Gao Hui
A foundation model enpowered by a multi-modal prompt engine for universal seismic geobody interpretation across surveys
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:Seismic geobody interpretation is crucial for structural geology studies and various engineering applications. Existing deep learning methods show promise but lack support for multi-modal inputs and struggle to generalize to different geobody types or surveys. We introduce a promptable foundation model for interpreting any geobodies across seismic surveys. This model integrates a pre-trained vision foundation model (VFM) with a sophisticated multi-modal prompt engine. The VFM, pre-trained on massive natural images and fine-tuned on seismic data, provides robust feature extraction for cross-survey generalization. The prompt engine incorporates multi-modal prior information to iteratively refine geobody delineation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the model's superior accuracy, scalability from 2D to 3D, and generalizability to various geobody types, including those unseen during training. To our knowledge, this is the first highly scalable and versatile multi-modal foundation model capable of interpreting any geobodies across surveys while supporting real-time interactions. Our approach establishes a new paradigm for geoscientific data interpretation, with broad potential for transfer to other tasks.
Design of Integrated Communication System under UAV Network
Nov 12, 2022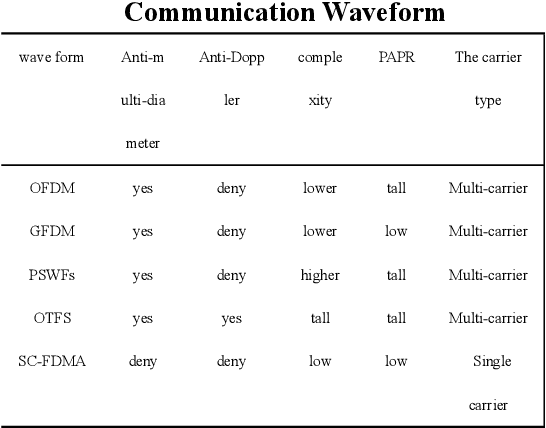
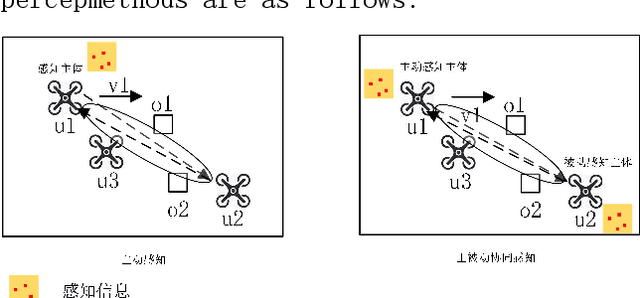
Abstract:It is becoming a key feature of UAV communication network to integrate sensing function into communication equipment to realize sensing communication integration.The existing perceptual communication fusion schemes focus on the design under a single waveform and single frequency band, and lack of discussion on the adaptation of scene and algorithm complexity.The current perception mode of UAV focuses on radar active detection and perception, and there is a problem of time delay in perception information sharing.For this reason, this paper first proposes a waveform library idea based on perceptual information drive to achieve the best cost performance ratio of the communication scheme adopted by UAVs in different flight scenarios.Based on the hybrid waveform concept, this paper proposes a design scheme of active passive fusion synchronous sensing, and matches with an adaptive sensing algorithm based on compressed sensing.Through simulation, it is proved that the overhead caused by sharing perceptual information among UAVs can be reduced, And improve the passive side sensing accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge