Guangpu Zhu
Using Large Language Models for Parametric Shape Optimization
Dec 11, 2024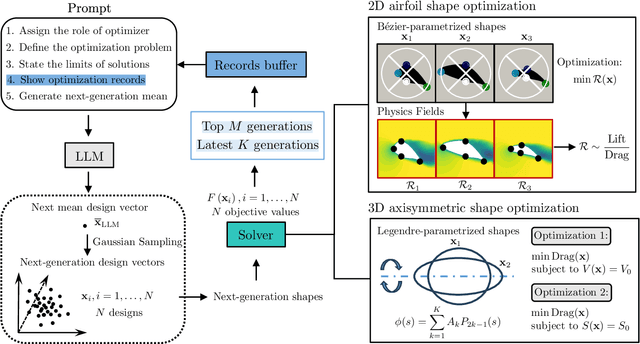

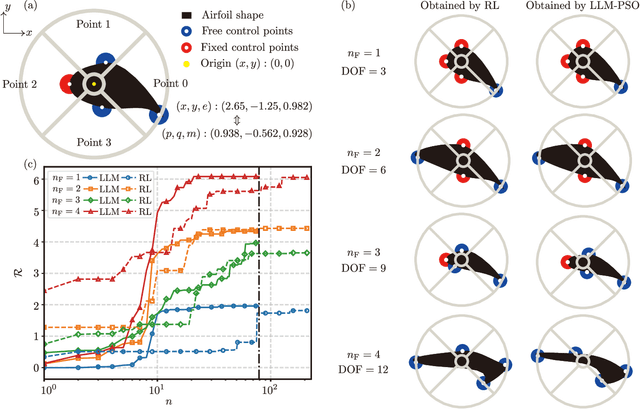
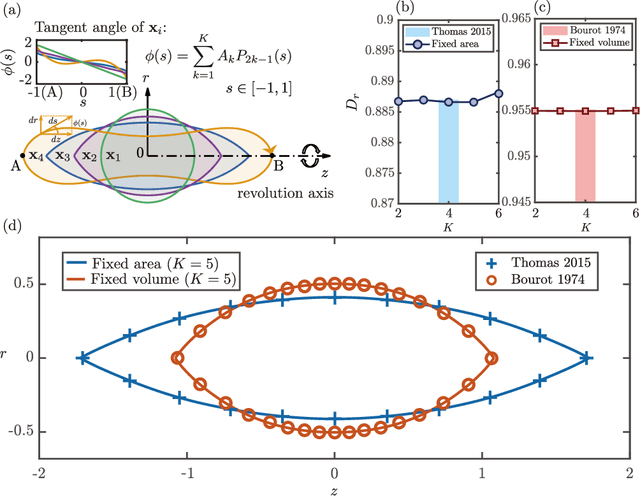
Abstract:Recent advanced large language models (LLMs) have showcased their emergent capability of in-context learning, facilitating intelligent decision-making through natural language prompts without retraining. This new machine learning paradigm has shown promise in various fields, including general control and optimization problems. Inspired by these advancements, we explore the potential of LLMs for a specific and essential engineering task: parametric shape optimization (PSO). We develop an optimization framework, LLM-PSO, that leverages an LLM to determine the optimal shape of parameterized engineering designs in the spirit of evolutionary strategies. Utilizing the ``Claude 3.5 Sonnet'' LLM, we evaluate LLM-PSO on two benchmark flow optimization problems, specifically aiming to identify drag-minimizing profiles for 1) a two-dimensional airfoil in laminar flow, and 2) a three-dimensional axisymmetric body in Stokes flow. In both cases, LLM-PSO successfully identifies optimal shapes in agreement with benchmark solutions. Besides, it generally converges faster than other classical optimization algorithms. Our preliminary exploration may inspire further investigations into harnessing LLMs for shape optimization and engineering design more broadly.
Constraint Latent Space Matters: An Anti-anomalous Waveform Transformation Solution from Photoplethysmography to Arterial Blood Pressure
Feb 23, 2024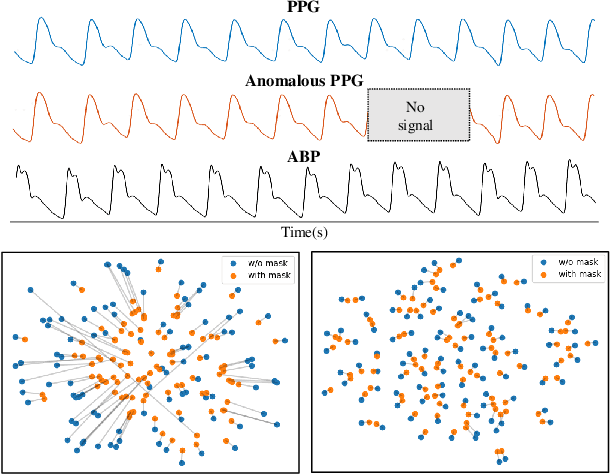
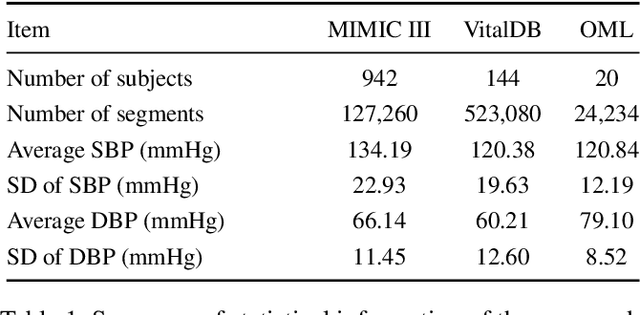
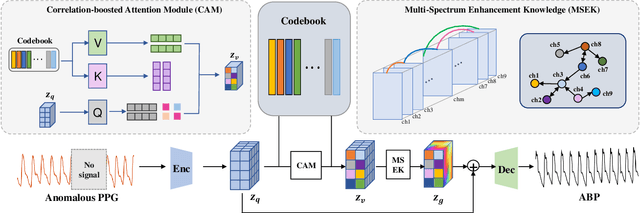
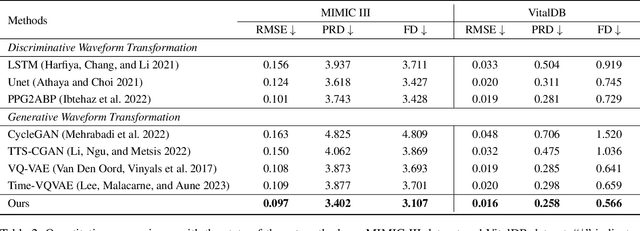
Abstract:Arterial blood pressure (ABP) holds substantial promise for proactive cardiovascular health management. Notwithstanding its potential, the invasive nature of ABP measurements confines their utility primarily to clinical environments, limiting their applicability for continuous monitoring beyond medical facilities. The conversion of photoplethysmography (PPG) signals into ABP equivalents has garnered significant attention due to its potential in revolutionizing cardiovascular disease management. Recent strides in PPG-to-ABP prediction encompass the integration of generative and discriminative models. Despite these advances, the efficacy of these models is curtailed by the latent space shift predicament, stemming from alterations in PPG data distribution across disparate hardware and individuals, potentially leading to distorted ABP waveforms. To tackle this problem, we present an innovative solution named the Latent Space Constraint Transformer (LSCT), leveraging a quantized codebook to yield robust latent spaces by employing multiple discretizing bases. To facilitate improved reconstruction, the Correlation-boosted Attention Module (CAM) is introduced to systematically query pertinent bases on a global scale. Furthermore, to enhance expressive capacity, we propose the Multi-Spectrum Enhancement Knowledge (MSEK), which fosters local information flow within the channels of latent code and provides additional embedding for reconstruction. Through comprehensive experimentation on both publicly available datasets and a private downstream task dataset, the proposed approach demonstrates noteworthy performance enhancements compared to existing methods. Extensive ablation studies further substantiate the effectiveness of each introduced module.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge