Haris I. Sair
Adaptive Label Error Detection: A Bayesian Approach to Mislabeled Data Detection
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Machine learning classification systems are susceptible to poor performance when trained with incorrect ground truth labels, even when data is well-curated by expert annotators. As machine learning becomes more widespread, it is increasingly imperative to identify and correct mislabeling to develop more powerful models. In this work, we motivate and describe Adaptive Label Error Detection (ALED), a novel method of detecting mislabeling. ALED extracts an intermediate feature space from a deep convolutional neural network, denoises the features, models the reduced manifold of each class with a multidimensional Gaussian distribution, and performs a simple likelihood ratio test to identify mislabeled samples. We show that ALED has markedly increased sensitivity, without compromising precision, compared to established label error detection methods, on multiple medical imaging datasets. We demonstrate an example where fine-tuning a neural network on corrected data results in a 33.8% decrease in test set errors, providing strong benefits to end users. The ALED detector is deployed in the Python package statlab.
Evidential Uncertainty Quantification: A Variance-Based Perspective
Nov 19, 2023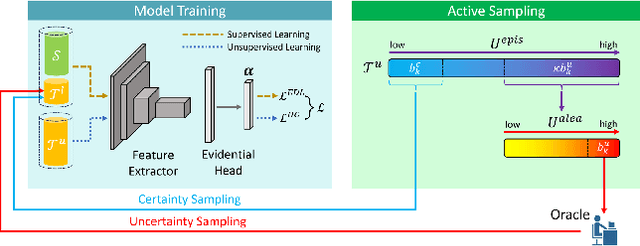
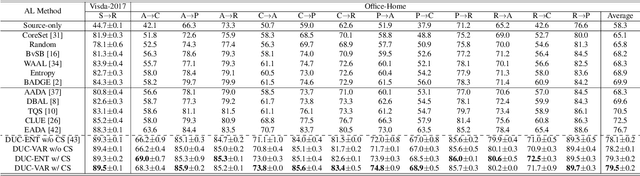
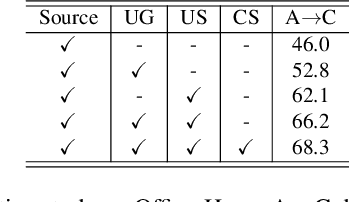
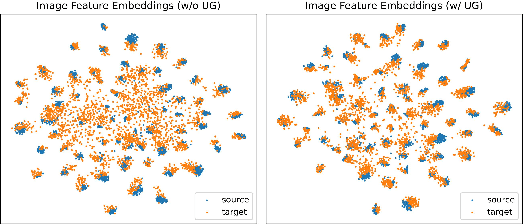
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification of deep neural networks has become an active field of research and plays a crucial role in various downstream tasks such as active learning. Recent advances in evidential deep learning shed light on the direct quantification of aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties with a single forward pass of the model. Most traditional approaches adopt an entropy-based method to derive evidential uncertainty in classification, quantifying uncertainty at the sample level. However, the variance-based method that has been widely applied in regression problems is seldom used in the classification setting. In this work, we adapt the variance-based approach from regression to classification, quantifying classification uncertainty at the class level. The variance decomposition technique in regression is extended to class covariance decomposition in classification based on the law of total covariance, and the class correlation is also derived from the covariance. Experiments on cross-domain datasets are conducted to illustrate that the variance-based approach not only results in similar accuracy as the entropy-based one in active domain adaptation but also brings information about class-wise uncertainties as well as between-class correlations. The code is available at https://github.com/KerryDRX/EvidentialADA. This alternative means of evidential uncertainty quantification will give researchers more options when class uncertainties and correlations are important in their applications.
A Multi-Task Deep Learning Framework to Localize the Eloquent Cortex in Brain Tumor Patients Using Dynamic Functional Connectivity
Nov 17, 2020



Abstract:We present a novel deep learning framework that uses dynamic functional connectivity to simultaneously localize the language and motor areas of the eloquent cortex in brain tumor patients. Our method leverages convolutional layers to extract graph-based features from the dynamic connectivity matrices and a long-short term memory (LSTM) attention network to weight the relevant time points during classification. The final stage of our model employs multi-task learning to identify different eloquent subsystems. Our unique training strategy finds a shared representation between the cognitive networks of interest, which enables us to handle missing patient data. We evaluate our method on resting-state fMRI data from 56 brain tumor patients while using task fMRI activations as surrogate ground-truth labels for training and testing. Our model achieves higher localization accuracies than conventional deep learning approaches and can identify bilateral language areas even when trained on left-hemisphere lateralized cases. Hence, our method may ultimately be useful for preoperative mapping in tumor patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge