Helian Feng
How Lexical is Bilingual Lexicon Induction?
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:In contemporary machine learning approaches to bilingual lexicon induction (BLI), a model learns a mapping between the embedding spaces of a language pair. Recently, retrieve-and-rank approach to BLI has achieved state of the art results on the task. However, the problem remains challenging in low-resource settings, due to the paucity of data. The task is complicated by factors such as lexical variation across languages. We argue that the incorporation of additional lexical information into the recent retrieve-and-rank approach should improve lexicon induction. We demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed approach on XLING, improving over the previous state of the art by an average of 2\% across all language pairs.
Search Optimization with Query Likelihood Boosting and Two-Level Approximate Search for Edge Devices
Dec 12, 2023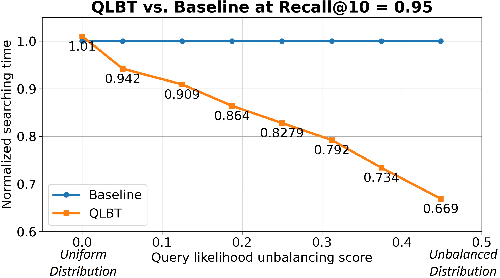
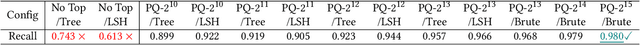
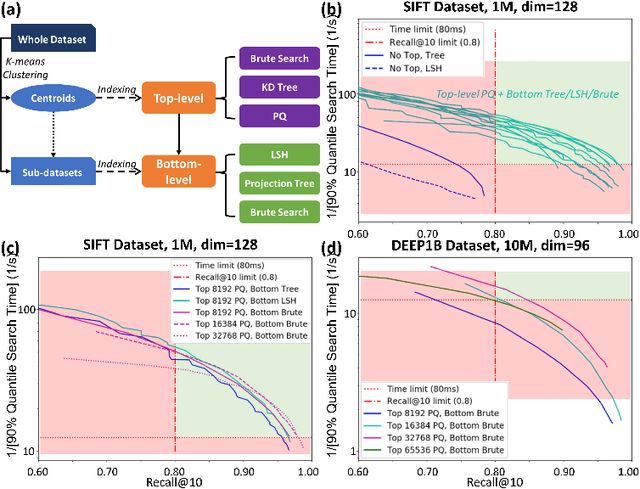
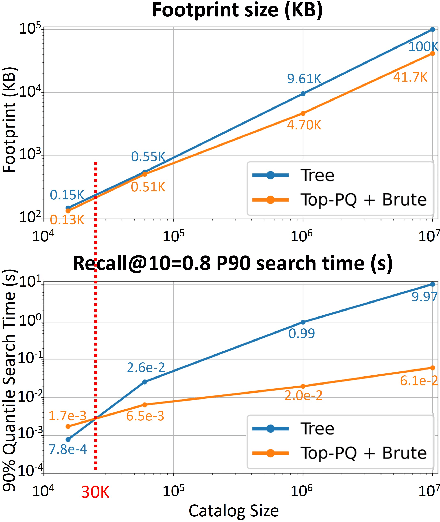
Abstract:We present a novel search optimization solution for approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search on resource-constrained edge devices. Traditional ANN approaches fall short in meeting the specific demands of real-world scenarios, e.g., skewed query likelihood distribution and search on large-scale indices with a low latency and small footprint. To address these limitations, we introduce two key components: a Query Likelihood Boosted Tree (QLBT) to optimize average search latency for frequently used small datasets, and a two-level approximate search algorithm to enable efficient retrieval with large datasets on edge devices. We perform thorough evaluation on simulated and real data and demonstrate QLBT can significantly reduce latency by 15% on real data and our two-level search algorithm successfully achieve deployable accuracy and latency on a 10 million dataset for edge devices. In addition, we provide a comprehensive protocol for configuring and optimizing on-device search algorithm through extensive empirical studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge