Honghao Zhu
SuperLoc: The Key to Robust LiDAR-Inertial Localization Lies in Predicting Alignment Risks
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Map-based LiDAR localization, while widely used in autonomous systems, faces significant challenges in degraded environments due to lacking distinct geometric features. This paper introduces SuperLoc, a robust LiDAR localization package that addresses key limitations in existing methods. SuperLoc features a novel predictive alignment risk assessment technique, enabling early detection and mitigation of potential failures before optimization. This approach significantly improves performance in challenging scenarios such as corridors, tunnels, and caves. Unlike existing degeneracy mitigation algorithms that rely on post-optimization analysis and heuristic thresholds, SuperLoc evaluates the localizability of raw sensor measurements. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods across various degraded environments. Our approach achieves a 54% increase in accuracy and exhibits the highest robustness. To facilitate further research, we release our implementation along with datasets from eight challenging scenarios
Pay Attention to How You Drive: Safe and Adaptive Model-Based Reinforcement Learning for Off-Road Driving
Oct 12, 2023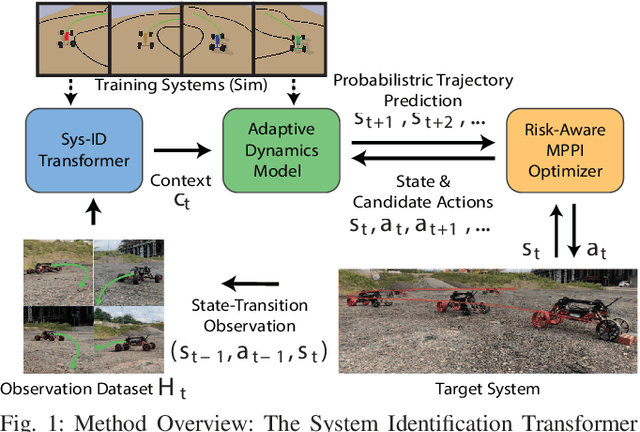
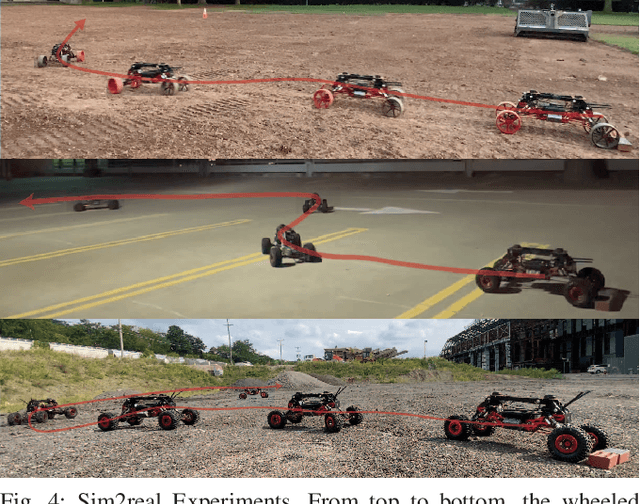
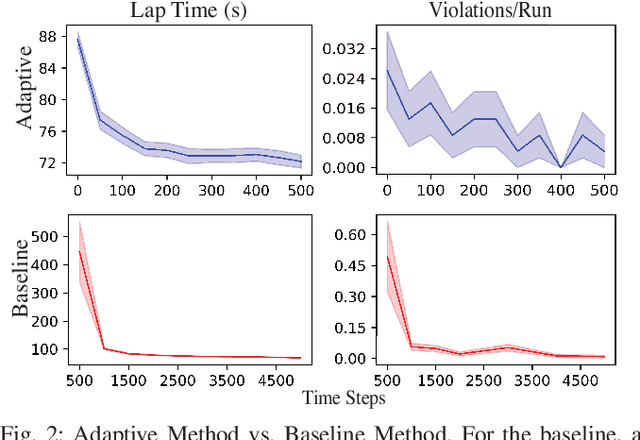
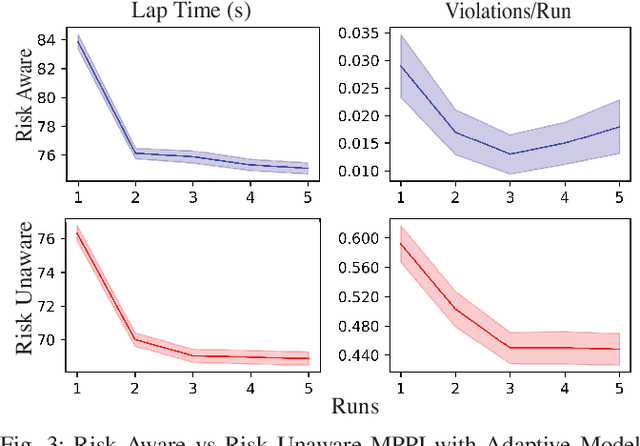

Abstract:Autonomous off-road driving is challenging as risky actions taken by the robot may lead to catastrophic damage. As such, developing controllers in simulation is often desirable as it provides a safer and more economical alternative. However, accurately modeling robot dynamics is difficult due to the complex robot dynamics and terrain interactions in unstructured environments. Domain randomization addresses this problem by randomizing simulation dynamics parameters, however this approach sacrifices performance for robustness leading to policies that are sub-optimal for any target dynamics. We introduce a novel model-based reinforcement learning approach that aims to balance robustness with adaptability. Our approach trains a System Identification Transformer (SIT) and an Adaptive Dynamics Model (ADM) under a variety of simulated dynamics. The SIT uses attention mechanisms to distill state-transition observations from the target system into a context vector, which provides an abstraction for its target dynamics. Conditioned on this, the ADM probabilistically models the system's dynamics. Online, we use a Risk-Aware Model Predictive Path Integral controller (MPPI) to safely control the robot under its current understanding of the dynamics. We demonstrate in simulation as well as in multiple real-world environments that this approach enables safer behaviors upon initialization and becomes less conservative (i.e. faster) as its understanding of the target system dynamics improves with more observations. In particular, our approach results in an approximately 41% improvement in lap-time over the non-adaptive baseline while remaining safe across different environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge