Gregory Abowd
Leveraging Context to Support Automated Food Recognition in Restaurants
Oct 07, 2015
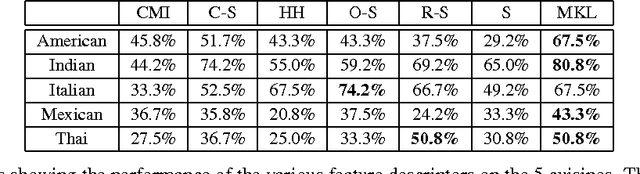


Abstract:The pervasiveness of mobile cameras has resulted in a dramatic increase in food photos, which are pictures reflecting what people eat. In this paper, we study how taking pictures of what we eat in restaurants can be used for the purpose of automating food journaling. We propose to leverage the context of where the picture was taken, with additional information about the restaurant, available online, coupled with state-of-the-art computer vision techniques to recognize the food being consumed. To this end, we demonstrate image-based recognition of foods eaten in restaurants by training a classifier with images from restaurant's online menu databases. We evaluate the performance of our system in unconstrained, real-world settings with food images taken in 10 restaurants across 5 different types of food (American, Indian, Italian, Mexican and Thai).
Predicting Daily Activities From Egocentric Images Using Deep Learning
Oct 06, 2015
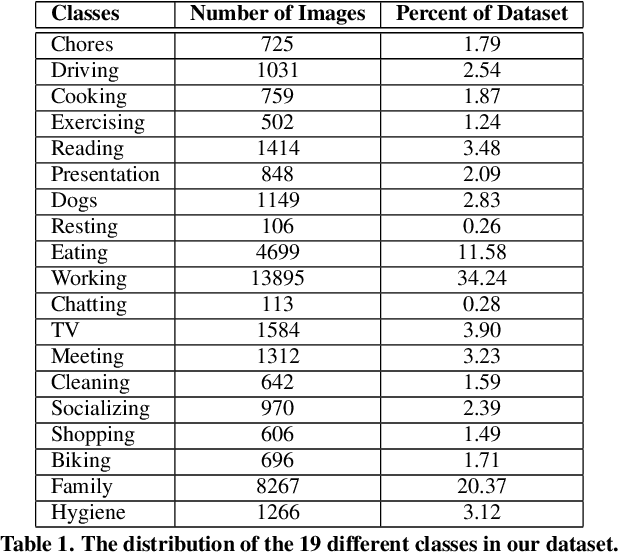

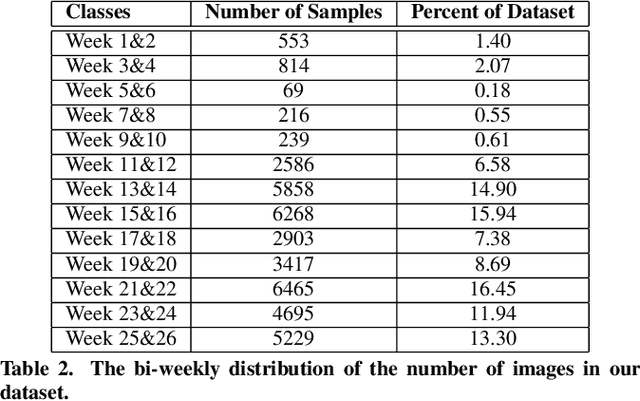
Abstract:We present a method to analyze images taken from a passive egocentric wearable camera along with the contextual information, such as time and day of week, to learn and predict everyday activities of an individual. We collected a dataset of 40,103 egocentric images over a 6 month period with 19 activity classes and demonstrate the benefit of state-of-the-art deep learning techniques for learning and predicting daily activities. Classification is conducted using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with a classification method we introduce called a late fusion ensemble. This late fusion ensemble incorporates relevant contextual information and increases our classification accuracy. Our technique achieves an overall accuracy of 83.07% in predicting a person's activity across the 19 activity classes. We also demonstrate some promising results from two additional users by fine-tuning the classifier with one day of training data.
* 8 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge