Haotang Li
Bridging Structure and Appearance: Topological Features for Robust Self-Supervised Segmentation
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised semantic segmentation methods often fail when faced with appearance ambiguities. We argue that this is due to an over-reliance on unstable, appearance-based features such as shadows, glare, and local textures. We propose \textbf{GASeg}, a novel framework that bridges appearance and geometry by leveraging stable topological information. The core of our method is Differentiable Box-Counting (\textbf{DBC}) module, which quantifies multi-scale topological statistics from two parallel streams: geometric-based features and appearance-based features. To force the model to learn these stable structural representations, we introduce Topological Augmentation (\textbf{TopoAug}), an adversarial strategy that simulates real-world ambiguities by applying morphological operators to the input images. A multi-objective loss, \textbf{GALoss}, then explicitly enforces cross-modal alignment between geometric-based and appearance-based features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GASeg achieves state-of-the-art performance on four benchmarks, including COCO-Stuff, Cityscapes, and PASCAL, validating our approach of bridging geometry and appearance via topological information.
LAA-Net: A Physical-prior-knowledge Based Network for Robust Nighttime Depth Estimation
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Existing self-supervised monocular depth estimation (MDE) models attempt to improve nighttime performance by using GANs to transfer nighttime images into their daytime versions. However, this can introduce inconsistencies due to the complexities of real-world daytime lighting variations, which may finally lead to inaccurate estimation results. To address this issue, we leverage physical-prior-knowledge about light wavelength and light attenuation during nighttime. Specifically, our model, Light-Attenuation-Aware Network (LAA-Net), incorporates physical insights from Rayleigh scattering theory for robust nighttime depth estimation: LAA-Net is trained based on red channel values because red light preserves more information under nighttime scenarios due to its longer wavelength. Additionally, based on Beer-Lambert law, we introduce Red Channel Attenuation (RCA) loss to guide LAA-Net's training. Experiments on the RobotCar-Night, nuScenes-Night, RobotCar-Day, and KITTI datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms SOTA models.
A Challenging Benchmark of Anime Style Recognition
Apr 29, 2022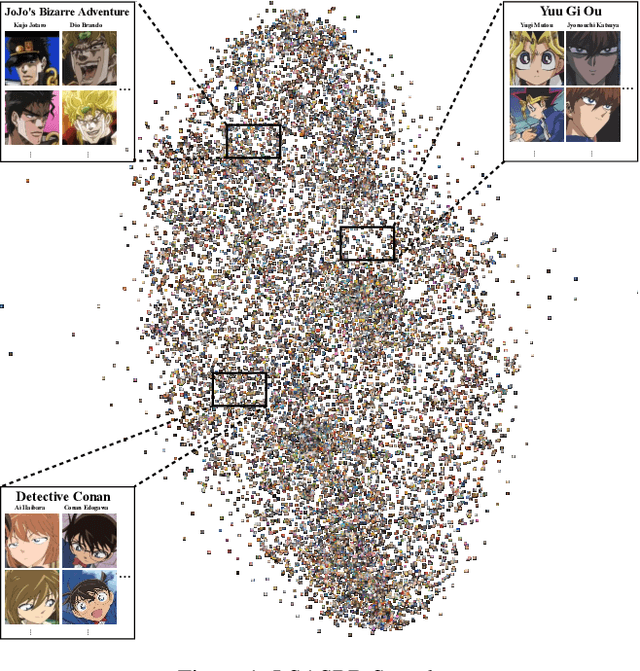
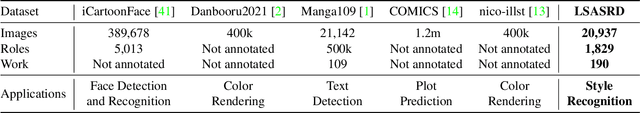
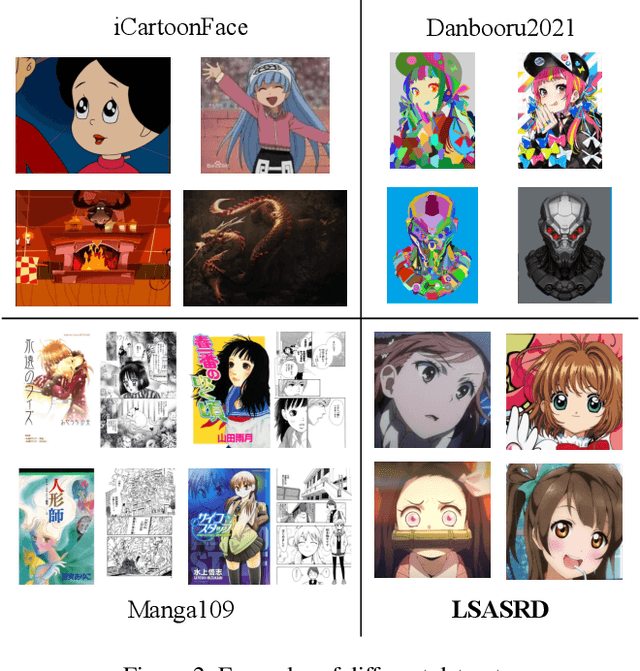
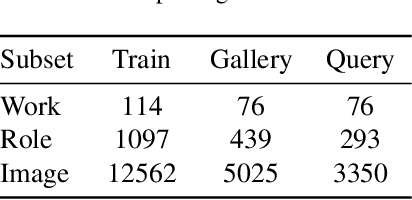
Abstract:Given two images of different anime roles, anime style recognition (ASR) aims to learn abstract painting style to determine whether the two images are from the same work, which is an interesting but challenging problem. Unlike biometric recognition, such as face recognition, iris recognition, and person re-identification, ASR suffers from a much larger semantic gap but receives less attention. In this paper, we propose a challenging ASR benchmark. Firstly, we collect a large-scale ASR dataset (LSASRD), which contains 20,937 images of 190 anime works and each work at least has ten different roles. In addition to the large-scale, LSASRD contains a list of challenging factors, such as complex illuminations, various poses, theatrical colors and exaggerated compositions. Secondly, we design a cross-role protocol to evaluate ASR performance, in which query and gallery images must come from different roles to validate an ASR model is to learn abstract painting style rather than learn discriminative features of roles. Finally, we apply two powerful person re-identification methods, namely, AGW and TransReID, to construct the baseline performance on LSASRD. Surprisingly, the recent transformer model (i.e., TransReID) only acquires a 42.24% mAP on LSASRD. Therefore, we believe that the ASR task of a huge semantic gap deserves deep and long-term research. We will open our dataset and code at https://github.com/nkjcqvcpi/ASR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge