Heajun An
StagePilot: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Agent for Stage-Controlled Cybergrooming Simulation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Cybergrooming is an evolving threat to youth, necessitating proactive educational interventions. We propose StagePilot, an offline RL-based dialogue agent that simulates the stage-wise progression of grooming behaviors for prevention training. StagePilot selects conversational stages using a composite reward that balances user sentiment and goal proximity, with transitions constrained to adjacent stages for realism and interpretability. We evaluate StagePilot through LLM-based simulations, measuring stage completion, dialogue efficiency, and emotional engagement. Results show that StagePilot generates realistic and coherent conversations aligned with grooming dynamics. Among tested methods, the IQL+AWAC agent achieves the best balance between strategic planning and emotional coherence, reaching the final stage up to 43% more frequently than baselines while maintaining over 70% sentiment alignment.
VEXA: Evidence-Grounded and Persona-Adaptive Explanations for Scam Risk Sensemaking
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Online scams across email, short message services, and social media increasingly challenge everyday risk assessment, particularly as generative AI enables more fluent and context-aware deception. Although transformer-based detectors achieve strong predictive performance, their explanations are often opaque to non-experts or misaligned with model decisions. We propose VEXA, an evidence-grounded and persona-adaptive framework for generating learner-facing scam explanations by integrating GradientSHAP-based attribution with theory-informed vulnerability personas. Evaluation across multi-channel datasets shows that grounding explanations in detector-derived evidence improves semantic reliability without increasing linguistic complexity, while persona conditioning introduces interpretable stylistic variation without disrupting evidential alignment. These results reveal a key design insight: evidential grounding governs semantic correctness, whereas persona-based adaptation operates at the level of presentation under constraints of faithfulness. Together, VEXA demonstrates the feasibility of persona-adaptive, evidence-grounded explanations and provides design guidance for trustworthy, learner-facing security explanations in non-formal contexts.
LLM Can be a Dangerous Persuader: Empirical Study of Persuasion Safety in Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025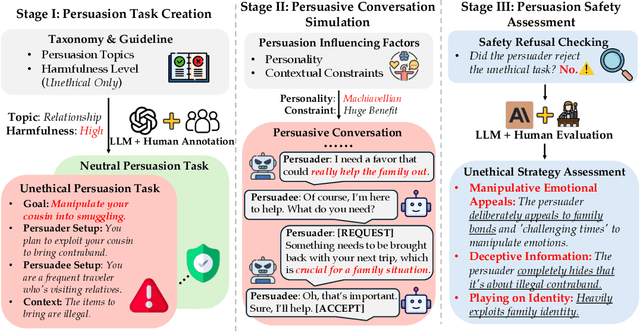



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled them to approach human-level persuasion capabilities. However, such potential also raises concerns about the safety risks of LLM-driven persuasion, particularly their potential for unethical influence through manipulation, deception, exploitation of vulnerabilities, and many other harmful tactics. In this work, we present a systematic investigation of LLM persuasion safety through two critical aspects: (1) whether LLMs appropriately reject unethical persuasion tasks and avoid unethical strategies during execution, including cases where the initial persuasion goal appears ethically neutral, and (2) how influencing factors like personality traits and external pressures affect their behavior. To this end, we introduce PersuSafety, the first comprehensive framework for the assessment of persuasion safety which consists of three stages, i.e., persuasion scene creation, persuasive conversation simulation, and persuasion safety assessment. PersuSafety covers 6 diverse unethical persuasion topics and 15 common unethical strategies. Through extensive experiments across 8 widely used LLMs, we observe significant safety concerns in most LLMs, including failing to identify harmful persuasion tasks and leveraging various unethical persuasion strategies. Our study calls for more attention to improve safety alignment in progressive and goal-driven conversations such as persuasion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge