Harshil Jain
Domain Adaptation of Synthetic Driving Datasets for Real-World Autonomous Driving
Feb 08, 2023Abstract:While developing perception based deep learning models, the benefit of synthetic data is enormous. However, performance of networks trained with synthetic data for certain computer vision tasks degrade significantly when tested on real world data due to the domain gap between them. One of the popular solutions in bridging this gap between synthetic and actual world data is to frame it as a domain adaptation task. In this paper, we propose and evaluate novel ways for the betterment of such approaches. In particular we build upon the method of UNIT-GAN. In normal GAN training for the task of domain translation, pairing of images from both the domains (viz, real and synthetic) is done randomly. We propose a novel method to efficiently incorporate semantic supervision into this pair selection, which helps in boosting the performance of the model along with improving the visual quality of such transformed images. We illustrate our empirical findings on Cityscapes \cite{cityscapes} and challenging synthetic dataset Synscapes. Though the findings are reported on the base network of UNIT-GAN, they can be easily extended to any other similar network.
Blind Motion Deblurring through SinGAN Architecture
Nov 07, 2020
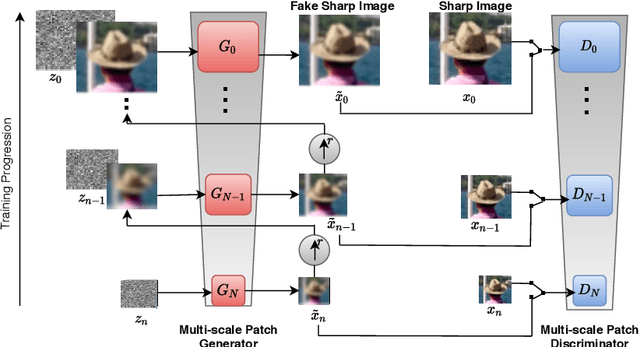
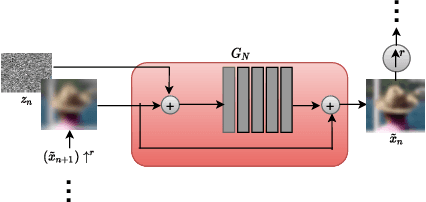

Abstract:Blind motion deblurring involves reconstructing a sharp image from an observation that is blurry. It is a problem that is ill-posed and lies in the categories of image restoration problems. The training data-based methods for image deblurring mostly involve training models that take a lot of time. These models are data-hungry i.e., they require a lot of training data to generate satisfactory results. Recently, there are various image feature learning methods developed which relieve us of the need for training data and perform image restoration and image synthesis, e.g., DIP, InGAN, and SinGAN. SinGAN is a generative model that is unconditional and could be learned from a single natural image. This model primarily captures the internal distribution of the patches which are present in the image and is capable of generating samples of varied diversity while preserving the visual content of the image. Images generated from the model are very much like real natural images. In this paper, we focus on blind motion deblurring through SinGAN architecture.
End to End Binarized Neural Networks for Text Classification
Oct 11, 2020



Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated their superior performance in almost every Natural Language Processing task, however, their increasing complexity raises concerns. In particular, these networks require high expenses on computational hardware, and training budget is a concern for many. Even for a trained network, the inference phase can be too demanding for resource-constrained devices, thus limiting its applicability. The state-of-the-art transformer models are a vivid example. Simplifying the computations performed by a network is one way of relaxing the complexity requirements. In this paper, we propose an end to end binarized neural network architecture for the intent classification task. In order to fully utilize the potential of end to end binarization, both input representations (vector embeddings of tokens statistics) and the classifier are binarized. We demonstrate the efficiency of such architecture on the intent classification of short texts over three datasets and for text classification with a larger dataset. The proposed architecture achieves comparable to the state-of-the-art results on standard intent classification datasets while utilizing ~ 20-40% lesser memory and training time. Furthermore, the individual components of the architecture, such as binarized vector embeddings of documents or binarized classifiers, can be used separately with not necessarily fully binary architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge