Horia Velicu
"Vorbeşti Româneşte?" A Recipe to Train Powerful Romanian LLMs with English Instructions
Jun 26, 2024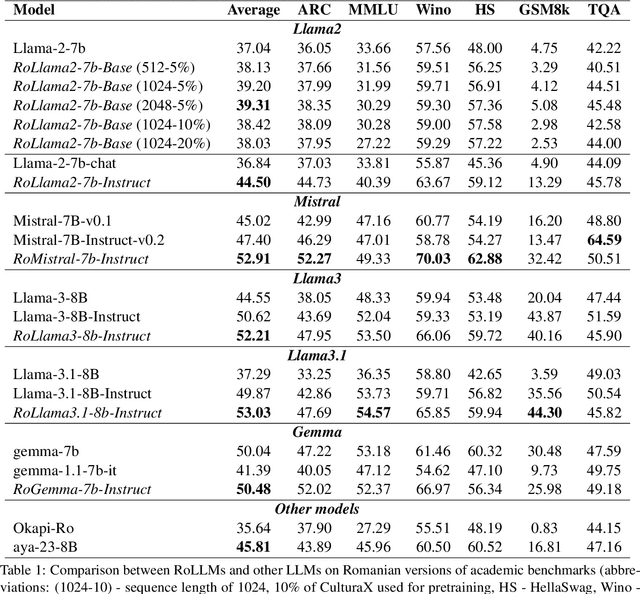
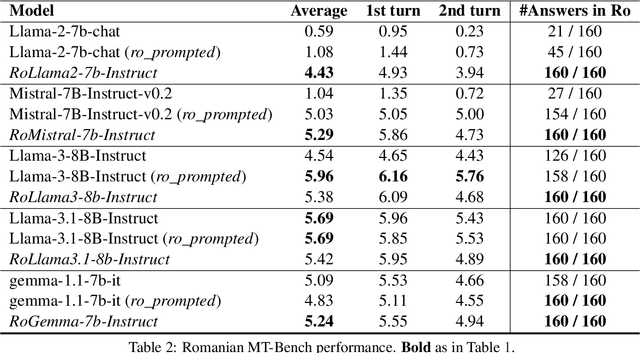
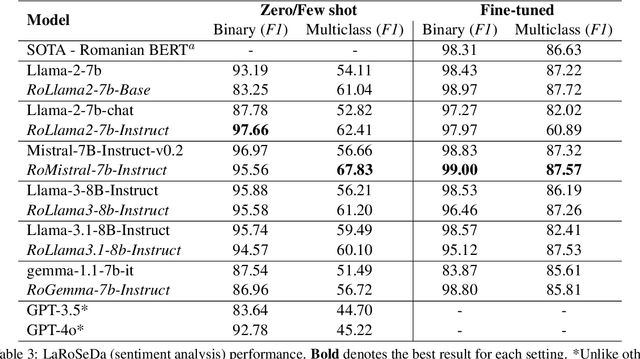
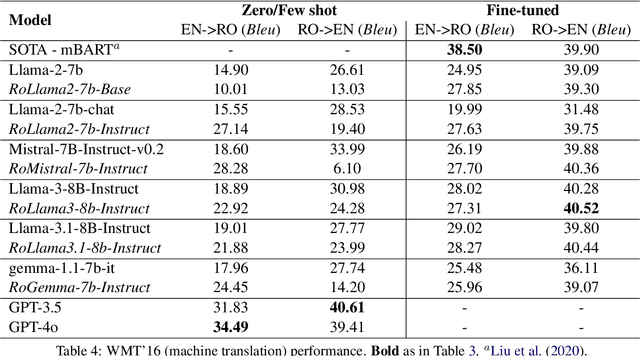
Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved almost human-like performance on various tasks. While some LLMs have been trained on multilingual data, most of the training data is in English; hence, their performance in English greatly exceeds other languages. To our knowledge, we are the first to collect and translate a large collection of texts, instructions, and benchmarks and train, evaluate, and release open-source LLMs tailored for Romanian. We evaluate our methods on four different categories, including academic benchmarks, MT-Bench (manually translated), and a professionally built historical, cultural, and social benchmark adapted to Romanian. We argue for the usefulness and high performance of RoLLMs by obtaining state-of-the-art results across the board. We publicly release all resources (i.e., data, training and evaluation code, models) to support and encourage research on Romanian LLMs while concurrently creating a generalizable recipe, adequate for other low or less-resourced languages.
OpenLLM-Ro -- Technical Report on Open-source Romanian LLMs
May 17, 2024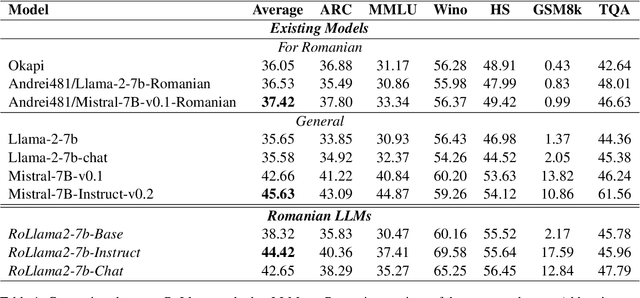
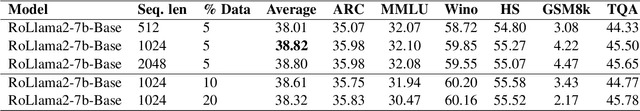
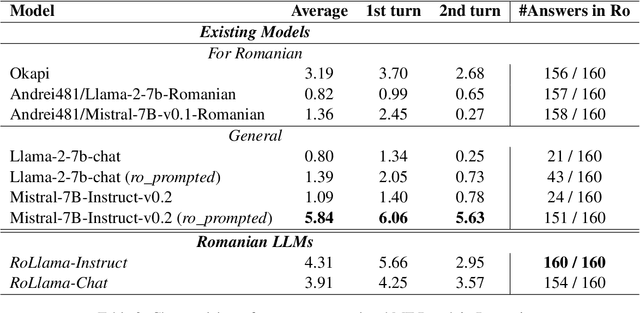
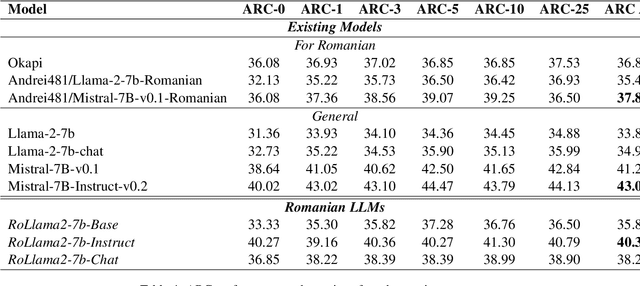
Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved almost human-like performance on various tasks. While some LLMs have been trained on multilingual data, most of the training data is in English. Hence, their performance in English greatly exceeds their performance in other languages. This document presents our approach to training and evaluating the first foundational and chat LLM specialized for Romanian.
Improving Legal Judgement Prediction in Romanian with Long Text Encoders
Mar 04, 2024



Abstract:In recent years,the entire field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has enjoyed amazing novel results achieving almost human-like performance on a variety of tasks. Legal NLP domain has also been part of this process, as it has seen an impressive growth. However, general-purpose models are not readily applicable for legal domain. Due to the nature of the domain (e.g. specialized vocabulary, long documents) specific models and methods are often needed for Legal NLP. In this work we investigate both specialized and general models for predicting the final ruling of a legal case, task known as Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP). We particularly focus on methods to extend to sequence length of Transformer-based models to better understand the long documents present in legal corpora. Extensive experiments on 4 LJP datasets in Romanian, originating from 2 sources with significantly different sizes and document lengths, show that specialized models and handling long texts are critical for a good performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge