Harsh Kohli
Cleared for Takeoff? Compositional & Conditional Reasoning may be the Achilles Heel to (Flight-Booking) Language Agents
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:The rapid progress of large language models (LLMs) has seen them excel and frequently surpass human performance on standard benchmarks. This has enabled many downstream applications, such as LLM agents, to rely on their sophisticated reasoning to navigate complex task requirements. However, LLMs are known to unexpectedly falter in simple tasks and under seemingly straightforward circumstances - underscoring the need for better and more diverse evaluation setups to measure their true capabilities. To this end, we choose to study compositional and conditional reasoning, two cornerstones of human cognition, and introduce GroundCocoa - a lexically diverse benchmark connecting these reasoning skills to the real-world problem of flight booking. Our task involves aligning detailed user preferences with available flight options presented in a multiple-choice format. Results indicate a significant disparity in performance among current state-of-the-art LLMs with even the best performing model, GPT-4 Turbo, not exceeding 67% accuracy despite advanced prompting techniques.
How Lexical is Bilingual Lexicon Induction?
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:In contemporary machine learning approaches to bilingual lexicon induction (BLI), a model learns a mapping between the embedding spaces of a language pair. Recently, retrieve-and-rank approach to BLI has achieved state of the art results on the task. However, the problem remains challenging in low-resource settings, due to the paucity of data. The task is complicated by factors such as lexical variation across languages. We argue that the incorporation of additional lexical information into the recent retrieve-and-rank approach should improve lexicon induction. We demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed approach on XLING, improving over the previous state of the art by an average of 2\% across all language pairs.
Learning Representations for Zero-Shot Retrieval over Structured Data
Oct 29, 2021
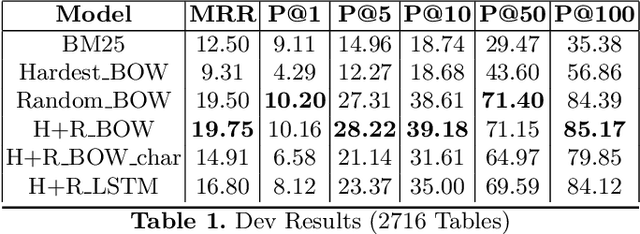
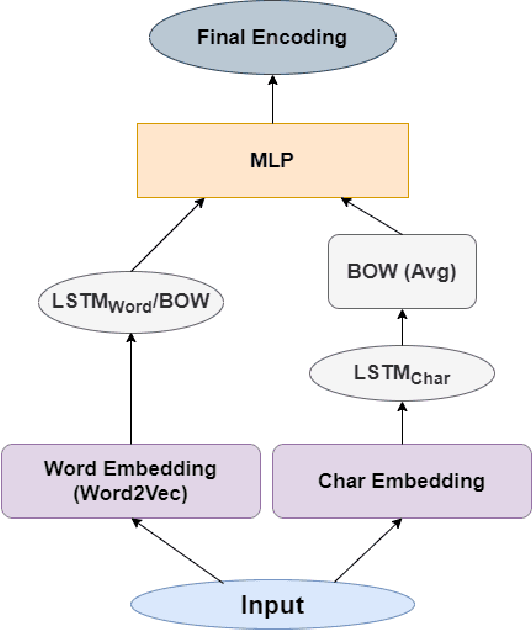
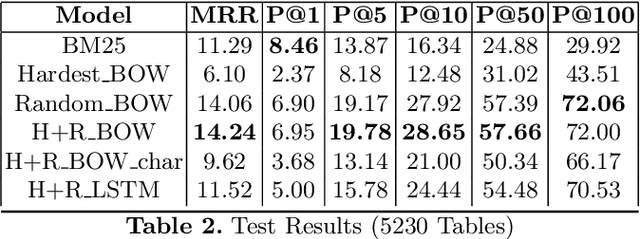
Abstract:Large Scale Question-Answering systems today are widely used in downstream applications such as chatbots and conversational dialogue agents. Typically, such systems consist of an Answer Passage retrieval layer coupled with Machine Comprehension models trained on natural language query-passage pairs. Recent studies have explored Question Answering over structured data sources such as web-tables and relational databases. However, architectures such as Seq2SQL assume the correct table a priori which is input to the model along with the free text question. Our proposed method, analogues to a passage retrieval model in traditional Question-Answering systems, describes an architecture to discern the correct table pertaining to a given query from amongst a large pool of candidate tables.
Training Mixed-Objective Pointing Decoders for Block-Level Optimization in Search Recommendation
May 21, 2021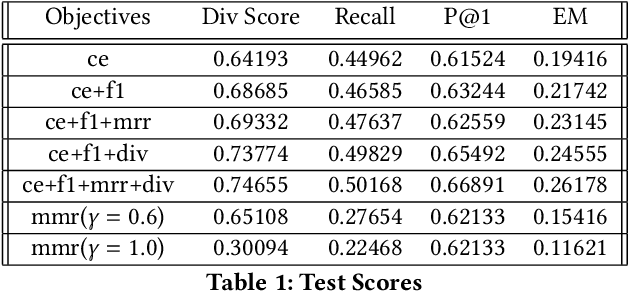
Abstract:Related or ideal follow-up suggestions to a web query in search engines are often optimized based on several different parameters -- relevance to the original query, diversity, click probability etc. One or many rankers may be trained to score each suggestion from a candidate pool based on these factors. These scorers are usually pairwise classification tasks where each training example consists of a user query and a single suggestion from the list of candidates. We propose an architecture that takes all candidate suggestions associated with a given query and outputs a suggestion block. We discuss the benefits of such an architecture over traditional approaches and experiment with further enforcing each individual metric through mixed-objective training.
Training Bi-Encoders for Word Sense Disambiguation
May 21, 2021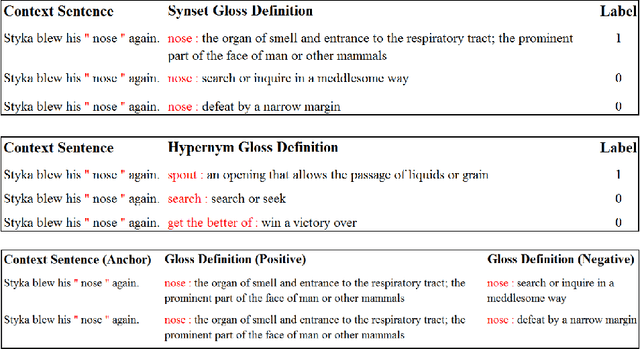
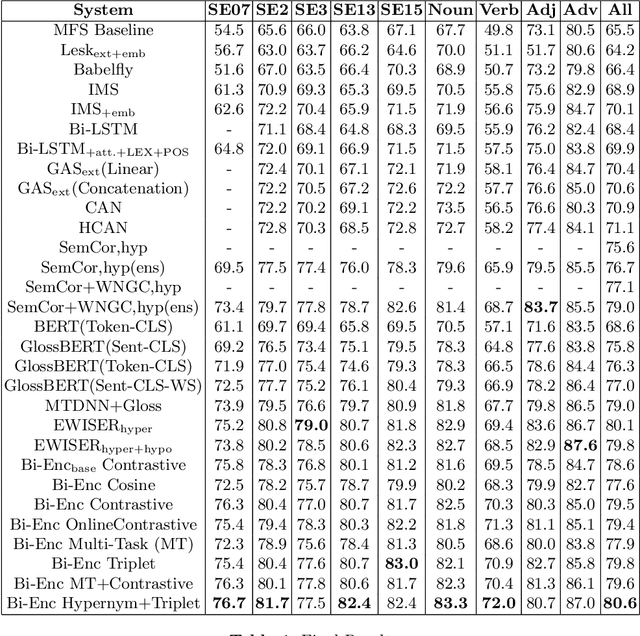
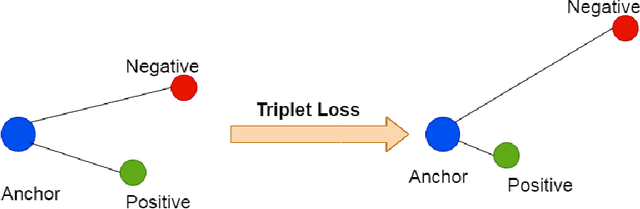
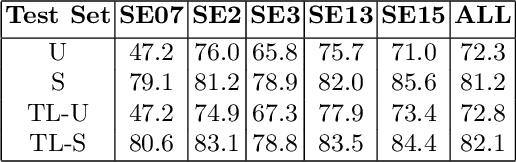
Abstract:Modern transformer-based neural architectures yield impressive results in nearly every NLP task and Word Sense Disambiguation, the problem of discerning the correct sense of a word in a given context, is no exception. State-of-the-art approaches in WSD today leverage lexical information along with pre-trained embeddings from these models to achieve results comparable to human inter-annotator agreement on standard evaluation benchmarks. In the same vein, we experiment with several strategies to optimize bi-encoders for this specific task and propose alternative methods of presenting lexical information to our model. Through our multi-stage pre-training and fine-tuning pipeline we further the state of the art in Word Sense Disambiguation.
Transfer Learning and Augmentation for Word Sense Disambiguation
Jan 10, 2021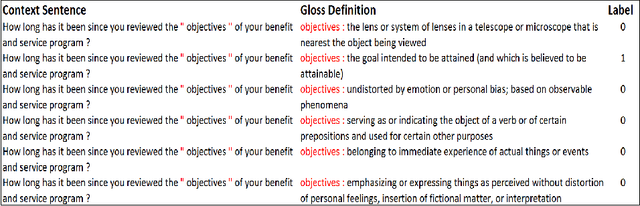
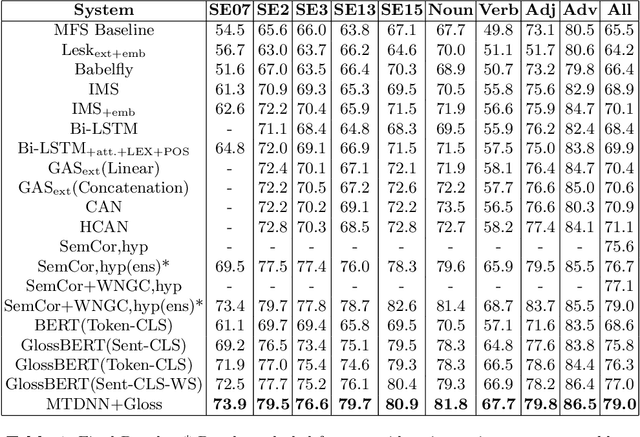
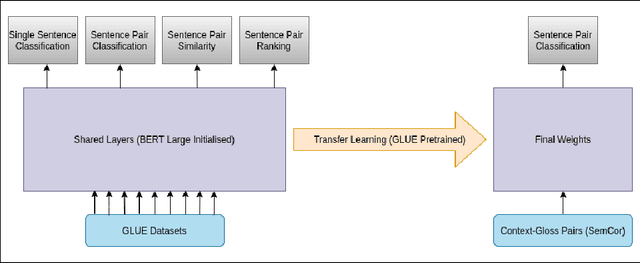
Abstract:Many downstream NLP tasks have shown significant improvement through continual pre-training, transfer learning and multi-task learning. State-of-the-art approaches in Word Sense Disambiguation today benefit from some of these approaches in conjunction with information sources such as semantic relationships and gloss definitions contained within WordNet. Our work builds upon these systems and uses data augmentation along with extensive pre-training on various different NLP tasks and datasets. Our transfer learning and augmentation pipeline achieves state-of-the-art single model performance in WSD and is at par with the best ensemble results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge