Heng Xie
MDPE: A Multimodal Deception Dataset with Personality and Emotional Characteristics
Jul 17, 2024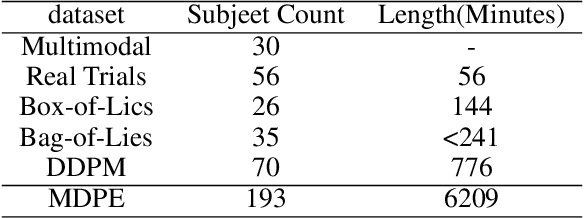


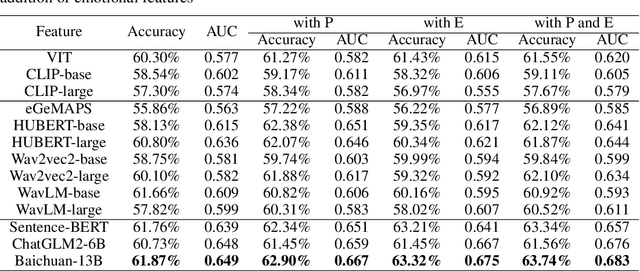
Abstract:Deception detection has garnered increasing attention in recent years due to the significant growth of digital media and heightened ethical and security concerns. It has been extensively studied using multimodal methods, including video, audio, and text. In addition, individual differences in deception production and detection are believed to play a crucial role.Although some studies have utilized individual information such as personality traits to enhance the performance of deception detection, current systems remain limited, partly due to a lack of sufficient datasets for evaluating performance. To address this issue, we introduce a multimodal deception dataset MDPE. Besides deception features, this dataset also includes individual differences information in personality and emotional expression characteristics. It can explore the impact of individual differences on deception behavior. It comprises over 104 hours of deception and emotional videos from 193 subjects. Furthermore, we conducted numerous experiments to provide valuable insights for future deception detection research. MDPE not only supports deception detection, but also provides conditions for tasks such as personality recognition and emotion recognition, and can even study the relationships between them. We believe that MDPE will become a valuable resource for promoting research in the field of affective computing.
Towards Cooperative Transport of a Suspended Payload via Two Aerial Robots with Inertial Sensing
Jul 29, 2020



Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of cooperative transport of a point mass hoisted by two aerial robots. Treating the robots as a leader and a follower, the follower stabilizes the system with respect to the leader using only feedback from its Inertial Measurement Units (IMU). This is accomplished by neglecting the acceleration of the leader, analyzing the system through the generalized coordinates or the cables' angles, and employing an observation model based on the IMU measurements. A lightweight estimator based on an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) and a controller are derived to stabilize the robot-payload-robot system. The proposed methods are verified with extensive flight experiments, first with a single robot and then with two robots. The results show that the follower is capable of realizing the desired quasi-static trajectory using only its IMU measurements. The outcomes demonstrate promising progress towards the goal of autonomous cooperative transport of a suspended payload via small flying robots with minimal sensing and computational requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge