Hebi Li
Supervised Whole DAG Causal Discovery
Jun 08, 2020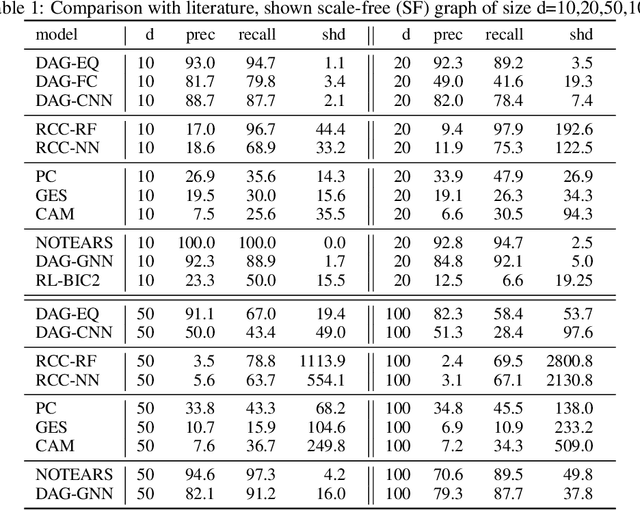

Abstract:We propose to address the task of causal structure learning from data in a supervised manner. Existing work on learning causal directions by supervised learning is restricted to learning pairwise relation, and not well suited for whole DAG discovery. We propose a novel approach of modeling the whole DAG structure discovery as a supervised learning. To fit the problem in hand, we propose to use permutation equivariant models that align well with the problem domain. We evaluate the proposed approach extensively on synthetic graphs of size 10,20,50,100 and real data, and show promising results compared with a variety of previous approaches.
End-to-end Semantics-based Summary Quality Assessment for Single-document Summarization
May 13, 2020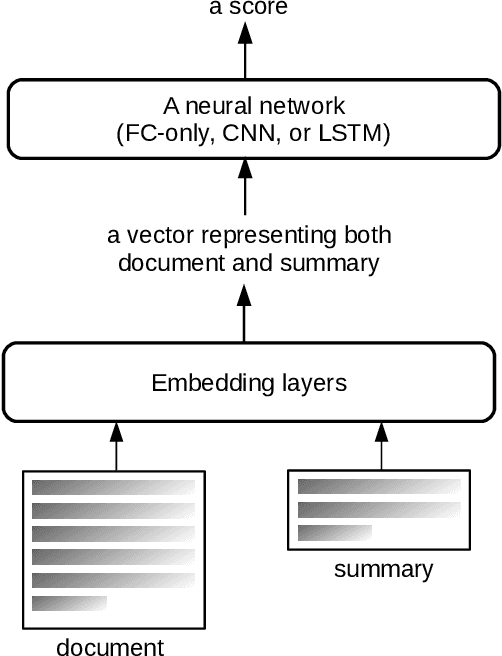
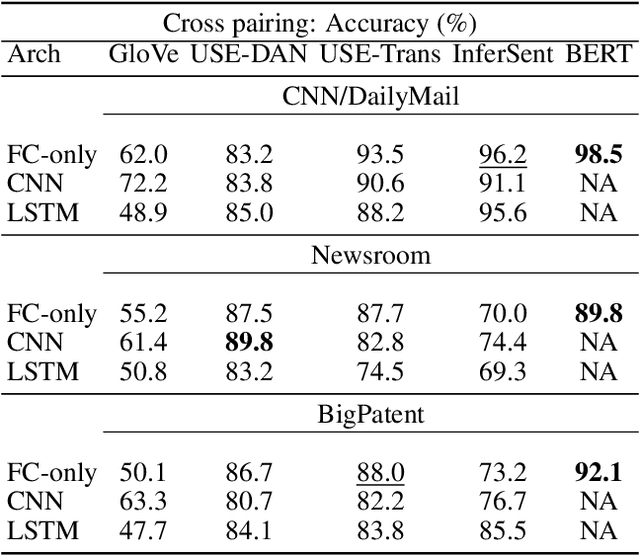

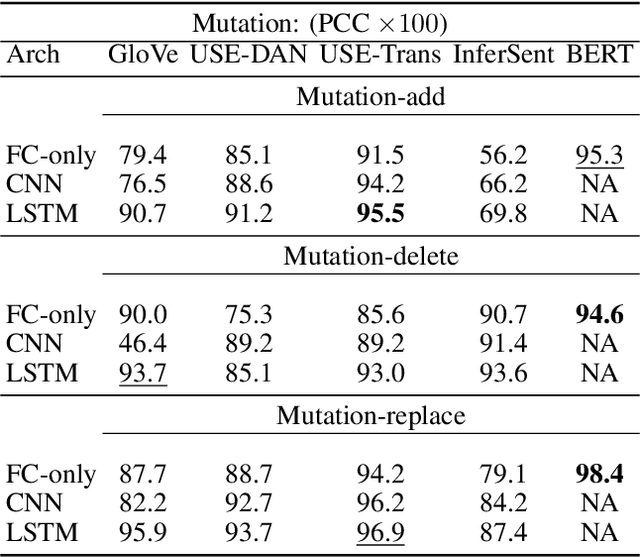
Abstract:ROUGE is the de facto criterion for summarization research. However, its two major drawbacks limit the research and application of automated summarization systems. First, ROUGE favors lexical similarity instead of semantic similarity, making it especially unfit for abstractive summarization. Second, ROUGE cannot function without a reference summary, which is expensive or impossible to obtain in many cases. Therefore, we introduce a new end-to-end metric system for summary quality assessment by leveraging the semantic similarities of words and/or sentences in deep learning. Models trained in our framework can evaluate a summary directly against the input document, without the need of a reference summary. The proposed approach exhibits very promising results on gold-standard datasets and suggests its great potential to future summarization research. The scores from our models have correlation coefficients up to 0.54 with human evaluations on machine generated summaries in TAC2010. Its performance is also very close to ROUGE metrics'.
Purifying Adversarial Perturbation with Adversarially Trained Auto-encoders
May 26, 2019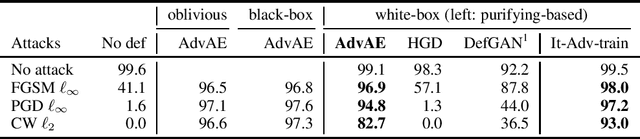
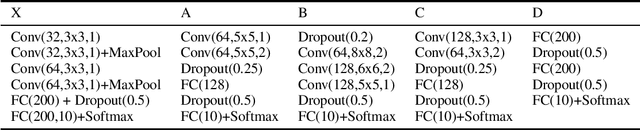
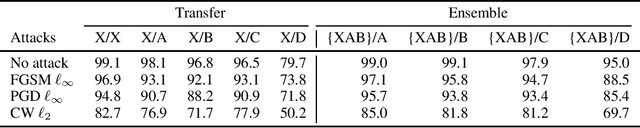
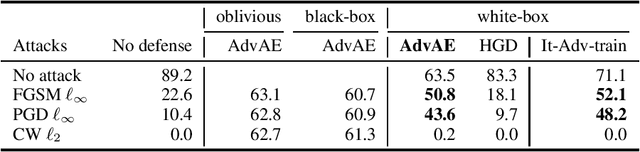
Abstract:Machine learning models are vulnerable to adversarial examples. Iterative adversarial training has shown promising results against strong white-box attacks. However, adversarial training is very expensive, and every time a model needs to be protected, such expensive training scheme needs to be performed. In this paper, we propose to apply iterative adversarial training scheme to an external auto-encoder, which once trained can be used to protect other models directly. We empirically show that our model outperforms other purifying-based methods against white-box attacks, and transfers well to directly protect other base models with different architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge