Geonuk Kim
Cycle-Consistency Uncertainty Estimation for Visual Prompting based One-Shot Defect Segmentation
Sep 21, 2024


Abstract:Industrial defect detection traditionally relies on supervised learning models trained on fixed datasets of known defect types. While effective within a closed set, these models struggle with new, unseen defects, necessitating frequent re-labeling and re-training. Recent advances in visual prompting offer a solution by allowing models to adaptively infer novel categories based on provided visual cues. However, a prevalent issue in these methods is the over-confdence problem, where models can mis-classify unknown objects as known objects with high certainty. To addresssing the fundamental concerns about the adaptability, we propose a solution to estimate uncertainty of the visual prompting process by cycle-consistency. We designed to check whether it can accurately restore the original prompt from its predictions. To quantify this, we measure the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) between the restored prompt mask and the originally provided prompt mask. Without using complex designs or ensemble methods with multiple networks, our approach achieved a yield rate of 0.9175 in the VISION24 one-shot industrial challenge.
Separating Novel Features for Logical Anomaly Detection: A Straightforward yet Effective Approach
Jul 25, 2024

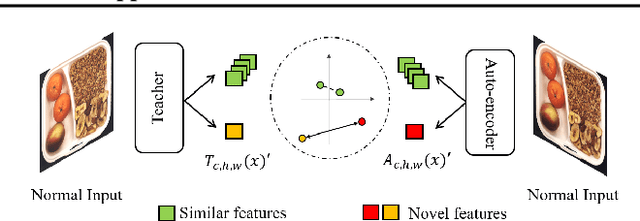
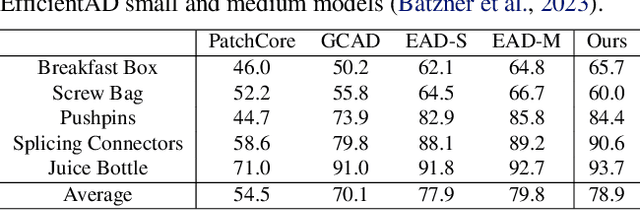
Abstract:Vision-based inspection algorithms have significantly contributed to quality control in industrial settings, particularly in addressing structural defects like dent and contamination which are prevalent in mass production. Extensive research efforts have led to the development of related benchmarks such as MVTec AD (Bergmann et al., 2019). However, in industrial settings, there can be instances of logical defects, where acceptable items are found in unsuitable locations or product pairs do not match as expected. Recent methods tackling logical defects effectively employ knowledge distillation to generate difference maps. Knowledge distillation (KD) is used to learn normal data distribution in unsupervised manner. Despite their effectiveness, these methods often overlook the potential false negatives. Excessive similarity between the teacher network and student network can hinder the generation of a suitable difference map for logical anomaly detection. This technical report provides insights on handling potential false negatives by utilizing a simple constraint in KD-based logical anomaly detection methods. We select EfficientAD as a state-of-the-art baseline and apply a margin-based constraint to its unsupervised learning scheme. Applying this constraint, we can improve the AUROC for MVTec LOCO AD by 1.3 %.
Spatial Reasoning for Few-Shot Object Detection
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:Although modern object detectors rely heavily on a significant amount of training data, humans can easily detect novel objects using a few training examples. The mechanism of the human visual system is to interpret spatial relationships among various objects and this process enables us to exploit contextual information by considering the co-occurrence of objects. Thus, we propose a spatial reasoning framework that detects novel objects with only a few training examples in a context. We infer geometric relatedness between novel and base RoIs (Region-of-Interests) to enhance the feature representation of novel categories using an object detector well trained on base categories. We employ a graph convolutional network as the RoIs and their relatedness are defined as nodes and edges, respectively. Furthermore, we present spatial data augmentation to overcome the few-shot environment where all objects and bounding boxes in an image are resized randomly. Using the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets, we demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and verify its efficacy through extensive ablation studies.
Character decomposition to resolve class imbalance problem in Hangul OCR
Aug 12, 2022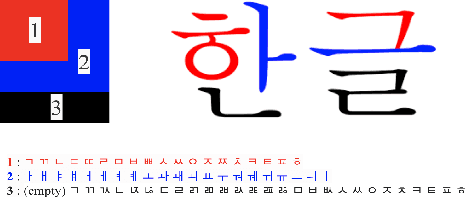
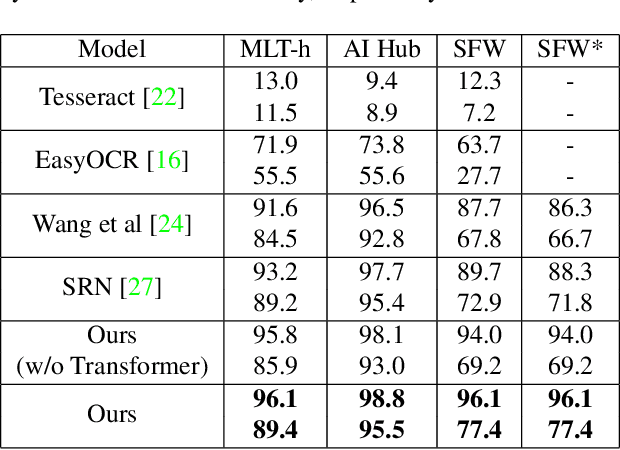
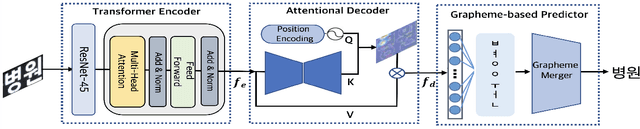
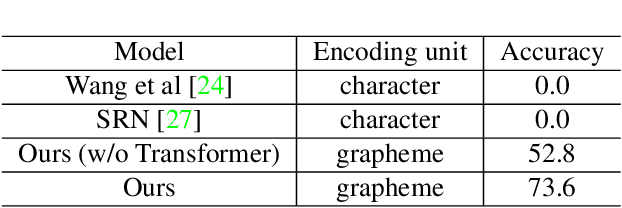
Abstract:We present a novel approach to OCR(Optical Character Recognition) of Korean character, Hangul. As a phonogram, Hangul can represent 11,172 different characters with only 52 graphemes, by describing each character with a combination of the graphemes. As the total number of the characters could overwhelm the capacity of a neural network, the existing OCR encoding methods pre-define a smaller set of characters that are frequently used. This design choice naturally compromises the performance on long-tailed characters in the distribution. In this work, we demonstrate that grapheme encoding is not only efficient but also performant for Hangul OCR. Benchmark tests show that our approach resolves two main problems of Hangul OCR: class imbalance and target class selection.
Few-Shot Object Detection via Knowledge Transfer
Aug 28, 2020
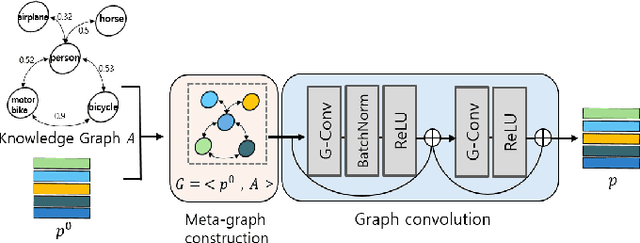


Abstract:Conventional methods for object detection usually require substantial amounts of training data and annotated bounding boxes. If there are only a few training data and annotations, the object detectors easily overfit and fail to generalize. It exposes the practical weakness of the object detectors. On the other hand, human can easily master new reasoning rules with only a few demonstrations using previously learned knowledge. In this paper, we introduce a few-shot object detection via knowledge transfer, which aims to detect objects from a few training examples. Central to our method is prototypical knowledge transfer with an attached meta-learner. The meta-learner takes support set images that include the few examples of the novel categories and base categories, and predicts prototypes that represent each category as a vector. Then, the prototypes reweight each RoI (Region-of-Interest) feature vector from a query image to remodels R-CNN predictor heads. To facilitate the remodeling process, we predict the prototypes under a graph structure, which propagates information of the correlated base categories to the novel categories with explicit guidance of prior knowledge that represents correlations among categories. Extensive experiments on the PASCAL VOC dataset verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge