Francisco Yandun
Evaluating Path Planning Strategies for Efficient Nitrate Sampling in Crop Rows
Mar 10, 2025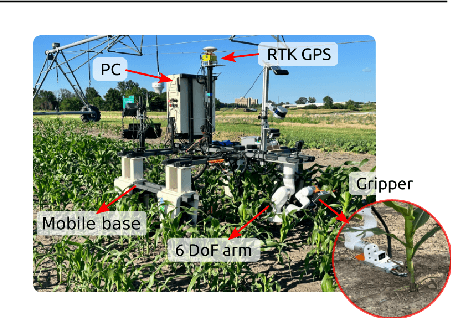
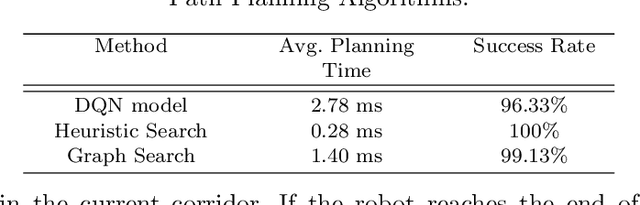
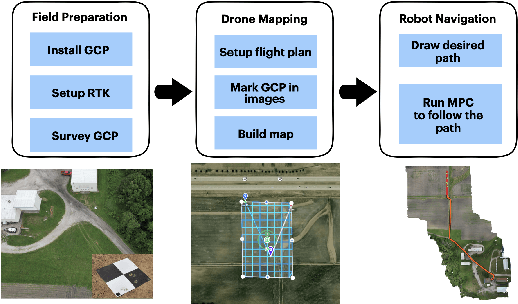
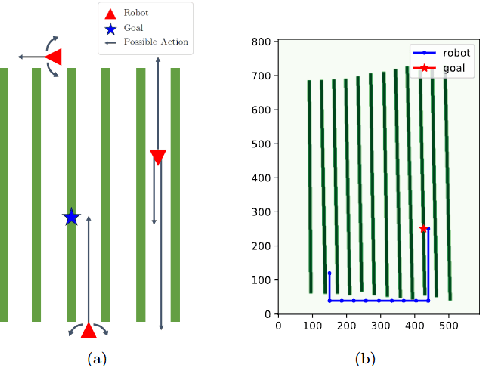
Abstract:This paper presents a pipeline that combines high-resolution orthomosaic maps generated from UAS imagery with GPS-based global navigation to guide a skid-steered ground robot. We evaluated three path planning strategies: A* Graph search, Deep Q-learning (DQN) model, and Heuristic search, benchmarking them on planning time and success rate in realistic simulation environments. Experimental results reveal that the Heuristic search achieves the fastest planning times (0.28 ms) and a 100% success rate, while the A* approach delivers near-optimal performance, and the DQN model, despite its adaptability, incurs longer planning delays and occasional suboptimal routing. These results highlight the advantages of deterministic rule-based methods in geometrically constrained crop-row environments and lay the groundwork for future hybrid strategies in precision agriculture.
SplatSim: Zero-Shot Sim2Real Transfer of RGB Manipulation Policies Using Gaussian Splatting
Sep 16, 2024



Abstract:Sim2Real transfer, particularly for manipulation policies relying on RGB images, remains a critical challenge in robotics due to the significant domain shift between synthetic and real-world visual data. In this paper, we propose SplatSim, a novel framework that leverages Gaussian Splatting as the primary rendering primitive to reduce the Sim2Real gap for RGB-based manipulation policies. By replacing traditional mesh representations with Gaussian Splats in simulators, SplatSim produces highly photorealistic synthetic data while maintaining the scalability and cost-efficiency of simulation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework by training manipulation policies within SplatSim}and deploying them in the real world in a zero-shot manner, achieving an average success rate of 86.25%, compared to 97.5% for policies trained on real-world data.
LiDAR-Based Crop Row Detection Algorithm for Over-Canopy Autonomous Navigation in Agriculture Fields
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous navigation is crucial for various robotics applications in agriculture. However, many existing methods depend on RTK-GPS systems, which are expensive and susceptible to poor signal coverage. This paper introduces a state-of-the-art LiDAR-based navigation system that can achieve over-canopy autonomous navigation in row-crop fields, even when the canopy fully blocks the interrow spacing. Our crop row detection algorithm can detect crop rows across diverse scenarios, encompassing various crop types, growth stages, weed presence, and discontinuities within the crop rows. Without utilizing the global localization of the robot, our navigation system can perform autonomous navigation in these challenging scenarios, detect the end of the crop rows, and navigate to the next crop row autonomously, providing a crop-agnostic approach to navigate the whole row-crop field. This navigation system has undergone tests in various simulated agricultural fields, achieving an average of $2.98cm$ autonomous driving accuracy without human intervention on the custom Amiga robot. In addition, the qualitative results of our crop row detection algorithm from the actual soybean fields validate our LiDAR-based crop row detection algorithm's potential for practical agricultural applications.
Bumblebee: A Path Towards Fully Autonomous Robotic Vine Pruning
Dec 01, 2021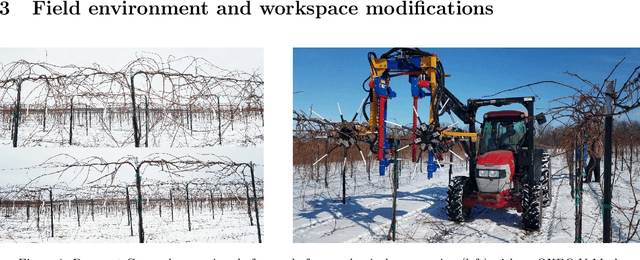

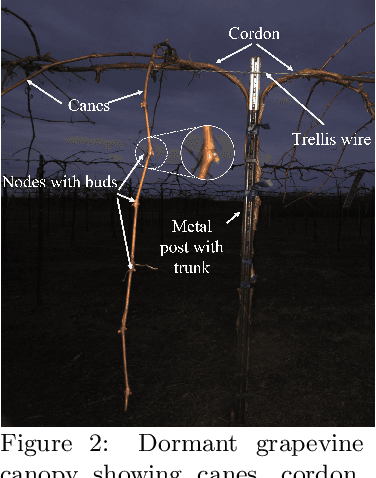
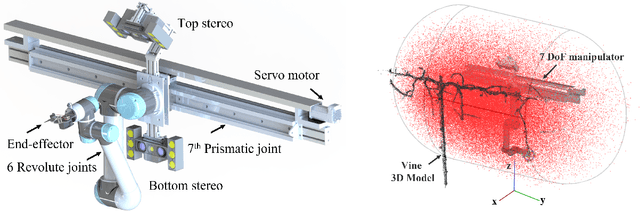
Abstract:Dormant season grapevine pruning requires skilled seasonal workers during the winter season which are becoming less available. As workers hasten to prune more vines in less time amid to the short-term seasonal hiring culture and low wages, vines are often pruned inconsistently leading to imbalanced grapevines. In addition to this, currently existing mechanical methods cannot selectively prune grapevines and manual follow-up operations are often required that further increase production cost. In this paper, we present the design and field evaluation of a rugged, and fully autonomous robot for end-to-end pruning of dormant season grapevines. The proposed design incorporates novel camera systems, a kinematically redundant manipulator, a ground robot, and novel algorithms in the perception system. The presented research prototype robot system was able to spur prune a row of vines from both sides completely in 213 sec/vine with a total pruning accuracy of 87%. Initial field tests of the autonomous system in a commercial vineyard have shown significant variability reduction in dormant season pruning when compared to mechanical pre-pruning trials. The design approach, system components, lessons learned, future enhancements as well as a brief economic analysis are described in the manuscript.
A Robust Illumination-Invariant Camera System for Agricultural Applications
Jan 06, 2021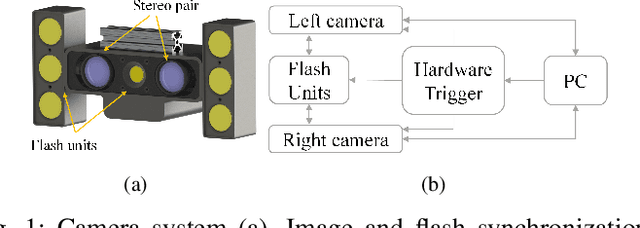
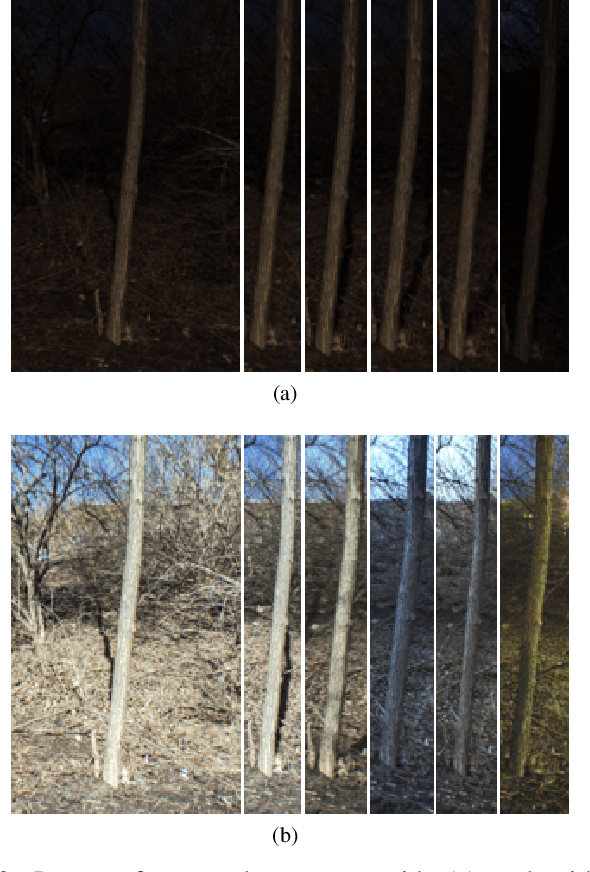

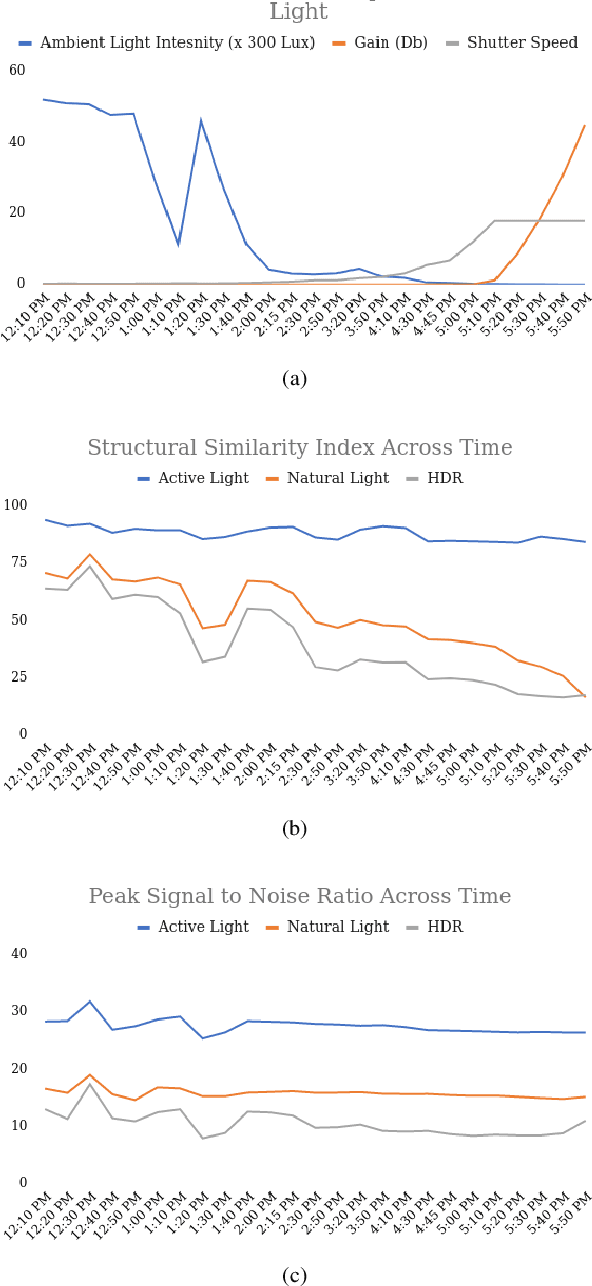
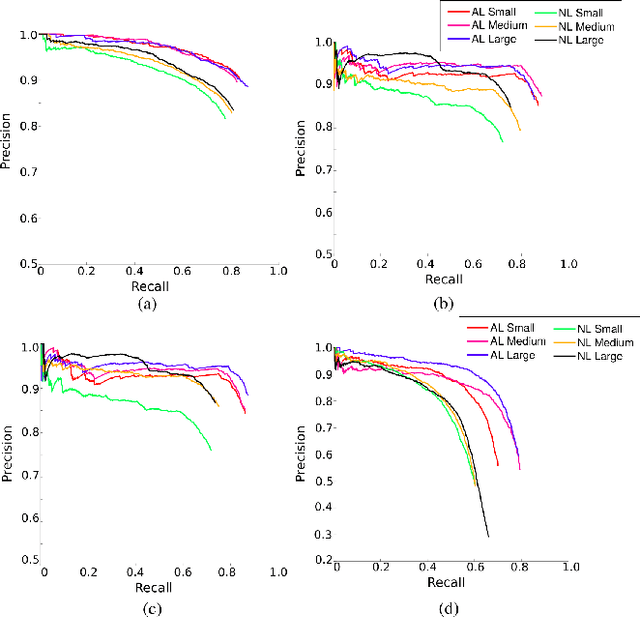
Abstract:Object detection and semantic segmentation are two of the most widely adopted deep learning algorithms in agricultural applications. One of the major sources of variability in image quality acquired in the outdoors for such tasks is changing lighting condition that can alter the appearance of the objects or the contents of the entire image. While transfer learning and data augmentation to some extent reduce the need for large amount of data to train deep neural networks, the large variety of cultivars and the lack of shared datasets in agriculture makes wide-scale field deployments difficult. In this paper, we present a high throughput robust active lighting-based camera system that generates consistent images in all lighting conditions. We detail experiments that show the consistency in images quality leading to relatively fewer images to train deep neural networks for the task of object detection. We further present results from field experiment under extreme lighting conditions where images without active lighting significantly lack to provide consistent results. The experimental results show that on average, deep nets for object detection trained on consistent data required nearly four times less data to achieve similar level of accuracy. This proposed work could potentially provide pragmatic solutions to computer vision needs in agriculture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge