Haonan Gong
Discriminative Graph-level Anomaly Detection via Dual-students-teacher Model
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Different from the current node-level anomaly detection task, the goal of graph-level anomaly detection is to find abnormal graphs that significantly differ from others in a graph set. Due to the scarcity of research on the work of graph-level anomaly detection, the detailed description of graph-level anomaly is insufficient. Furthermore, existing works focus on capturing anomalous graph information to learn better graph representations, but they ignore the importance of an effective anomaly score function for evaluating abnormal graphs. Thus, in this work, we first define anomalous graph information including node and graph property anomalies in a graph set and adopt node-level and graph-level information differences to identify them, respectively. Then, we introduce a discriminative graph-level anomaly detection framework with dual-students-teacher model, where the teacher model with a heuristic loss are trained to make graph representations more divergent. Then, two competing student models trained by normal and abnormal graphs respectively fit graph representations of the teacher model in terms of node-level and graph-level representation perspectives. Finally, we combine representation errors between two student models to discriminatively distinguish anomalous graphs. Extensive experiment analysis demonstrates that our method is effective for the graph-level anomaly detection task on graph datasets in the real world.
Multi-representations Space Separation based Graph-level Anomaly-aware Detection
Jul 22, 2023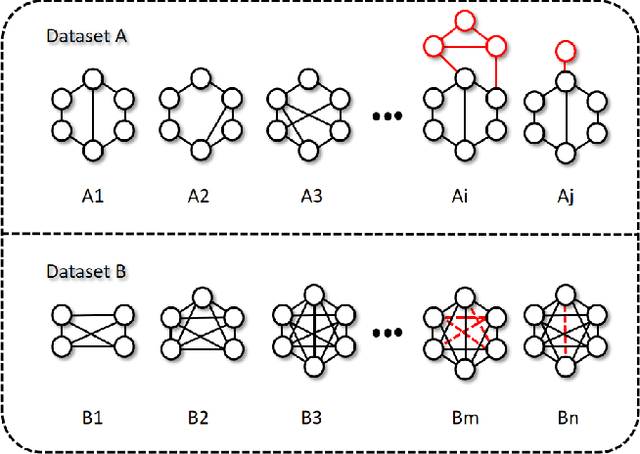
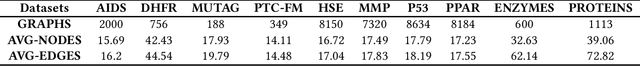
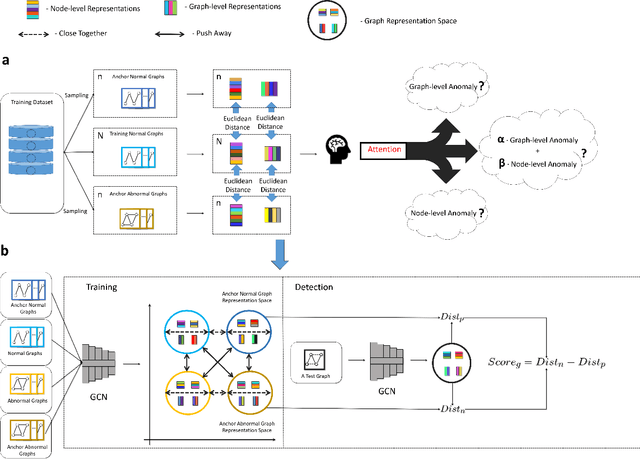
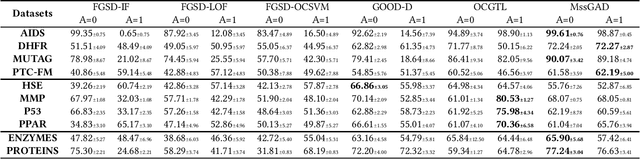
Abstract:Graph structure patterns are widely used to model different area data recently. How to detect anomalous graph information on these graph data has become a popular research problem. The objective of this research is centered on the particular issue that how to detect abnormal graphs within a graph set. The previous works have observed that abnormal graphs mainly show node-level and graph-level anomalies, but these methods equally treat two anomaly forms above in the evaluation of abnormal graphs, which is contrary to the fact that different types of abnormal graph data have different degrees in terms of node-level and graph-level anomalies. Furthermore, abnormal graphs that have subtle differences from normal graphs are easily escaped detection by the existing methods. Thus, we propose a multi-representations space separation based graph-level anomaly-aware detection framework in this paper. To consider the different importance of node-level and graph-level anomalies, we design an anomaly-aware module to learn the specific weight between them in the abnormal graph evaluation process. In addition, we learn strictly separate normal and abnormal graph representation spaces by four types of weighted graph representations against each other including anchor normal graphs, anchor abnormal graphs, training normal graphs, and training abnormal graphs. Based on the distance error between the graph representations of the test graph and both normal and abnormal graph representation spaces, we can accurately determine whether the test graph is anomalous. Our approach has been extensively evaluated against baseline methods using ten public graph datasets, and the results demonstrate its effectiveness.
* 11 pages, 12 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge