Guohua Liu
FAQ: Mitigating Quantization Error via Regenerating Calibration Data with Family-Aware Quantization
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Although post-training quantization (PTQ) provides an efficient numerical compression scheme for deploying large language models (LLMs) on resource-constrained devices, the representativeness and universality of calibration data remain a core bottleneck in determining the accuracy of quantization parameters. Traditional PTQ methods typically rely on limited samples, making it difficult to capture the activation distribution during the inference phase, leading to biases in quantization parameters. To address this, we propose \textbf{FAQ} (Family-Aware Quantization), a calibration data regeneration framework that leverages prior knowledge from LLMs of the same family to generate high-fidelity calibration samples. Specifically, FAQ first inputs the original calibration samples into a larger LLM from the same family as the target model, regenerating a series of high-fidelity calibration data using a highly consistent knowledge system. Subsequently, this data, carrying Chain-of-Thought reasoning and conforming to the expected activation distribution, undergoes group competition under expert guidance to select the best samples, which are then re-normalized to enhance the effectiveness of standard PTQ. Experiments on multiple model series, including Qwen3-8B, show that FAQ reduces accuracy loss by up to 28.5\% compared to the baseline with original calibration data, demonstrating its powerful potential and contribution.
Automated Segmentation of Brain Gray Matter Nuclei on Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Aug 03, 2020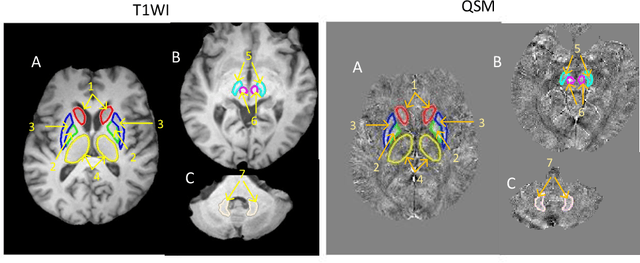
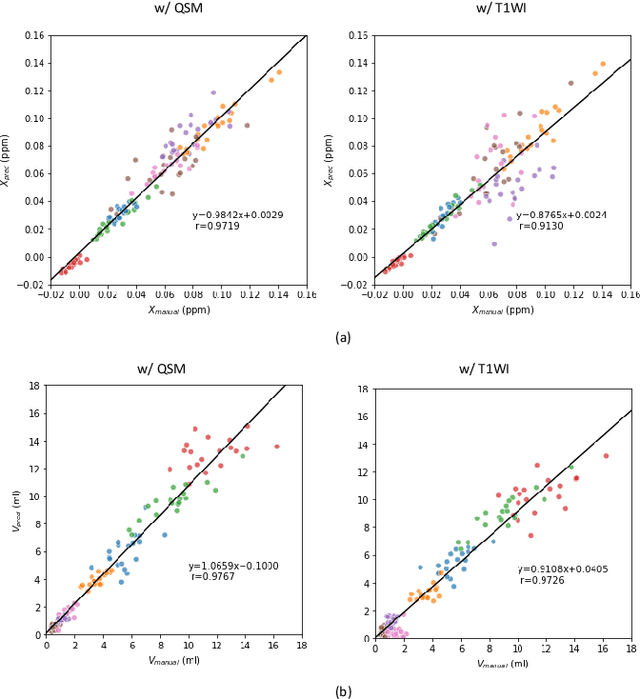
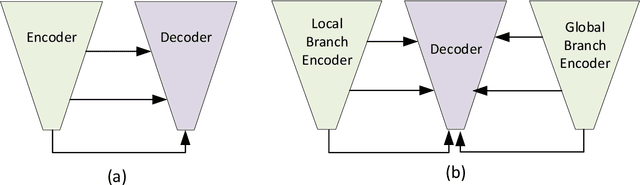
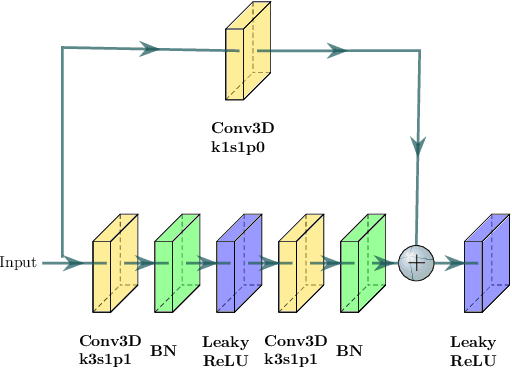
Abstract:Abnormal iron accumulation in the brain subcortical nuclei has been reported to be correlated to various neurodegenerative diseases, which can be measured through the magnetic susceptibility from the quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). To quantitively measure the magnetic susceptibility, the nuclei should be accurately segmented, which is a tedious task for clinicians. In this paper, we proposed a double-branch residual-structured U-Net (DB-ResUNet) based on 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) to automatically segment such brain gray matter nuclei. To better tradeoff between segmentation accuracy and the memory efficiency, the proposed DB-ResUNet fed image patches with high resolution and the patches with low resolution but larger field of view into the local and global branches, respectively. Experimental results revealed that by jointly using QSM and T$_\text{1}$ weighted imaging (T$_\text{1}$WI) as inputs, the proposed method was able to achieve better segmentation accuracy over its single-branch counterpart, as well as the conventional atlas-based method and the classical 3D-UNet structure. The susceptibility values and the volumes were also measured, which indicated that the measurements from the proposed DB-ResUNet are able to present high correlation with values from the manually annotated regions of interest.
Automatic acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation using semi-supervised learning
Aug 10, 2019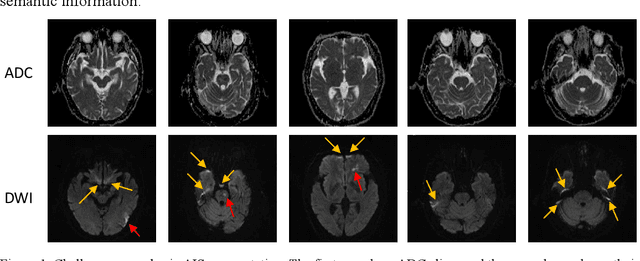
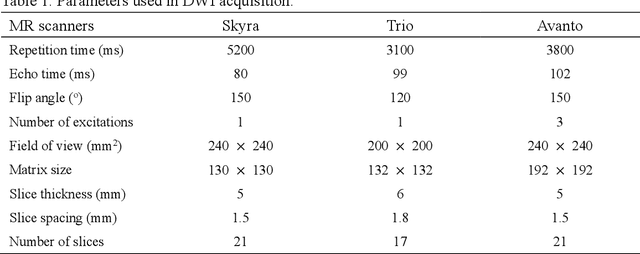

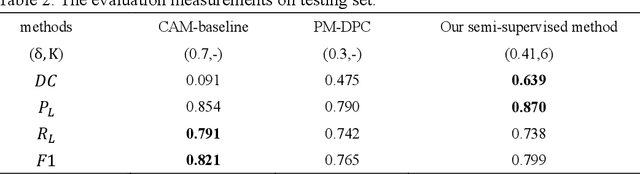
Abstract:Ischemic stroke is a common disease in the elderly population, which can cause long-term disability and even death. However, the time window for treatment of ischemic stroke in its acute stage is very short. To fast localize and quantitively evaluate the acute ischemic stroke (AIS) lesions, many deep-learning-based lesion segmentation methods have been proposed in the literature, where a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) was trained on hundreds of fully labeled subjects with accurate annotations of AIS lesions. Despite that high segmentation accuracy can be achieved, the accurate labels should be annotated by experienced clinicians, and it is therefore very time-consuming to obtain a large number of fully labeled subjects. In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised method to automatically segment AIS lesions in diffusion weighted images and apparent diffusion coefficient maps. By using a large number of weakly labeled subjects and a small number of fully labeled subjects, our proposed method is able to accurately detect and segment the AIS lesions. In particular, our proposed method consists of three parts: 1) a double-path classification net (DPC-Net) trained in a weakly-supervised way is used to detect the suspicious regions of AIS lesions; 2) a pixel-level K-Means clustering algorithm is used to identify the hyperintensive regions on the DWIs; and 3) a region-growing algorithm combines the outputs of the DPC-Net and the K-Means to obtain the final precise lesion segmentation. In our experiment, we use 460 weakly labeled subjects and 15 fully labeled subjects to train and fine-tune the proposed method. By evaluating on a clinical dataset with 150 fully labeled subjects, our proposed method achieves a mean dice coefficient of 0.639, and a lesion-wise F1 score of 0.799.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge