Henry Chen
Discount Model Search for Quality Diversity Optimization in High-Dimensional Measure Spaces
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Quality diversity (QD) optimization searches for a collection of solutions that optimize an objective while attaining diverse outputs of a user-specified, vector-valued measure function. Contemporary QD algorithms focus on low-dimensional measures because high-dimensional measures are prone to distortion, where many solutions found by the QD algorithm map to similar measures. For example, the CMA-MAE algorithm guides measure space exploration with a histogram in measure space that records so-called discount values. However, CMA-MAE stagnates in domains with high-dimensional measure spaces because solutions with similar measures fall into the same histogram cell and thus receive identical discount values. To address these limitations, we propose Discount Model Search (DMS), which guides exploration with a model that provides a smooth, continuous representation of discount values. In high-dimensional measure spaces, this model enables DMS to distinguish between solutions with similar measures and thus continue exploration. We show that DMS facilitates new QD applications by introducing two domains where the measure space is the high-dimensional space of images, which enables users to specify their desired measures by providing a dataset of images rather than hand-designing the measure function. Results in these domains and on high-dimensional benchmarks show that DMS outperforms CMA-MAE and other black-box QD algorithms.
Autonomous Vehicle Visual Signals for Pedestrians: Experiments and Design Recommendations
Oct 10, 2020

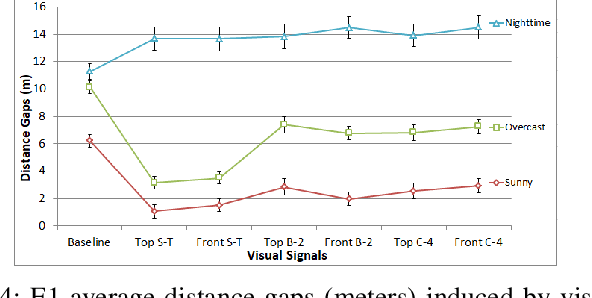
Abstract:Autonomous Vehicles (AV) will transform transportation, but also the interaction between vehicles and pedestrians. In the absence of a driver, it is not clear how an AV can communicate its intention to pedestrians. One option is to use visual signals. To advance their design, we conduct four human-participant experiments and evaluate six representative AV visual signals for visibility, intuitiveness, persuasiveness, and usability at pedestrian crossings. Based on the results, we distill twelve practical design recommendations for AV visual signals, with focus on signal pattern design and placement. Moreover, the paper advances the methodology for experimental evaluation of visual signals, including lab, closed-course, and public road tests using an autonomous vehicle. In addition, the paper also reports insights on pedestrian crosswalk behaviours and the impacts of pedestrian trust towards AVs on the behaviors. We hope that this work will constitute valuable input to the ongoing development of international standards for AV lamps, and thus help mature automated driving in general.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge