Henan Sun
OpenDDI: A Comprehensive Benchmark for DDI Prediction
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Drug-Drug Interactions (DDIs) significantly influence therapeutic efficacy and patient safety. As experimental discovery is resource-intensive and time-consuming, efficient computational methodologies have become essential. The predominant paradigm formulates DDI prediction as a drug graph-based link prediction task. However, further progress is hindered by two fundamental challenges: (1) lack of high-quality data: most studies rely on small-scale DDI datasets and single-modal drug representations; (2) lack of standardized evaluation: inconsistent scenarios, varied metrics, and diverse baselines. To address the above issues, we propose OpenDDI, a comprehensive benchmark for DDI prediction. Specifically, (1) from the data perspective, OpenDDI unifies 6 widely used DDI datasets and 2 existing forms of drug representation, while additionally contributing 3 new large-scale LLM-augmented datasets and a new multimodal drug representation covering 5 modalities. (2) From the evaluation perspective, OpenDDI unifies 20 SOTA model baselines across 3 downstream tasks, with standardized protocols for data quality, effectiveness, generalization, robustness, and efficiency. Based on OpenDDI, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation and derive 10 valuable insights for DDI prediction while exposing current limitations to provide critical guidance for this rapidly evolving field. Our code is available at https://github.com/xiaoriwuguang/OpenDDI
LION: A Clifford Neural Paradigm for Multimodal-Attributed Graph Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recently, the rapid advancement of multimodal domains has driven a data-centric paradigm shift in graph ML, transitioning from text-attributed to multimodal-attributed graphs. This advancement significantly enhances data representation and expands the scope of graph downstream tasks, such as modality-oriented tasks, thereby improving the practical utility of graph ML. Despite its promise, limitations exist in the current neural paradigms: (1) Neglect Context in Modality Alignment: Most existing methods adopt topology-constrained or modality-specific operators as tokenizers. These aligners inevitably neglect graph context and inhibit modality interaction, resulting in suboptimal alignment. (2) Lack of Adaptation in Modality Fusion: Most existing methods are simple adaptations for 2-modality graphs and fail to adequately exploit aligned tokens equipped with topology priors during fusion, leading to poor generalizability and performance degradation. To address the above issues, we propose LION (c\underline{LI}ff\underline{O}rd \underline{N}eural paradigm) based on the Clifford algebra and decoupled graph neural paradigm (i.e., propagation-then-aggregation) to implement alignment-then-fusion in multimodal-attributed graphs. Specifically, we first construct a modality-aware geometric manifold grounded in Clifford algebra. This geometric-induced high-order graph propagation efficiently achieves modality interaction, facilitating modality alignment. Then, based on the geometric grade properties of aligned tokens, we propose adaptive holographic aggregation. This module integrates the energy and scale of geometric grades with learnable parameters to improve modality fusion. Extensive experiments on 9 datasets demonstrate that LION significantly outperforms SOTA baselines across 3 graph and 3 modality downstream tasks.
DANCE: Dynamic, Available, Neighbor-gated Condensation for Federated Text-Attributed Graphs
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Federated graph learning (FGL) enables collaborative training on graph data across multiple clients. With the rise of large language models (LLMs), textual attributes in FGL graphs are gaining attention. Text-attributed graph federated learning (TAG-FGL) improves FGL by explicitly leveraging LLMs to process and integrate these textual features. However, current TAG-FGL methods face three main challenges: \textbf{(1) Overhead.} LLMs for processing long texts incur high token and computation costs. To make TAG-FGL practical, we introduce graph condensation (GC) to reduce computation load, but this choice also brings new issues. \textbf{(2) Suboptimal.} To reduce LLM overhead, we introduce GC into TAG-FGL by compressing multi-hop texts/neighborhoods into a condensed core with fixed LLM surrogates. However, this one-shot condensation is often not client-adaptive, leading to suboptimal performance. \textbf{(3) Interpretability.} LLM-based condensation further introduces a black-box bottleneck: summaries lack faithful attribution and clear grounding to specific source spans, making local inspection and auditing difficult. To address the above issues, we propose \textbf{DANCE}, a new TAG-FGL paradigm with GC. To improve \textbf{suboptimal} performance, DANCE performs round-wise, model-in-the-loop condensation refresh using the latest global model. To enhance \textbf{interpretability}, DANCE preserves provenance by storing locally inspectable evidence packs that trace predictions to selected neighbors and source text spans. Across 8 TAG datasets, DANCE improves accuracy by \textbf{2.33\%} at an \textbf{8\%} condensation ratio, with \textbf{33.42\%} fewer tokens than baselines.
BoostFGL: Boosting Fairness in Federated Graph Learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Federated graph learning (FGL) enables collaborative training of graph neural networks (GNNs) across decentralized subgraphs without exposing raw data. While existing FGL methods often achieve high overall accuracy, we show that this average performance can conceal severe degradation on disadvantaged node groups. From a fairness perspective, these disparities arise systematically from three coupled sources: label skew toward majority patterns, topology confounding in message propagation, and aggregation dilution of updates from hard clients. To address this, we propose \textbf{BoostFGL}, a boosting-style framework for fairness-aware FGL. BoostFGL introduces three coordinated mechanisms: \ding{182} \emph{Client-side node boosting}, which reshapes local training signals to emphasize systematically under-served nodes; \ding{183} \emph{Client-side topology boosting}, which reallocates propagation emphasis toward reliable yet underused structures and attenuates misleading neighborhoods; and \ding{184} \emph{Server-side model boosting}, which performs difficulty- and reliability-aware aggregation to preserve informative updates from hard clients while stabilizing the global model. Extensive experiments on 9 datasets show that BoostFGL delivers substantial fairness gains, improving Overall-F1 by 8.43\%, while preserving competitive overall performance against strong FGL baselines.
AlgBench: To What Extent Do Large Reasoning Models Understand Algorithms?
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Reasoning ability has become a central focus in the advancement of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs). Although notable progress has been achieved on several reasoning benchmarks such as MATH500 and LiveCodeBench, existing benchmarks for algorithmic reasoning remain limited, failing to answer a critical question: Do LRMs truly master algorithmic reasoning? To answer this question, we propose AlgBench, an expert-curated benchmark that evaluates LRMs under an algorithm-centric paradigm. AlgBench consists of over 3,000 original problems spanning 27 algorithms, constructed by ACM algorithmic experts and organized under a comprehensive taxonomy, including Euclidean-structured, non-Euclidean-structured, non-optimized, local-optimized, global-optimized, and heuristic-optimized categories. Empirical evaluations on leading LRMs (e.g., Gemini-3-Pro, DeepSeek-v3.2-Speciale and GPT-o3) reveal substantial performance heterogeneity: while models perform well on non-optimized tasks (up to 92%), accuracy drops sharply to around 49% on globally optimized algorithms such as dynamic programming. Further analysis uncovers \textbf{strategic over-shifts}, wherein models prematurely abandon correct algorithmic designs due to necessary low-entropy tokens. These findings expose fundamental limitations of problem-centric reinforcement learning and highlight the necessity of an algorithm-centric training paradigm for robust algorithmic reasoning.
Rethinking Graph Out-Of-Distribution Generalization: A Learnable Random Walk Perspective
May 09, 2025Abstract:Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) generalization has gained increasing attentions for machine learning on graphs, as graph neural networks (GNNs) often exhibit performance degradation under distribution shifts. Existing graph OOD methods tend to follow the basic ideas of invariant risk minimization and structural causal models, interpreting the invariant knowledge across datasets under various distribution shifts as graph topology or graph spectrum. However, these interpretations may be inconsistent with real-world scenarios, as neither invariant topology nor spectrum is assured. In this paper, we advocate the learnable random walk (LRW) perspective as the instantiation of invariant knowledge, and propose LRW-OOD to realize graph OOD generalization learning. Instead of employing fixed probability transition matrix (i.e., degree-normalized adjacency matrix), we parameterize the transition matrix with an LRW-sampler and a path encoder. Furthermore, we propose the kernel density estimation (KDE)-based mutual information (MI) loss to generate random walk sequences that adhere to OOD principles. Extensive experiment demonstrates that our model can effectively enhance graph OOD generalization under various types of distribution shifts and yield a significant accuracy improvement of 3.87% over state-of-the-art graph OOD generalization baselines.
Towards Data-centric Machine Learning on Directed Graphs: a Survey
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have made significant advances in processing structured data. However, most of them primarily adopted a model-centric approach, which simplifies graphs by converting it into undirected formats and emphasizes model designs. This approach is inherently constrained in real-world applications due to inevitable information loss in simple undirected graphs and data-driven model optimization dilemmas associated with exceeding the upper bounds of representational capacity. As a result, there has been a shift toward data-centric methods that prioritize improving graph quality and representation. Specifically, various types of graphs can be derived from naturally structured data, including heterogeneous graphs, hypergraphs, and directed graphs. Among these, directed graphs offer distinct advantages in topological systems by modeling causal relationships, and directed GNNs have been extensively studied in recent years. However, a comprehensive survey of this emerging topic is still lacking. Therefore, we aim to provide a comprehensive review of directed graph learning, with a particular focus on a data-centric perspective. Specifically, we first introduce a novel taxonomy for existing studies. Subsequently, we re-examine these methods from the data-centric perspective, with an emphasis on understanding and improving data representation. It demonstrates that a deep understanding of directed graphs and its quality plays a crucial role in model performance. Additionally, we explore the diverse applications of directed GNNs across 10+ domains, highlighting their broad applicability. Finally, we identify key opportunities and challenges within the field, offering insights that can guide future research and development in directed graph learning.
AdaFGL: A New Paradigm for Federated Node Classification with Topology Heterogeneity
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Recently, Federated Graph Learning (FGL) has attracted significant attention as a distributed framework based on graph neural networks, primarily due to its capability to break data silos. Existing FGL studies employ community split on the homophilous global graph by default to simulate federated semi-supervised node classification settings. Such a strategy assumes the consistency of topology between the multi-client subgraphs and the global graph, where connected nodes are highly likely to possess similar feature distributions and the same label. However, in real-world implementations, the varying perspectives of local data engineering result in various subgraph topologies, posing unique heterogeneity challenges in FGL. Unlike the well-known label Non-independent identical distribution (Non-iid) problems in federated learning, FGL heterogeneity essentially reveals the topological divergence among multiple clients, namely homophily or heterophily. To simulate and handle this unique challenge, we introduce the concept of structure Non-iid split and then present a new paradigm called \underline{Ada}ptive \underline{F}ederated \underline{G}raph \underline{L}earning (AdaFGL), a decoupled two-step personalized approach. To begin with, AdaFGL employs standard multi-client federated collaborative training to acquire the federated knowledge extractor by aggregating uploaded models in the final round at the server. Then, each client conducts personalized training based on the local subgraph and the federated knowledge extractor. Extensive experiments on the 12 graph benchmark datasets validate the superior performance of AdaFGL over state-of-the-art baselines. Specifically, in terms of test accuracy, our proposed AdaFGL outperforms baselines by significant margins of 3.24\% and 5.57\% on community split and structure Non-iid split, respectively.
Breaking the Entanglement of Homophily and Heterophily in Semi-supervised Node Classification
Dec 07, 2023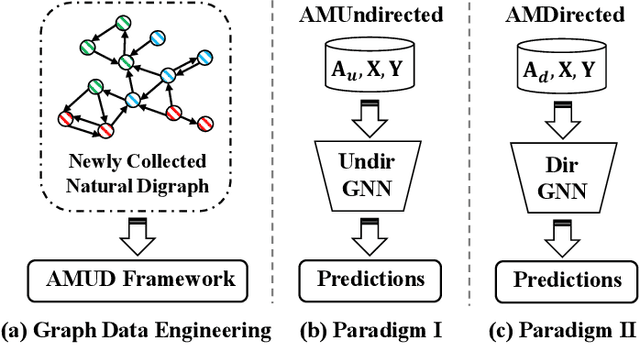
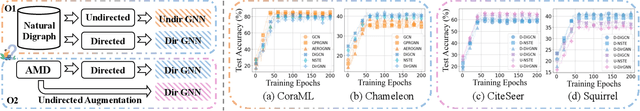
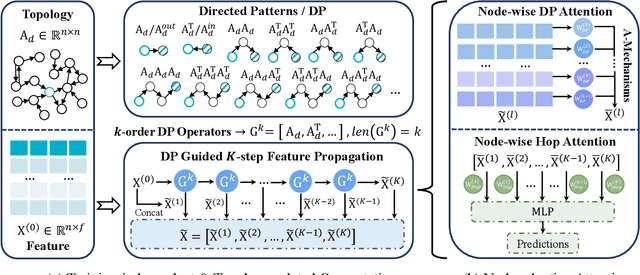
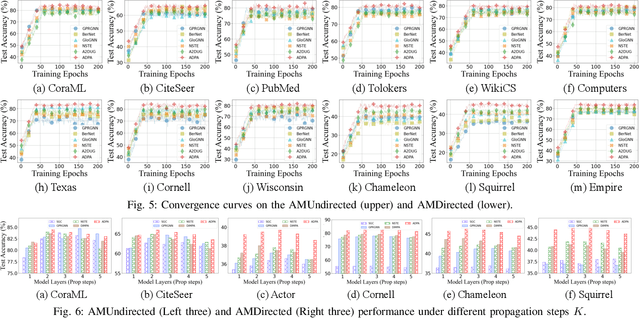
Abstract:Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown prominent performance in semi-supervised node classification by leveraging knowledge from the graph database. However, most existing GNNs follow the homophily assumption, where connected nodes are more likely to exhibit similar feature distributions and the same labels, and such an assumption has proven to be vulnerable in a growing number of practical applications. As a supplement, heterophily reflects dissimilarity in connected nodes, which has gained significant attention in graph learning. To this end, data engineers aim to develop a powerful GNN model that can ensure performance under both homophily and heterophily. Despite numerous attempts, most existing GNNs struggle to achieve optimal node representations due to the constraints of undirected graphs. The neglect of directed edges results in sub-optimal graph representations, thereby hindering the capacity of GNNs. To address this issue, we introduce AMUD, which quantifies the relationship between node profiles and topology from a statistical perspective, offering valuable insights for \underline{A}daptively \underline{M}odeling the natural directed graphs as the \underline{U}ndirected or \underline{D}irected graph to maximize the benefits from subsequent graph learning. Furthermore, we propose \underline{A}daptive \underline{D}irected \underline{P}attern \underline{A}ggregation (ADPA) as a new directed graph learning paradigm for AMUD. Empirical studies have demonstrated that AMUD guides efficient graph learning. Meanwhile, extensive experiments on 14 benchmark datasets substantiate the impressive performance of ADPA, outperforming baselines by significant margins of 3.96\%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge