Guillem Braso
Multi-Object Tracking and Segmentation via Neural Message Passing
Jul 15, 2022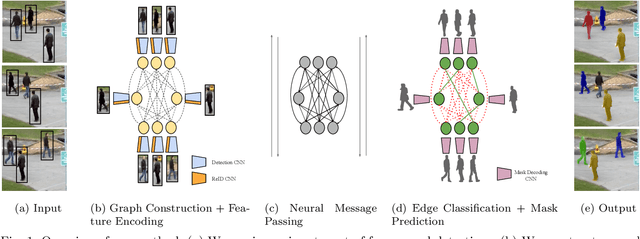
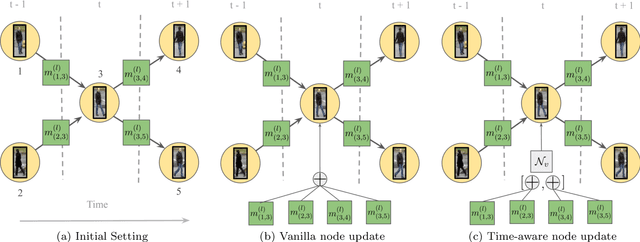

Abstract:Graphs offer a natural way to formulate Multiple Object Tracking (MOT) and Multiple Object Tracking and Segmentation (MOTS) within the tracking-by-detection paradigm. However, they also introduce a major challenge for learning methods, as defining a model that can operate on such structured domain is not trivial. In this work, we exploit the classical network flow formulation of MOT to define a fully differentiable framework based on Message Passing Networks (MPNs). By operating directly on the graph domain, our method can reason globally over an entire set of detections and exploit contextual features. It then jointly predicts both final solutions for the data association problem and segmentation masks for all objects in the scene while exploiting synergies between the two tasks. We achieve state-of-the-art results for both tracking and segmentation in several publicly available datasets. Our code is available at github.com/ocetintas/MPNTrackSeg.
MOTSynth: How Can Synthetic Data Help Pedestrian Detection and Tracking?
Aug 21, 2021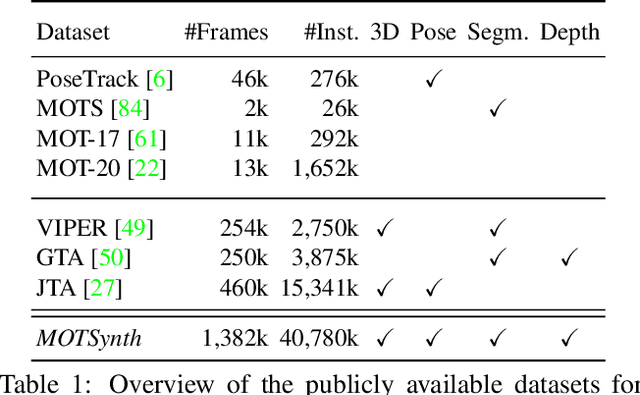

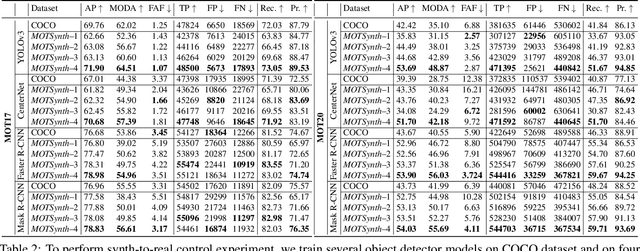
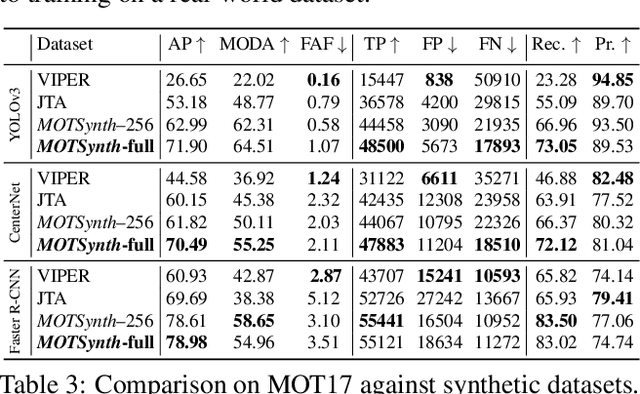
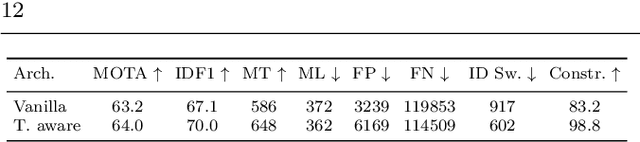
Abstract:Deep learning-based methods for video pedestrian detection and tracking require large volumes of training data to achieve good performance. However, data acquisition in crowded public environments raises data privacy concerns -- we are not allowed to simply record and store data without the explicit consent of all participants. Furthermore, the annotation of such data for computer vision applications usually requires a substantial amount of manual effort, especially in the video domain. Labeling instances of pedestrians in highly crowded scenarios can be challenging even for human annotators and may introduce errors in the training data. In this paper, we study how we can advance different aspects of multi-person tracking using solely synthetic data. To this end, we generate MOTSynth, a large, highly diverse synthetic dataset for object detection and tracking using a rendering game engine. Our experiments show that MOTSynth can be used as a replacement for real data on tasks such as pedestrian detection, re-identification, segmentation, and tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge