Gilbert Bahati
Risk-Aware Safety Filters with Poisson Safety Functions and Laplace Guidance Fields
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Robotic systems navigating in real-world settings require a semantic understanding of their environment to properly determine safe actions. This work aims to develop the mathematical underpinnings of such a representation -- specifically, the goal is to develop safety filters that are risk-aware. To this end, we take a two step approach: encoding an understanding of the environment via Poisson's equation, and associated risk via Laplace guidance fields. That is, we first solve a Dirichlet problem for Poisson's equation to generate a safety function that encodes system safety as its 0-superlevel set. We then separately solve a Dirichlet problem for Laplace's equation to synthesize a safe \textit{guidance field} that encodes variable levels of caution around obstacles -- by enforcing a tunable flux boundary condition. The safety function and guidance fields are then combined to define a safety constraint and used to synthesize a risk-aware safety filter which, given a semantic understanding of an environment with associated risk levels of environmental features, guarantees safety while prioritizing avoidance of higher risk obstacles. We demonstrate this method in simulation and discuss how \textit{a priori} understandings of obstacle risk can be directly incorporated into the safety filter to generate safe behaviors that are risk-aware.
Dynamic Safety in Complex Environments: Synthesizing Safety Filters with Poisson's Equation
May 11, 2025



Abstract:Synthesizing safe sets for robotic systems operating in complex and dynamically changing environments is a challenging problem. Solving this problem can enable the construction of safety filters that guarantee safe control actions -- most notably by employing Control Barrier Functions (CBFs). This paper presents an algorithm for generating safe sets from perception data by leveraging elliptic partial differential equations, specifically Poisson's equation. Given a local occupancy map, we solve Poisson's equation subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions, with a novel forcing function. Specifically, we design a smooth guidance vector field, which encodes gradient information required for safety. The result is a variational problem for which the unique minimizer -- a safety function -- characterizes the safe set. After establishing our theoretical result, we illustrate how safety functions can be used in CBF-based safety filtering. The real-time utility of our synthesis method is highlighted through hardware demonstrations on quadruped and humanoid robots navigating dynamically changing obstacle-filled environments.
Characterizing Smooth Safety Filters via the Implicit Function Theorem
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:Optimization-based safety filters, such as control barrier function (CBF) based quadratic programs (QPs), have demonstrated success in controlling autonomous systems to achieve complex goals. These CBF-QPs can be shown to be continuous, but are generally not smooth, let alone continuously differentiable. In this paper, we present a general characterization of smooth safety filters -- smooth controllers that guarantee safety in a minimally invasive fashion -- based on the Implicit Function Theorem. This characterization leads to families of smooth universal formulas for safety-critical controllers that quantify the conservatism of the resulting safety filter, the utility of which is demonstrated through illustrative examples.
Multi-Adversarial Safety Analysis for Autonomous Vehicles
Dec 29, 2021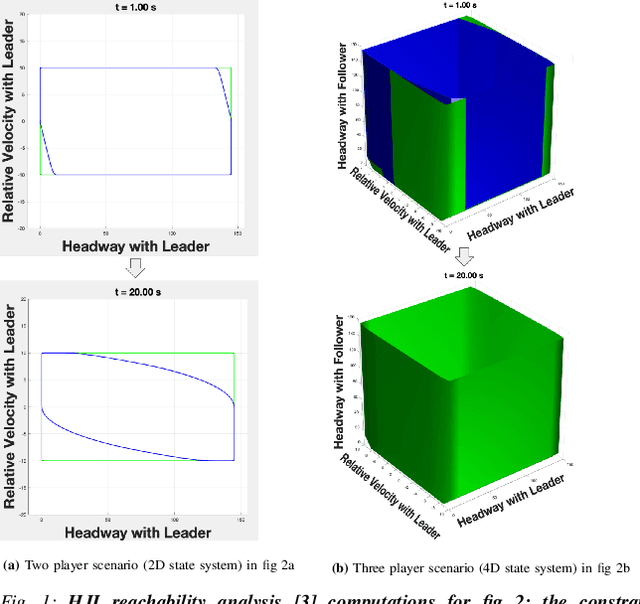

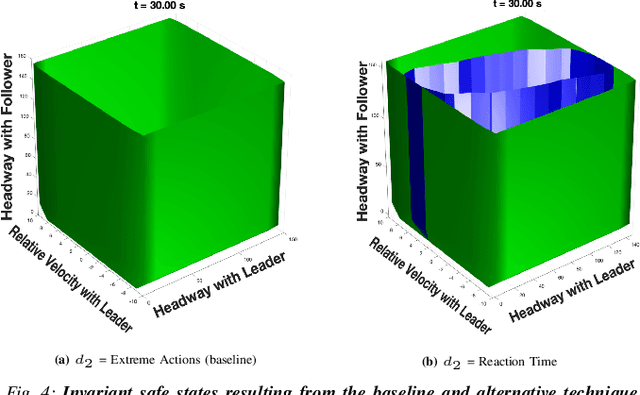
Abstract:This work in progress considers reachability-based safety analysis in the domain of autonomous driving in multi-agent systems. We formulate the safety problem for a car following scenario as a differential game and study how different modelling strategies yield very different behaviors regardless of the validity of the strategies in other scenarios. Given the nature of real-life driving scenarios, we propose a modeling strategy in our formulation that accounts for subtle interactions between agents, and compare its Hamiltonian results to other baselines. Our formulation encourages reduction of conservativeness in Hamilton-Jacobi safety analysis to provide better safety guarantees during navigation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge