George Church
CodonMPNN for Organism Specific and Codon Optimal Inverse Folding
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:Generating protein sequences conditioned on protein structures is an impactful technique for protein engineering. When synthesizing engineered proteins, they are commonly translated into DNA and expressed in an organism such as yeast. One difficulty in this process is that the expression rates can be low due to suboptimal codon sequences for expressing a protein in a host organism. We propose CodonMPNN, which generates a codon sequence conditioned on a protein backbone structure and an organism label. If naturally occurring DNA sequences are close to codon optimality, CodonMPNN could learn to generate codon sequences with higher expression yields than heuristic codon choices for generated amino acid sequences. Experiments show that CodonMPNN retains the performance of previous inverse folding approaches and recovers wild-type codons more frequently than baselines. Furthermore, CodonMPNN has a higher likelihood of generating high-fitness codon sequences than low-fitness codon sequences for the same protein sequence. Code is available at https://github.com/HannesStark/CodonMPNN.
Large Language Models in Drug Discovery and Development: From Disease Mechanisms to Clinical Trials
Sep 06, 2024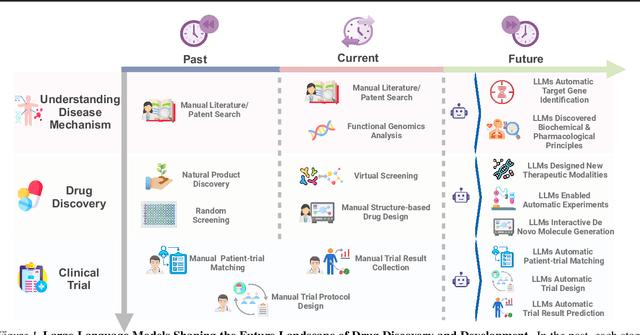
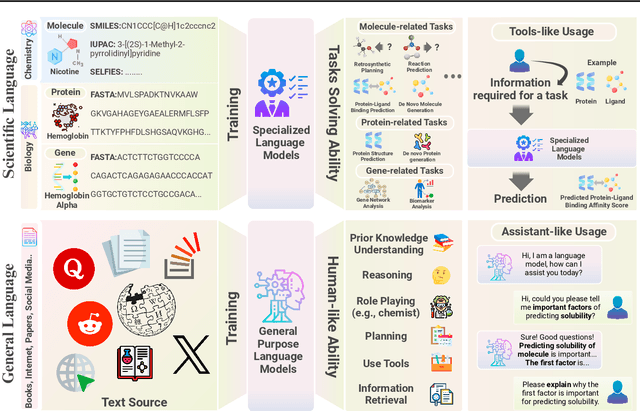
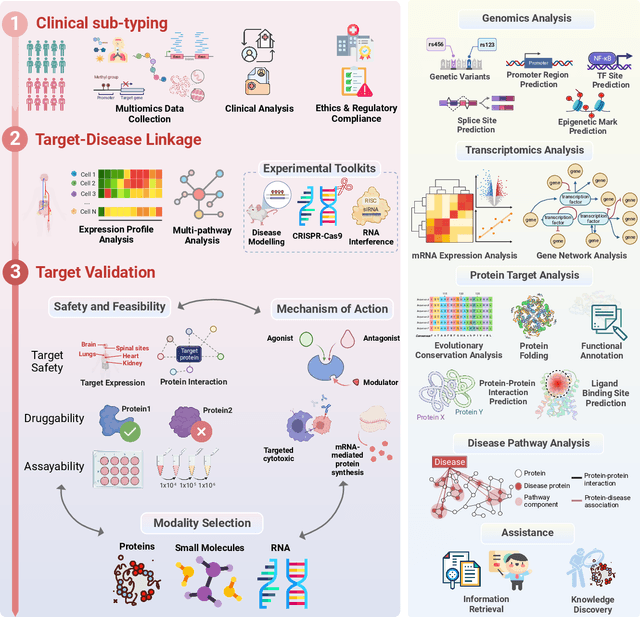
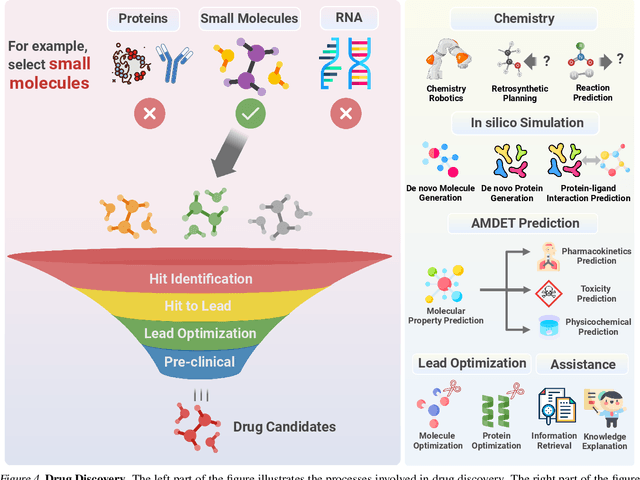
Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into the drug discovery and development field marks a significant paradigm shift, offering novel methodologies for understanding disease mechanisms, facilitating drug discovery, and optimizing clinical trial processes. This review highlights the expanding role of LLMs in revolutionizing various stages of the drug development pipeline. We investigate how these advanced computational models can uncover target-disease linkage, interpret complex biomedical data, enhance drug molecule design, predict drug efficacy and safety profiles, and facilitate clinical trial processes. Our paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview for researchers and practitioners in computational biology, pharmacology, and AI4Science by offering insights into the potential transformative impact of LLMs on drug discovery and development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge