Ashish Anand
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
AWED-FiNER: Agents, Web applications, and Expert Detectors for Fine-grained Named Entity Recognition across 36 Languages for 6.6 Billion Speakers
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We introduce AWED-FiNER, an open-source ecosystem designed to bridge the gap in Fine-grained Named Entity Recognition (FgNER) for 36 global languages spoken by more than 6.6 billion people. While Large Language Models (LLMs) dominate general Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, they often struggle with low-resource languages and fine-grained NLP tasks. AWED-FiNER provides a collection of agentic toolkits, web applications, and several state-of-the-art expert models that provides FgNER solutions across 36 languages. The agentic tools enable to route multilingual text to specialized expert models and fetch FgNER annotations within seconds. The web-based platforms provide ready-to-use FgNER annotation service for non-technical users. Moreover, the collection of language specific extremely small sized open-source state-of-the-art expert models facilitate offline deployment in resource contraint scenerios including edge devices. AWED-FiNER covers languages spoken by over 6.6 billion people, including a specific focus on vulnerable languages such as Bodo, Manipuri, Bishnupriya, and Mizo. The resources can be accessed here: Agentic Tool (https://github.com/PrachuryyaKaushik/AWED-FiNER), Web Application (https://hf.co/spaces/prachuryyaIITG/AWED-FiNER), and 49 Expert Detector Models (https://hf.co/collections/prachuryyaIITG/awed-finer).
Malware Classification using Diluted Convolutional Neural Network with Fast Gradient Sign Method
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Android malware has become an increasingly critical threat to organizations, society and individuals, posing significant risks to privacy, data security and infrastructure. As malware continues to evolve in terms of complexity and sophistication, the mitigation and detection of these malicious software instances have become more time consuming and challenging particularly due to the requirement of large number of features to identify potential malware. To address these challenges, this research proposes Fast Gradient Sign Method with Diluted Convolutional Neural Network (FGSM DICNN) method for malware classification. DICNN contains diluted convolutions which increases receptive field, enabling the model to capture dispersed malware patterns across long ranges using fewer features without adding parameters. Additionally, the FGSM strategy enhance the accuracy by using one-step perturbations during training that provides more defensive advantage of lower computational cost. This integration helps to manage high classification accuracy while reducing the dependence on extensive feature sets. The proposed FGSM DICNN model attains 99.44% accuracy while outperforming other existing approaches such as Custom Deep Neural Network (DCNN).
AmalREC: A Dataset for Relation Extraction and Classification Leveraging Amalgamation of Large Language Models
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:Existing datasets for relation classification and extraction often exhibit limitations such as restricted relation types and domain-specific biases. This work presents a generic framework to generate well-structured sentences from given tuples with the help of Large Language Models (LLMs). This study has focused on the following major questions: (i) how to generate sentences from relation tuples, (ii) how to compare and rank them, (iii) can we combine strengths of individual methods and amalgamate them to generate an even bette quality of sentences, and (iv) how to evaluate the final dataset? For the first question, we employ a multifaceted 5-stage pipeline approach, leveraging LLMs in conjunction with template-guided generation. We introduce Sentence Evaluation Index(SEI) that prioritizes factors like grammatical correctness, fluency, human-aligned sentiment, accuracy, and complexity to answer the first part of the second question. To answer the second part of the second question, this work introduces a SEI-Ranker module that leverages SEI to select top candidate generations. The top sentences are then strategically amalgamated to produce the final, high-quality sentence. Finally, we evaluate our dataset on LLM-based and SOTA baselines for relation classification. The proposed dataset features 255 relation types, with 15K sentences in the test set and around 150k in the train set organized in, significantly enhancing relational diversity and complexity. This work not only presents a new comprehensive benchmark dataset for RE/RC task, but also compare different LLMs for generation of quality sentences from relational tuples.
Enhancing Event Extraction from Short Stories through Contextualized Prompts
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Event extraction is an important natural language processing (NLP) task of identifying events in an unstructured text. Although a plethora of works deal with event extraction from new articles, clinical text etc., only a few works focus on event extraction from literary content. Detecting events in short stories presents several challenges to current systems, encompassing a different distribution of events as compared to other domains and the portrayal of diverse emotional conditions. This paper presents \texttt{Vrittanta-EN}, a collection of 1000 English short stories annotated for real events. Exploring this field could result in the creation of techniques and resources that support literary scholars in improving their effectiveness. This could simultaneously influence the field of Natural Language Processing. Our objective is to clarify the intricate idea of events in the context of short stories. Towards the objective, we collected 1,000 short stories written mostly for children in the Indian context. Further, we present fresh guidelines for annotating event mentions and their categories, organized into \textit{seven distinct classes}. The classes are {\tt{COGNITIVE-MENTAL-STATE(CMS), COMMUNICATION(COM), CONFLICT(CON), GENERAL-ACTIVITY(GA), LIFE-EVENT(LE), MOVEMENT(MOV), and OTHERS(OTH)}}. Subsequently, we apply these guidelines to annotate the short story dataset. Later, we apply the baseline methods for automatically detecting and categorizing events. We also propose a prompt-based method for event detection and classification. The proposed method outperforms the baselines, while having significant improvement of more than 4\% for the class \texttt{CONFLICT} in event classification task.
End-to-End Argument Mining as Augmented Natural Language Generation
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:Argument Mining (AM) is a crucial aspect of computational argumentation, which deals with the identification and extraction of Argumentative Components (ACs) and their corresponding Argumentative Relations (ARs). Most prior works have solved these problems by dividing them into multiple subtasks. And the available end-to-end setups are mostly based on the dependency parsing approach. This work proposes a unified end-to-end framework based on a generative paradigm, in which the argumentative structures are framed into label-augmented text, called Augmented Natural Language (ANL). Additionally, we explore the role of different types of markers in solving AM tasks. Through different marker-based fine-tuning strategies, we present an extensive study by integrating marker knowledge into our generative model. The proposed framework achieves competitive results to the state-of-the-art (SoTA) model and outperforms several baselines.
Noise in Relation Classification Dataset TACRED: Characterization and Reduction
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:The overarching objective of this paper is two-fold. First, to explore model-based approaches to characterize the primary cause of the noise. in the RE dataset TACRED Second, to identify the potentially noisy instances. Towards the first objective, we analyze predictions and performance of state-of-the-art (SOTA) models to identify the root cause of noise in the dataset. Our analysis of TACRED shows that the majority of the noise in the dataset originates from the instances labeled as no-relation which are negative examples. For the second objective, we explore two nearest-neighbor-based strategies to automatically identify potentially noisy examples for elimination and reannotation. Our first strategy, referred to as Intrinsic Strategy (IS), is based on the assumption that positive examples are clean. Thus, we have used false-negative predictions to identify noisy negative examples. Whereas, our second approach, referred to as Extrinsic Strategy, is based on using a clean subset of the dataset to identify potentially noisy negative examples. Finally, we retrained the SOTA models on the eliminated and reannotated dataset. Our empirical results based on two SOTA models trained on TACRED-E following the IS show an average 4% F1-score improvement, whereas reannotation (TACRED-R) does not improve the original results. However, following ES, SOTA models show the average F1-score improvement of 3.8% and 4.4% when trained on respective eliminated (TACRED-EN) and reannotated (TACRED-RN) datasets respectively. We further extended the ES for cleaning positive examples as well, which resulted in an average performance improvement of 5.8% and 5.6% for the eliminated (TACRED-ENP) and reannotated (TACRED-RNP) datasets respectively.
VQA with Cascade of Self- and Co-Attention Blocks
Feb 28, 2023
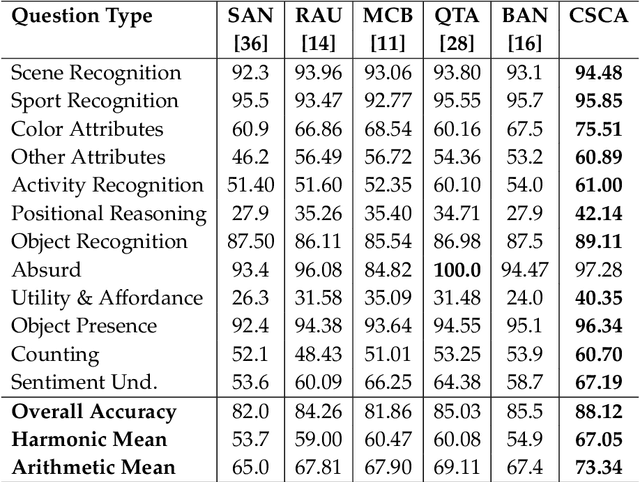
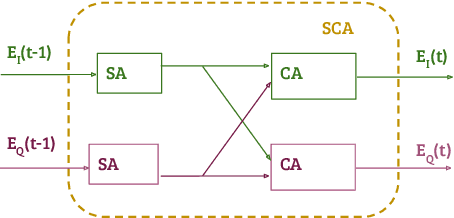
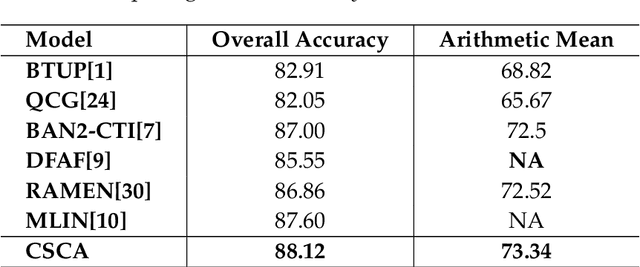
Abstract:The use of complex attention modules has improved the performance of the Visual Question Answering (VQA) task. This work aims to learn an improved multi-modal representation through dense interaction of visual and textual modalities. The proposed model has an attention block containing both self-attention and co-attention on image and text. The self-attention modules provide the contextual information of objects (for an image) and words (for a question) that are crucial for inferring an answer. On the other hand, co-attention aids the interaction of image and text. Further, fine-grained information is obtained from two modalities by using a Cascade of Self- and Co-Attention blocks (CSCA). This proposal is benchmarked on the widely used VQA2.0 and TDIUC datasets. The efficacy of key components of the model and cascading of attention modules are demonstrated by experiments involving ablation analysis.
Budget Sensitive Reannotation of Noisy Relation Classification Data Using Label Hierarchy
Dec 26, 2021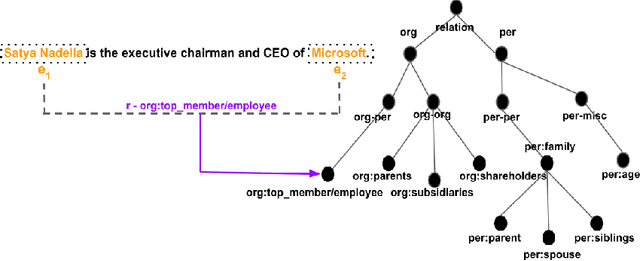
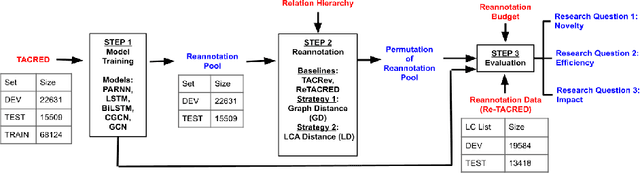

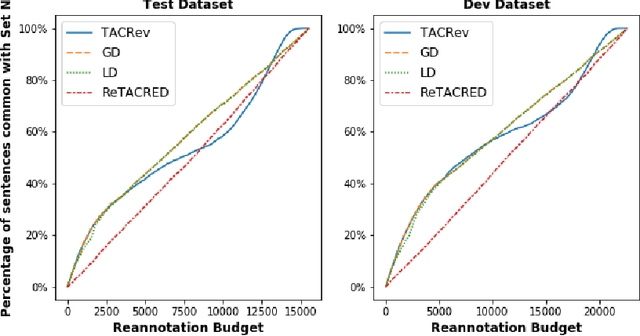
Abstract:Large crowd-sourced datasets are often noisy and relation classification (RC) datasets are no exception. Reannotating the entire dataset is one probable solution however it is not always viable due to time and budget constraints. This paper addresses the problem of efficient reannotation of a large noisy dataset for the RC. Our goal is to catch more annotation errors in the dataset while reannotating fewer instances. Existing work on RC dataset reannotation lacks the flexibility about how much data to reannotate. We introduce the concept of a reannotation budget to overcome this limitation. The immediate follow-up problem is: Given a specific reannotation budget, which subset of the data should we reannotate? To address this problem, we present two strategies to selectively reannotate RC datasets. Our strategies utilize the taxonomic hierarchy of relation labels. The intuition of our work is to rely on the graph distance between actual and predicted relation labels in the label hierarchy graph. We evaluate our reannotation strategies on the well-known TACRED dataset. We design our experiments to answer three specific research questions. First, does our strategy select novel candidates for reannotation? Second, for a given reannotation budget is our reannotation strategy more efficient at catching annotation errors? Third, what is the impact of data reannotation on RC model performance measurement? Experimental results show that our both reannotation strategies are novel and efficient. Our analysis indicates that the current reported performance of RC models on noisy TACRED data is inflated.
CL-NERIL: A Cross-Lingual Model for NER in Indian Languages
Nov 23, 2021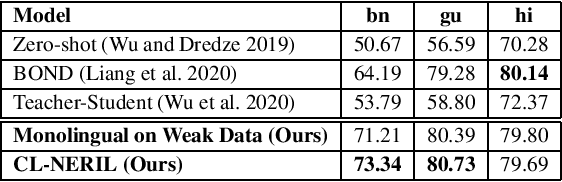
Abstract:Developing Named Entity Recognition (NER) systems for Indian languages has been a long-standing challenge, mainly owing to the requirement of a large amount of annotated clean training instances. This paper proposes an end-to-end framework for NER for Indian languages in a low-resource setting by exploiting parallel corpora of English and Indian languages and an English NER dataset. The proposed framework includes an annotation projection method that combines word alignment score and NER tag prediction confidence score on source language (English) data to generate weakly labeled data in a target Indian language. We employ a variant of the Teacher-Student model and optimize it jointly on the pseudo labels of the Teacher model and predictions on the generated weakly labeled data. We also present manually annotated test sets for three Indian languages: Hindi, Bengali, and Gujarati. We evaluate the performance of the proposed framework on the test sets of the three Indian languages. Empirical results show a minimum 10% performance improvement compared to the zero-shot transfer learning model on all languages. This indicates that weakly labeled data generated using the proposed annotation projection method in target Indian languages can complement well-annotated source language data to enhance performance. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/aksh555/CL-NERIL
IQ-VQA: Intelligent Visual Question Answering
Jul 08, 2020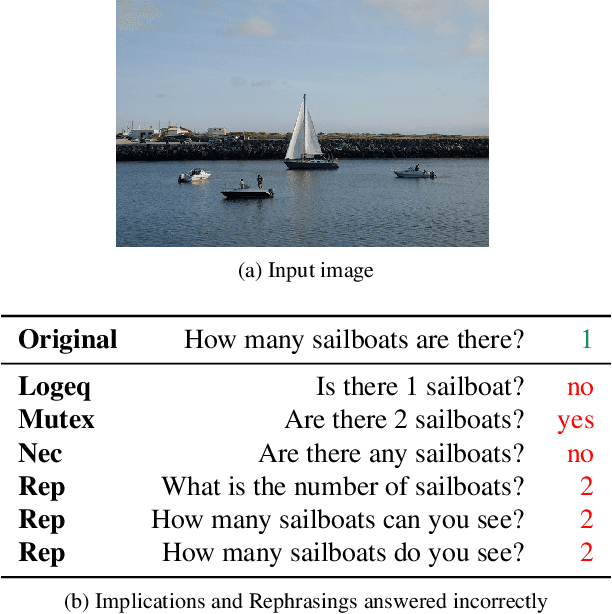
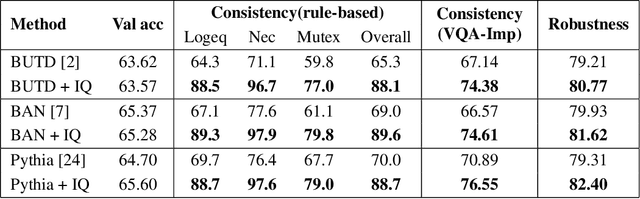

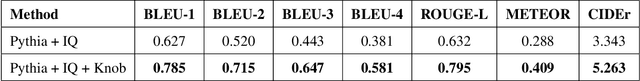
Abstract:Even though there has been tremendous progress in the field of Visual Question Answering, models today still tend to be inconsistent and brittle. To this end, we propose a model-independent cyclic framework which increases consistency and robustness of any VQA architecture. We train our models to answer the original question, generate an implication based on the answer and then also learn to answer the generated implication correctly. As a part of the cyclic framework, we propose a novel implication generator which can generate implied questions from any question-answer pair. As a baseline for future works on consistency, we provide a new human annotated VQA-Implications dataset. The dataset consists of ~30k questions containing implications of 3 types - Logical Equivalence, Necessary Condition and Mutual Exclusion - made from the VQA v2.0 validation dataset. We show that our framework improves consistency of VQA models by ~15% on the rule-based dataset, ~7% on VQA-Implications dataset and robustness by ~2%, without degrading their performance. In addition, we also quantitatively show improvement in attention maps which highlights better multi-modal understanding of vision and language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge