Huidong Tang
A Reinforcement Learning-Driven Transformer GAN for Molecular Generation
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Generating molecules with desired chemical properties presents a critical challenge in fields such as chemical synthesis and drug discovery. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning have significantly contributed to data-driven molecular generation. However, challenges persist due to the inherent sensitivity of simplified molecular input line entry system (SMILES) representations and the difficulties in applying generative adversarial networks (GANs) to discrete data. This study introduces RL-MolGAN, a novel Transformer-based discrete GAN framework designed to address these challenges. Unlike traditional Transformer architectures, RL-MolGAN utilizes a first-decoder-then-encoder structure, facilitating the generation of drug-like molecules from both $de~novo$ and scaffold-based designs. In addition, RL-MolGAN integrates reinforcement learning (RL) and Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) techniques to enhance the stability of GAN training and optimize the chemical properties of the generated molecules. To further improve the model's performance, RL-MolWGAN, an extension of RL-MolGAN, incorporates Wasserstein distance and mini-batch discrimination, which together enhance the stability of the GAN. Experimental results on two widely used molecular datasets, QM9 and ZINC, validate the effectiveness of our models in generating high-quality molecular structures with diverse and desirable chemical properties.
Tailored Federated Learning: Leveraging Direction Regulation & Knowledge Distillation
Sep 29, 2024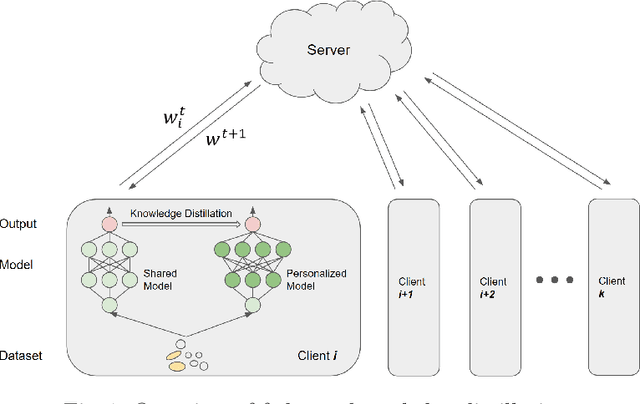
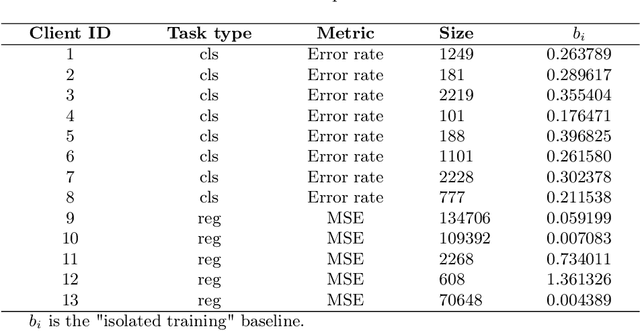
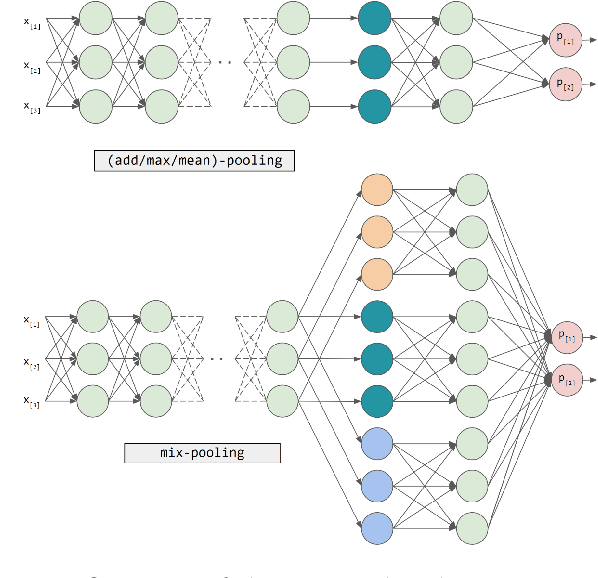
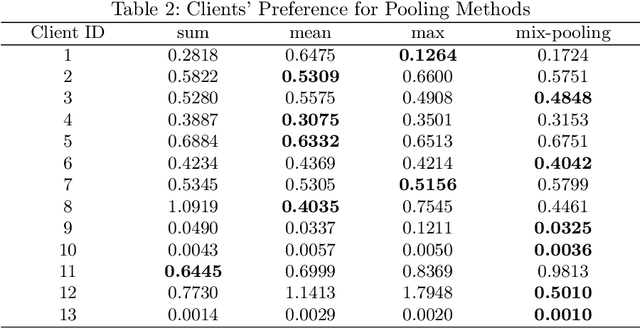
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a transformative training paradigm, particularly invaluable in privacy-sensitive domains like healthcare. However, client heterogeneity in data, computing power, and tasks poses a significant challenge. To address such a challenge, we propose an FL optimization algorithm that integrates model delta regularization, personalized models, federated knowledge distillation, and mix-pooling. Model delta regularization optimizes model updates centrally on the server, efficiently updating clients with minimal communication costs. Personalized models and federated knowledge distillation strategies are employed to tackle task heterogeneity effectively. Additionally, mix-pooling is introduced to accommodate variations in the sensitivity of readout operations. Experimental results demonstrate the remarkable accuracy and rapid convergence achieved by model delta regularization. Additionally, the federated knowledge distillation algorithm notably improves FL performance, especially in scenarios with diverse data. Moreover, mix-pooling readout operations provide tangible benefits for clients, showing the effectiveness of our proposed methods.
When Molecular GAN Meets Byte-Pair Encoding
Sep 29, 2024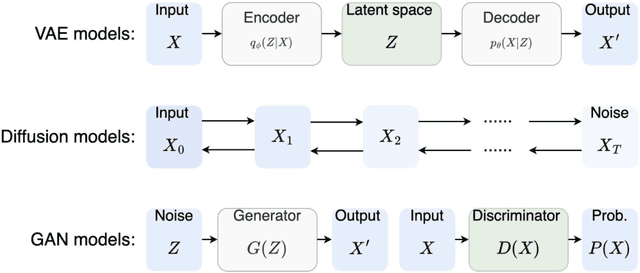
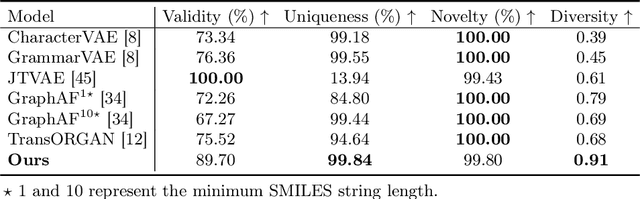
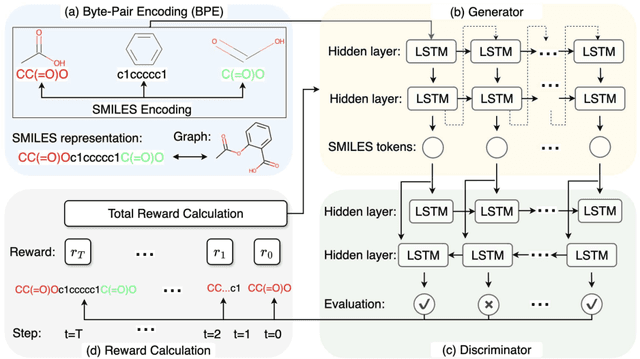
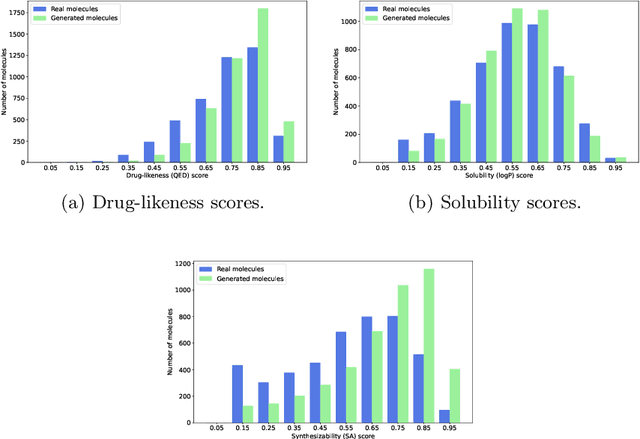
Abstract:Deep generative models, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), are pivotal in discovering novel drug-like candidates via de novo molecular generation. However, traditional character-wise tokenizers often struggle with identifying novel and complex sub-structures in molecular data. In contrast, alternative tokenization methods have demonstrated superior performance. This study introduces a molecular GAN that integrates a byte level byte-pair encoding tokenizer and employs reinforcement learning to enhance de novo molecular generation. Specifically, the generator functions as an actor, producing SMILES strings, while the discriminator acts as a critic, evaluating their quality. Our molecular GAN also integrates innovative reward mechanisms aimed at improving computational efficiency. Experimental results assessing validity, uniqueness, novelty, and diversity, complemented by detailed visualization analysis, robustly demonstrate the effectiveness of our GAN.
Enhancing the Performance of Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis Systems
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis aims to predict sentiment polarity with fine granularity. While Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) are widely utilized for sentimental feature extraction, their naive application for syntactic feature extraction can compromise information preservation. This study introduces an innovative edge-enhanced GCN, named SentiSys, to navigate the syntactic graph while preserving intact feature information, leading to enhanced performance. Specifically,we first integrate a bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) network and a self-attention-based transformer. This combination facilitates effective text encoding, preventing the loss of information and predicting long dependency text. A bidirectional GCN (Bi-GCN) with message passing is then employed to encode relationships between entities. Additionally, unnecessary information is filtered out using an aspect-specific masking technique. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed model, we conduct extensive evaluation experiments and ablation studies on four benchmark datasets. The results consistently demonstrate improved performance in aspect-based sentiment analysis when employing SentiSys. This approach successfully addresses the challenges associated with syntactic feature extraction, highlighting its potential for advancing sentiment analysis methodologies.
Molecular Generative Adversarial Network with Multi-Property Optimization
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Deep generative models, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), have been employed for $de~novo$ molecular generation in drug discovery. Most prior studies have utilized reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms, particularly Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS), to handle the discrete nature of molecular representations in GANs. However, due to the inherent instability in training GANs and RL models, along with the high computational cost associated with MCTS sampling, MCTS RL-based GANs struggle to scale to large chemical databases. To tackle these challenges, this study introduces a novel GAN based on actor-critic RL with instant and global rewards, called InstGAN, to generate molecules at the token-level with multi-property optimization. Furthermore, maximized information entropy is leveraged to alleviate the mode collapse. The experimental results demonstrate that InstGAN outperforms other baselines, achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art models, and efficiently generates molecules with multi-property optimization. The source code will be released upon acceptance of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge