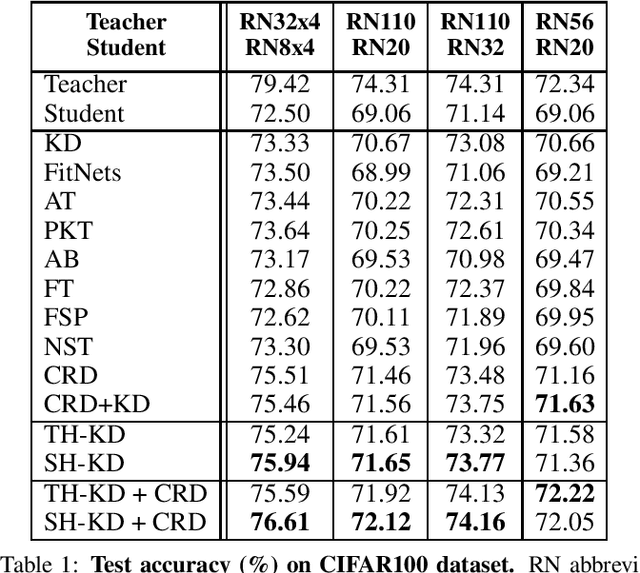
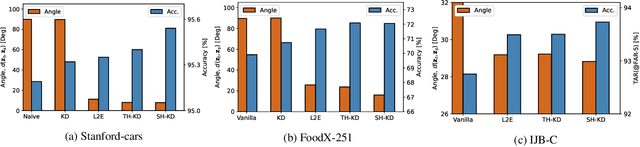
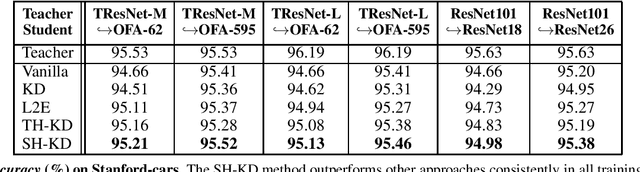
Abstract:Representation knowledge distillation aims at transferring rich information from one model to another. Current approaches for representation distillation mainly focus on the direct minimization of distance metrics between the models' embedding vectors. Such direct methods may be limited in transferring high-order dependencies embedded in the representation vectors, or in handling the capacity gap between the teacher and student models. In this paper, we introduce two approaches for enhancing representation distillation using classifier sharing between the teacher and student. Specifically, we first show that connecting the teacher's classifier to the student backbone and freezing its parameters is beneficial for the process of representation distillation, yielding consistent improvements. Then, we propose an alternative approach that asks to tailor the teacher model to a student with limited capacity. This approach competes with and in some cases surpasses the first method. Via extensive experiments and analysis, we show the effectiveness of the proposed methods on various datasets and tasks, including image classification, fine-grained classification, and face verification. For example, we achieve state-of-the-art performance for face verification on the IJB-C dataset for a MobileFaceNet model: TAR@(FAR=1e-5)=93.7\%. Code is available at https://github.com/Alibaba-MIIL/HeadSharingKD.
TResNet: High Performance GPU-Dedicated Architecture
Mar 30, 2020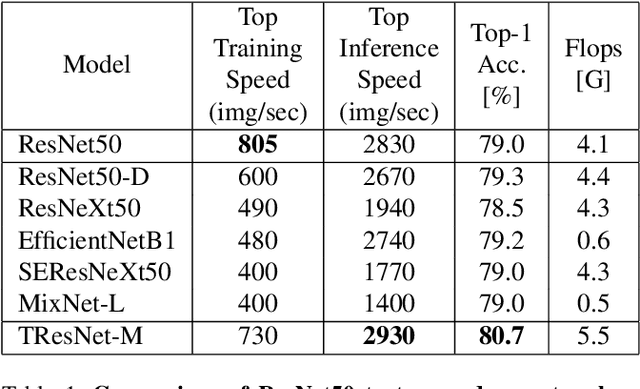
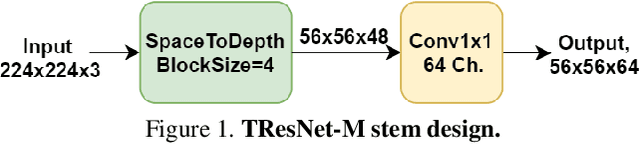
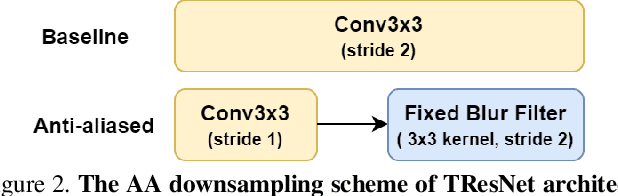
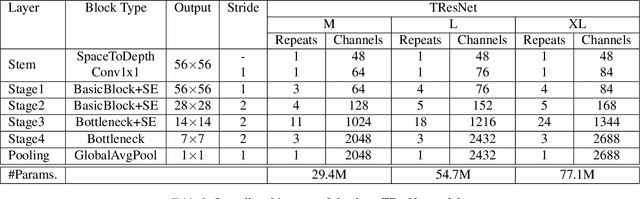
Abstract:Many deep learning models, developed in recent years, reach higher ImageNet accuracy than ResNet50, with fewer or comparable FLOPS count. While FLOPs are often seen as a proxy for network efficiency, when measuring actual GPU training and inference throughput, vanilla ResNet50 is usually significantly faster than its recent competitors, offering better throughput-accuracy trade-off. In this work, we introduce a series of architecture modifications that aim to boost neural networks' accuracy, while retaining their GPU training and inference efficiency. We first demonstrate and discuss the bottlenecks induced by FLOPs-optimizations. We then suggest alternative designs that better utilize GPU structure and assets. Finally, we introduce a new family of GPU-dedicated models, called TResNet, which achieve better accuracy and efficiency than previous ConvNets. Using a TResNet model, with similar GPU throughput to ResNet50, we reach 80.7% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet. Our TResNet models also transfer well and achieve state-of-the-art accuracy on competitive datasets such as Stanford cars (96.0%), CIFAR-10 (99.0%), CIFAR-100 (91.5%) and Oxford-Flowers (99.1%). Implementation is available at: https://github.com/mrT23/TResNet
Attention Network Robustification for Person ReID
Oct 29, 2019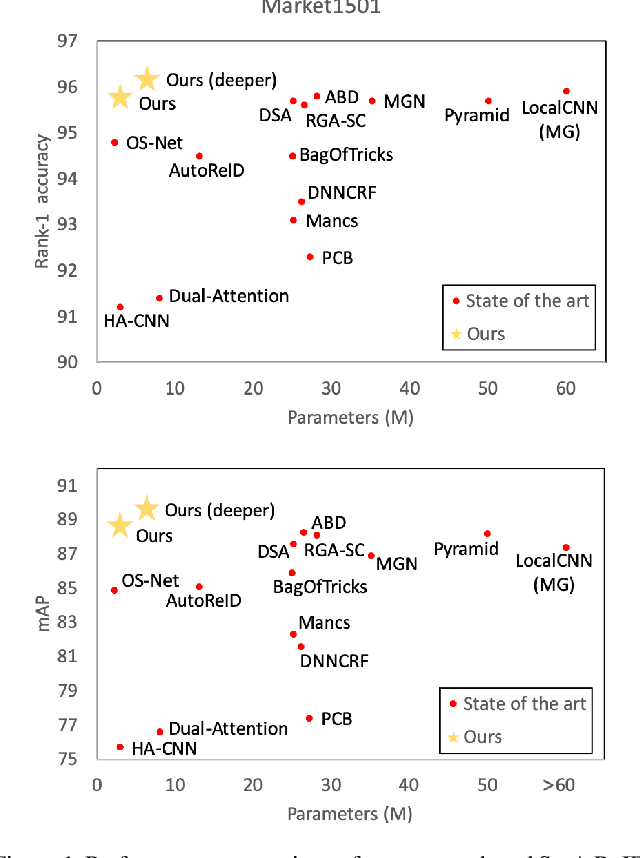
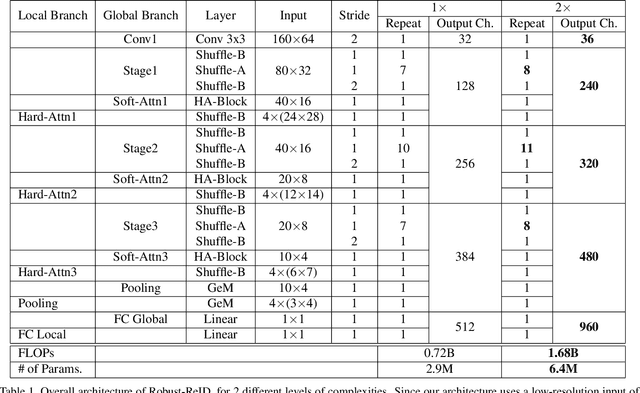
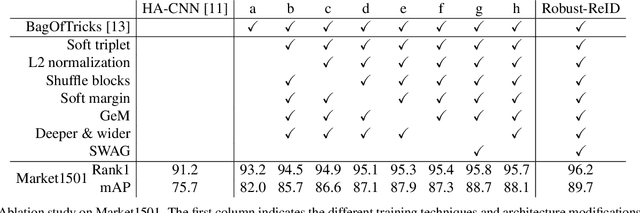
Abstract:The task of person re-identification (ReID) has attracted growing attention in recent years with improving performance but lack of focus on real-world applications. Most state of the art methods use large pre-trained models, e.g., ResNet50 (~25M parameters), as their backbone, which makes it tedious to explore different architecture modifications. In this study, we focus on small-sized randomly initialized models which enable us to easily introduce network and training modifications suitable for person ReID public datasets and real-world setups. We show the robustness of our network and training improvements by outperforming state of the art results in terms of rank-1 accuracy and mAP on Market1501 (96.2, 89.7) and DukeMTMC (89.8, 80.3) with only 6.4M parameters and without using re-ranking. Finally, we show the applicability of the proposed ReID network for multi-object tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge