Frederic Branchaud-Charron
A Weakly Supervised Region-Based Active Learning Method for COVID-19 Segmentation in CT Images
Jul 07, 2020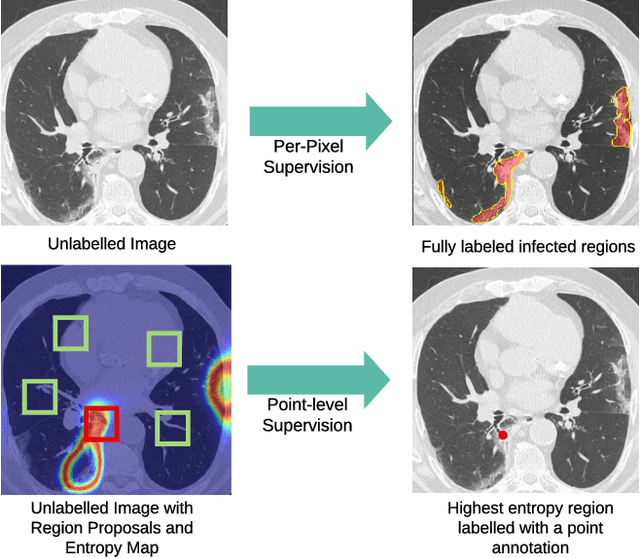
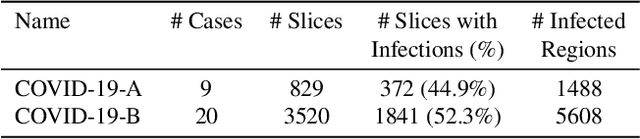
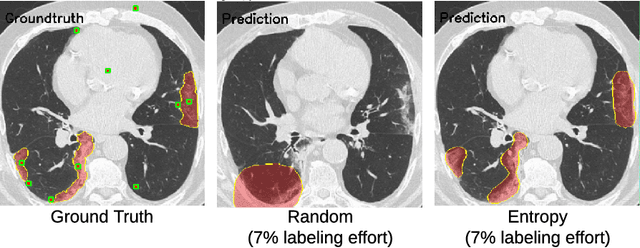
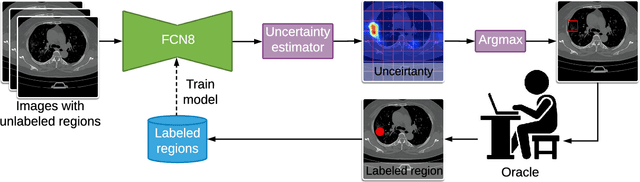
Abstract:One of the key challenges in the battle against the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic is to detect and quantify the severity of the disease in a timely manner. Computed tomographies (CT) of the lungs are effective for assessing the state of the infection. Unfortunately, labeling CT scans can take a lot of time and effort, with up to 150 minutes per scan. We address this challenge introducing a scalable, fast, and accurate active learning system that accelerates the labeling of CT scan images. Conventionally, active learning methods require the labelers to annotate whole images with full supervision, but that can lead to wasted efforts as many of the annotations could be redundant. Thus, our system presents the annotator with unlabeled regions that promise high information content and low annotation cost. Further, the system allows annotators to label regions using point-level supervision, which is much cheaper to acquire than per-pixel annotations. Our experiments on open-source COVID-19 datasets show that using an entropy-based method to rank unlabeled regions yields to significantly better results than random labeling of these regions. Also, we show that labeling small regions of images is more efficient than labeling whole images. Finally, we show that with only 7\% of the labeling effort required to label the whole training set gives us around 90\% of the performance obtained by training the model on the fully annotated training set. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/IssamLaradji/covid19_active_learning}.
Spectral Metric for Dataset Complexity Assessment
May 17, 2019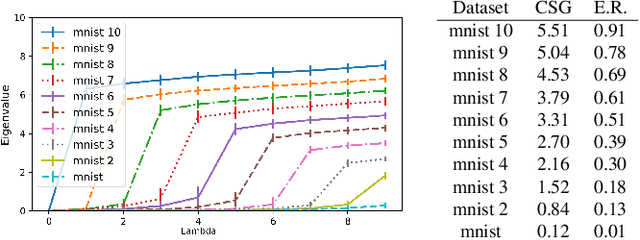
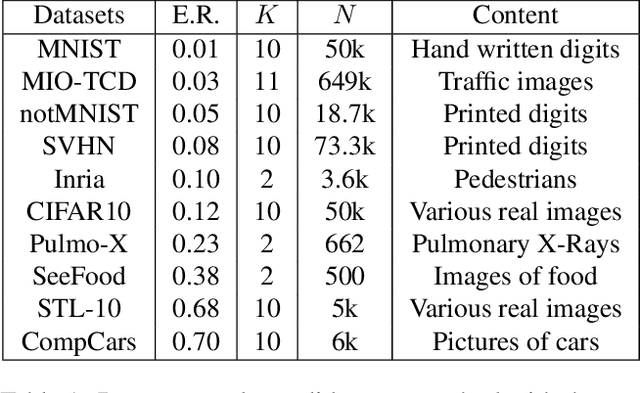
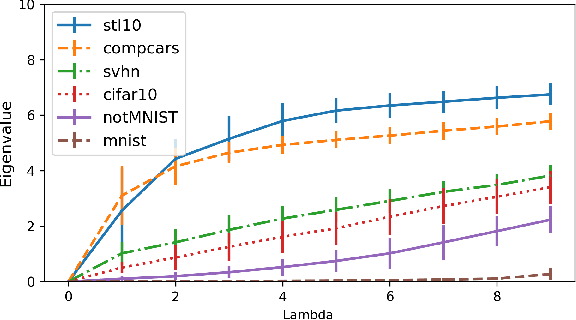
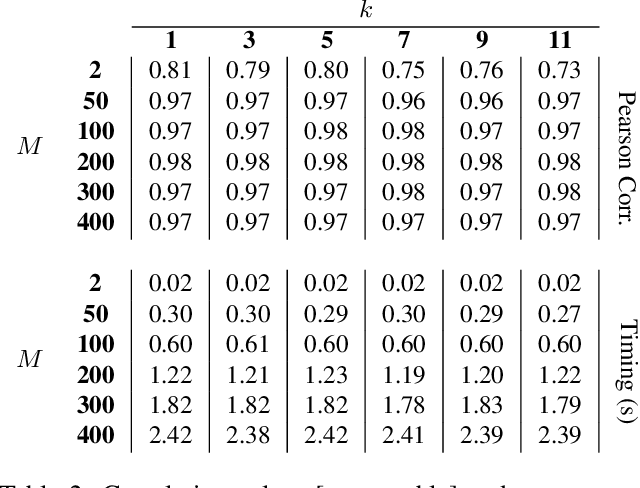
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new measure to gauge the complexity of image classification problems. Given an annotated image dataset, our method computes a complexity measure called the cumulative spectral gradient (CSG) which strongly correlates with the test accuracy of convolutional neural networks (CNN). The CSG measure is derived from the probabilistic divergence between classes in a spectral clustering framework. We show that this metric correlates with the overall separability of the dataset and thus its inherent complexity. As will be shown, our metric can be used for dataset reduction, to assess which classes are more difficult to disentangle, and approximate the accuracy one could expect to get with a CNN. Results obtained on 11 datasets and three CNN models reveal that our method is more accurate and faster than previous complexity measures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge