Hannah Janmohamed
Preference-Conditioned Gradient Variations for Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity
Nov 19, 2024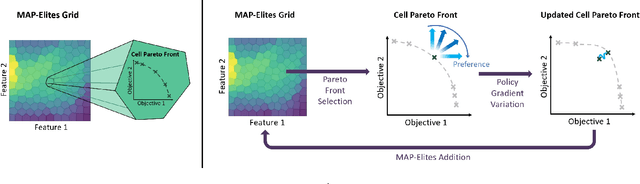
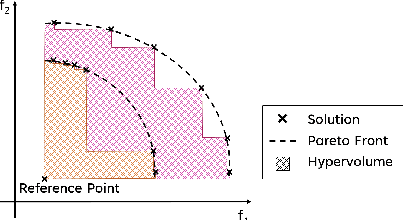
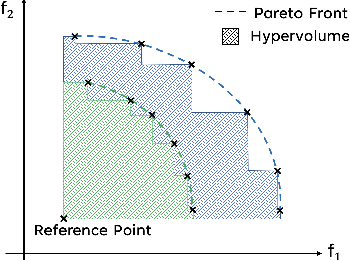
Abstract:In a variety of domains, from robotics to finance, Quality-Diversity algorithms have been used to generate collections of both diverse and high-performing solutions. Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity algorithms have emerged as a promising approach for applying these methods to complex, multi-objective problems. However, existing methods are limited by their search capabilities. For example, Multi-Objective Map-Elites depends on random genetic variations which struggle in high-dimensional search spaces. Despite efforts to enhance search efficiency with gradient-based mutation operators, existing approaches consider updating solutions to improve on each objective separately rather than achieving desired trade-offs. In this work, we address this limitation by introducing Multi-Objective Map-Elites with Preference-Conditioned Policy-Gradient and Crowding Mechanisms: a new Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity algorithm that uses preference-conditioned policy-gradient mutations to efficiently discover promising regions of the objective space and crowding mechanisms to promote a uniform distribution of solutions on the Pareto front. We evaluate our approach on six robotics locomotion tasks and show that our method outperforms or matches all state-of-the-art Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity methods in all six, including two newly proposed tri-objective tasks. Importantly, our method also achieves a smoother set of trade-offs, as measured by newly-proposed sparsity-based metrics. This performance comes at a lower computational storage cost compared to previous methods.
Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity for Crystal Structure Prediction
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:Crystal structures are indispensable across various domains, from batteries to solar cells, and extensive research has been dedicated to predicting their properties based on their atomic configurations. However, prevailing Crystal Structure Prediction methods focus on identifying the most stable solutions that lie at the global minimum of the energy function. This approach overlooks other potentially interesting materials that lie in neighbouring local minima and have different material properties such as conductivity or resistance to deformation. By contrast, Quality-Diversity algorithms provide a promising avenue for Crystal Structure Prediction as they aim to find a collection of high-performing solutions that have diverse characteristics. However, it may also be valuable to optimise for the stability of crystal structures alongside other objectives such as magnetism or thermoelectric efficiency. Therefore, in this work, we harness the power of Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity algorithms in order to find crystal structures which have diverse features and achieve different trade-offs of objectives. We analyse our approach on 5 crystal systems and demonstrate that it is not only able to re-discover known real-life structures, but also find promising new ones. Moreover, we propose a method for illuminating the objective space to gain an understanding of what trade-offs can be achieved.
Quality-Diversity Optimisation on a Physical Robot Through Dynamics-Aware and Reset-Free Learning
Apr 24, 2023
Abstract:Learning algorithms, like Quality-Diversity (QD), can be used to acquire repertoires of diverse robotics skills. This learning is commonly done via computer simulation due to the large number of evaluations required. However, training in a virtual environment generates a gap between simulation and reality. Here, we build upon the Reset-Free QD (RF-QD) algorithm to learn controllers directly on a physical robot. This method uses a dynamics model, learned from interactions between the robot and the environment, to predict the robot's behaviour and improve sample efficiency. A behaviour selection policy filters out uninteresting or unsafe policies predicted by the model. RF-QD also includes a recovery policy that returns the robot to a safe zone when it has walked outside of it, allowing continuous learning. We demonstrate that our method enables a physical quadruped robot to learn a repertoire of behaviours in two hours without human supervision. We successfully test the solution repertoire using a maze navigation task. Finally, we compare our approach to the MAP-Elites algorithm. We show that dynamics awareness and a recovery policy are required for training on a physical robot for optimal archive generation. Video available at https://youtu.be/BgGNvIsRh7Q
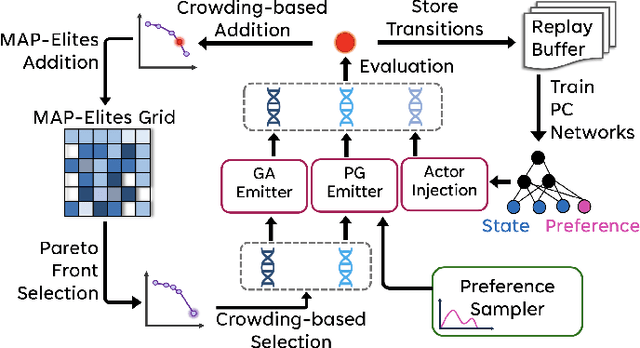
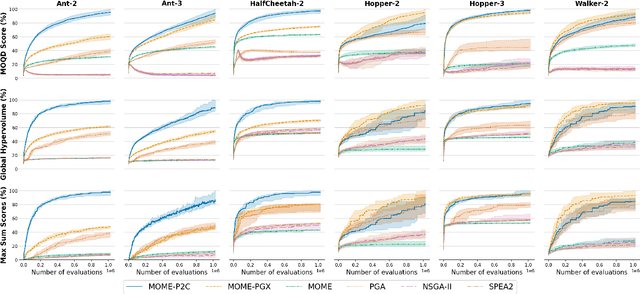
Improving the Data Efficiency of Multi-Objective Quality-Diversity through Gradient Assistance and Crowding Exploration
Feb 24, 2023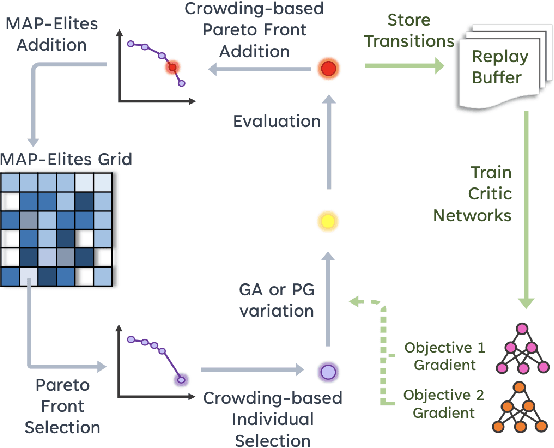

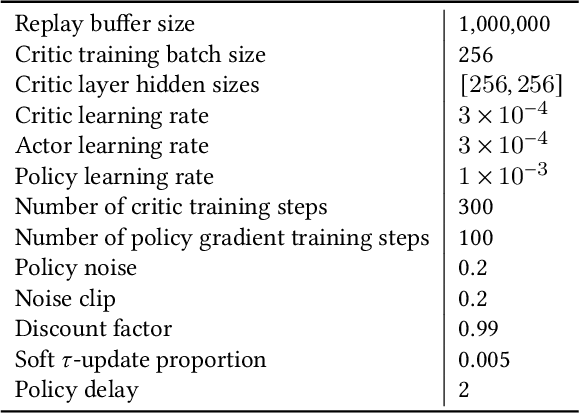
Abstract:Quality-Diversity (QD) algorithms have recently gained traction as optimisation methods due to their effectiveness at escaping local optima and capability of generating wide-ranging and high-performing solutions. Recently, Multi-Objective MAP-Elites (MOME) extended the QD paradigm to the multi-objective setting by maintaining a Pareto front in each cell of a map-elites grid. MOME achieved a global performance that competed with NSGA-II and SPEA2, two well-established Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms (MOEA), while also acquiring a diverse repertoire of solutions. However, MOME is limited by non-directed genetic search mechanisms which struggle in high-dimensional search spaces. In this work, we present Multi-Objective MAP-Elites with Policy-Gradient Assistance and Crowding-based Exploration (MOME-PGX): a new QD algorithm that extends MOME to improve its data efficiency and performance. MOME-PGX uses gradient-based optimisation to efficiently drive solutions towards higher performance. It also introduces crowding-based mechanisms to create an improved exploration strategy and to encourage uniformity across Pareto fronts. We evaluate MOME-PGX in four simulated robot locomotion tasks and demonstrate that it converges faster and to a higher performance than all other baselines. We show that MOME-PGX is between 4.3 and 42 times more data-efficient than MOME and doubles the performance of MOME, NSGA-II and SPEA2 in challenging environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge