Garima Malik
Data Augmentation for Conflict and Duplicate Detection in Software Engineering Sentence Pairs
May 16, 2023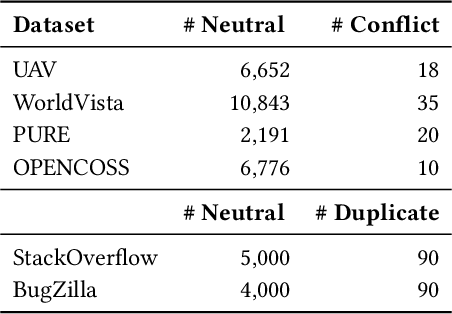
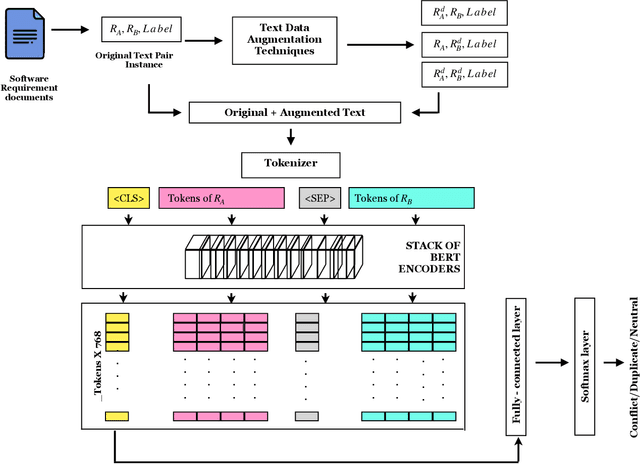
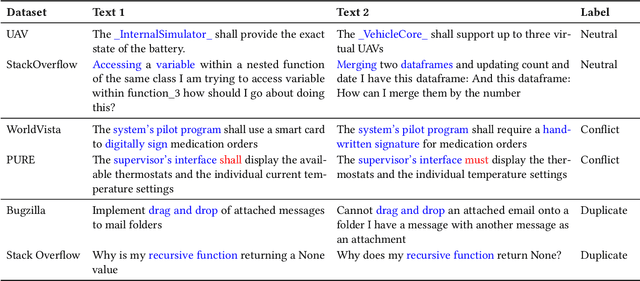
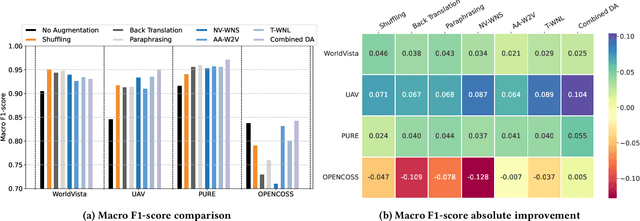
Abstract:This paper explores the use of text data augmentation techniques to enhance conflict and duplicate detection in software engineering tasks through sentence pair classification. The study adapts generic augmentation techniques such as shuffling, back translation, and paraphrasing and proposes new data augmentation techniques such as Noun-Verb Substitution, target-lemma replacement and Actor-Action Substitution for software requirement texts. A comprehensive empirical analysis is conducted on six software text datasets to identify conflicts and duplicates among sentence pairs. The results demonstrate that data augmentation techniques have a significant impact on the performance of all software pair text datasets. On the other hand, in cases where the datasets are relatively balanced, the use of augmentation techniques may result in a negative effect on the classification performance.
Transfer learning for conflict and duplicate detection in software requirement pairs
Jan 09, 2023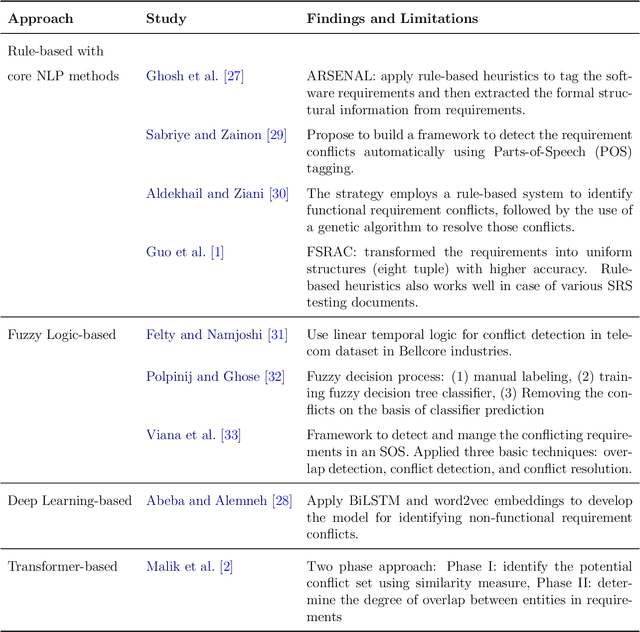
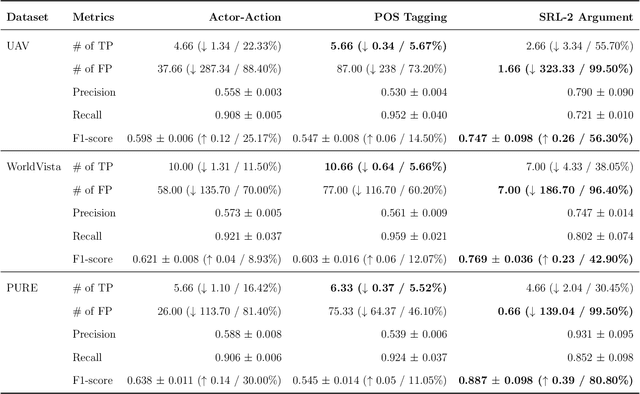
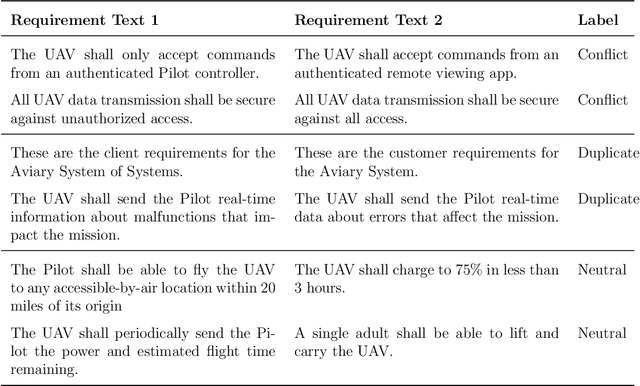
Abstract:Consistent and holistic expression of software requirements is important for the success of software projects. In this study, we aim to enhance the efficiency of the software development processes by automatically identifying conflicting and duplicate software requirement specifications. We formulate the conflict and duplicate detection problem as a requirement pair classification task. We design a novel transformers-based architecture, SR-BERT, which incorporates Sentence-BERT and Bi-encoders for the conflict and duplicate identification task. Furthermore, we apply supervised multi-stage fine-tuning to the pre-trained transformer models. We test the performance of different transfer models using four different datasets. We find that sequentially trained and fine-tuned transformer models perform well across the datasets with SR-BERT achieving the best performance for larger datasets. We also explore the cross-domain performance of conflict detection models and adopt a rule-based filtering approach to validate the model classifications. Our analysis indicates that the sentence pair classification approach and the proposed transformer-based natural language processing strategies can contribute significantly to achieving automation in conflict and duplicate detection
Fine-grained Entity Recognition with Reduced False Negatives and Large Type Coverage
Apr 30, 2019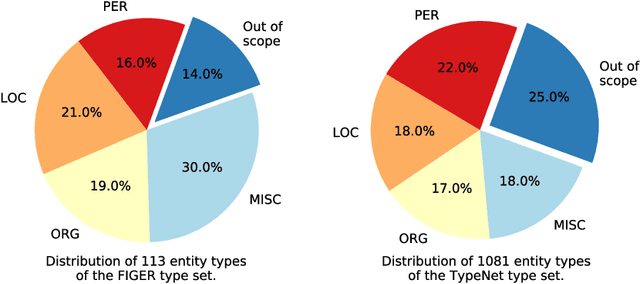
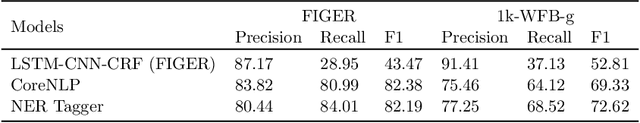
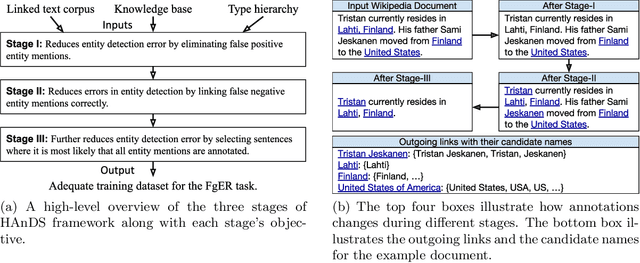
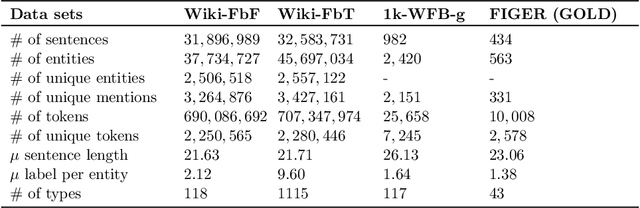
Abstract:Fine-grained Entity Recognition (FgER) is the task of detecting and classifying entity mentions to a large set of types spanning diverse domains such as biomedical, finance and sports. We observe that when the type set spans several domains, detection of entity mention becomes a limitation for supervised learning models. The primary reason being lack of dataset where entity boundaries are properly annotated while covering a large spectrum of entity types. Our work directly addresses this issue. We propose Heuristics Allied with Distant Supervision (HAnDS) framework to automatically construct a quality dataset suitable for the FgER task. HAnDS framework exploits the high interlink among Wikipedia and Freebase in a pipelined manner, reducing annotation errors introduced by naively using distant supervision approach. Using HAnDS framework, we create two datasets, one suitable for building FgER systems recognizing up to 118 entity types based on the FIGER type hierarchy and another for up to 1115 entity types based on the TypeNet hierarchy. Our extensive empirical experimentation warrants the quality of the generated datasets. Along with this, we also provide a manually annotated dataset for benchmarking FgER systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge