François Aioun
Analysis over vision-based models for pedestrian action anticipation
May 27, 2023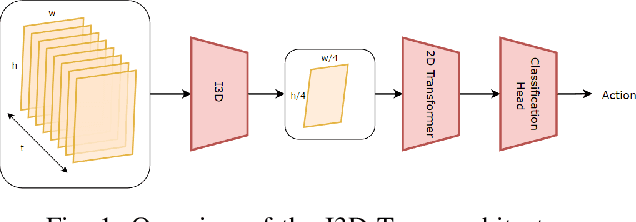
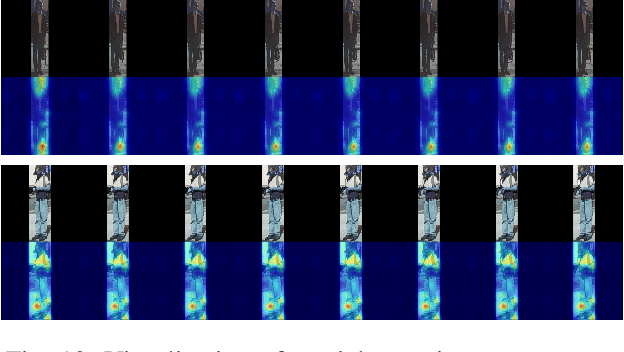
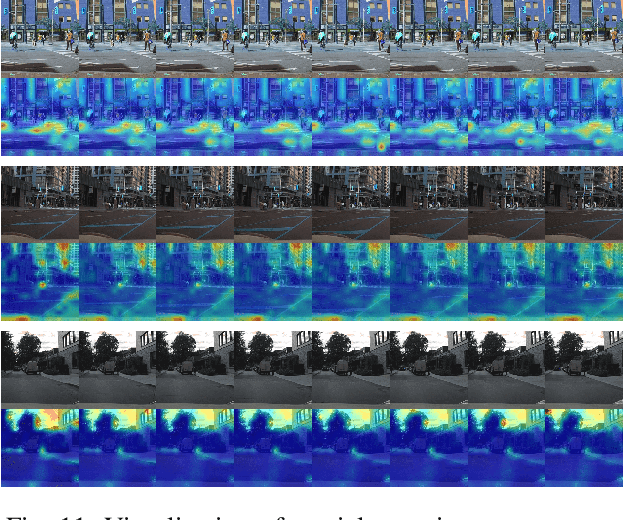
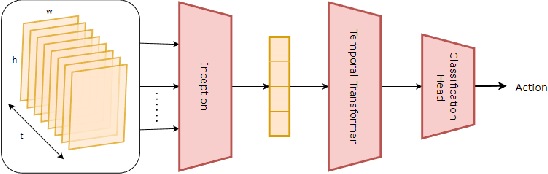
Abstract:Anticipating human actions in front of autonomous vehicles is a challenging task. Several papers have recently proposed model architectures to address this problem by combining multiple input features to predict pedestrian crossing actions. This paper focuses specifically on using images of the pedestrian's context as an input feature. We present several spatio-temporal model architectures that utilize standard CNN and Transformer modules to serve as a backbone for pedestrian anticipation. However, the objective of this paper is not to surpass state-of-the-art benchmarks but rather to analyze the positive and negative predictions of these models. Therefore, we provide insights on the explainability of vision-based Transformer models in the context of pedestrian action prediction. We will highlight cases where the model can achieve correct quantitative results but falls short in providing human-like explanations qualitatively, emphasizing the importance of investing in explainability for pedestrian action anticipation problems.
Learning from Naturalistic Driving Data for Human-like Autonomous Highway Driving
May 23, 2020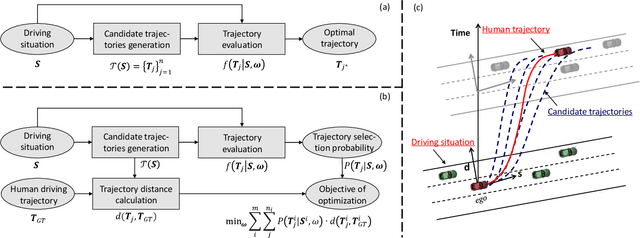
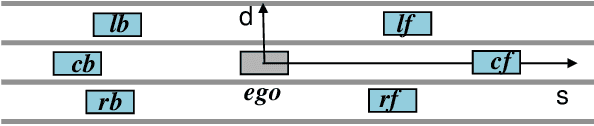
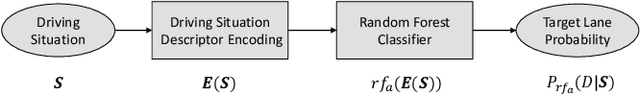
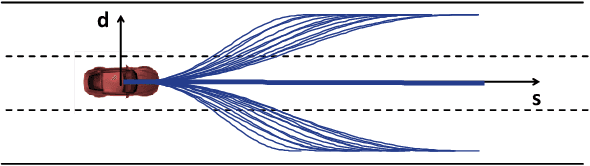
Abstract:Driving in a human-like manner is important for an autonomous vehicle to be a smart and predictable traffic participant. To achieve this goal, parameters of the motion planning module should be carefully tuned, which needs great effort and expert knowledge. In this study, a method of learning cost parameters of a motion planner from naturalistic driving data is proposed. The learning is achieved by encouraging the selected trajectory to approximate the human driving trajectory under the same traffic situation. The employed motion planner follows a widely accepted methodology that first samples candidate trajectories in the trajectory space, then select the one with minimal cost as the planned trajectory. Moreover, in addition to traditional factors such as comfort, efficiency and safety, the cost function is proposed to incorporate incentive of behavior decision like a human driver, so that both lane change decision and motion planning are coupled into one framework. Two types of lane incentive cost -- heuristic and learning based -- are proposed and implemented. To verify the validity of the proposed method, a data set is developed by using the naturalistic trajectory data of human drivers collected on the motorways in Beijing, containing samples of lane changes to the left and right lanes, and car followings. Experiments are conducted with respect to both lane change decision and motion planning, and promising results are achieved.
Driver Identification through Stochastic Multi-State Car-Following Modeling
May 22, 2020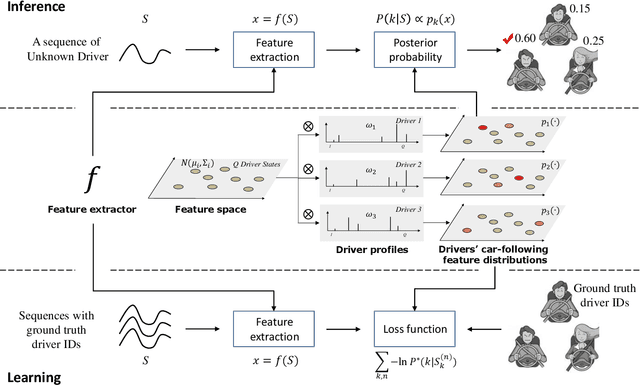
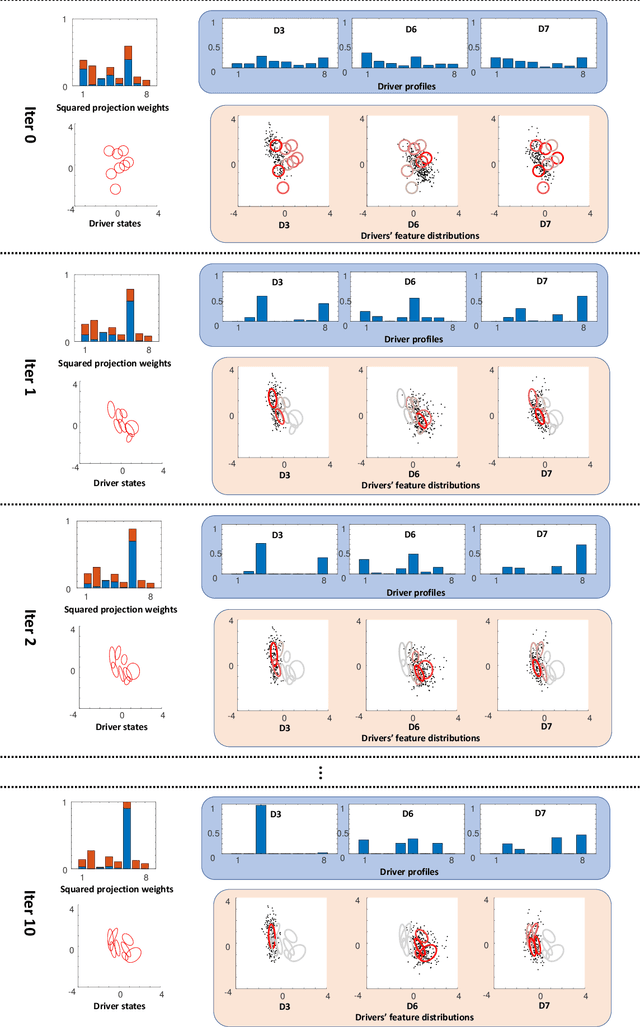
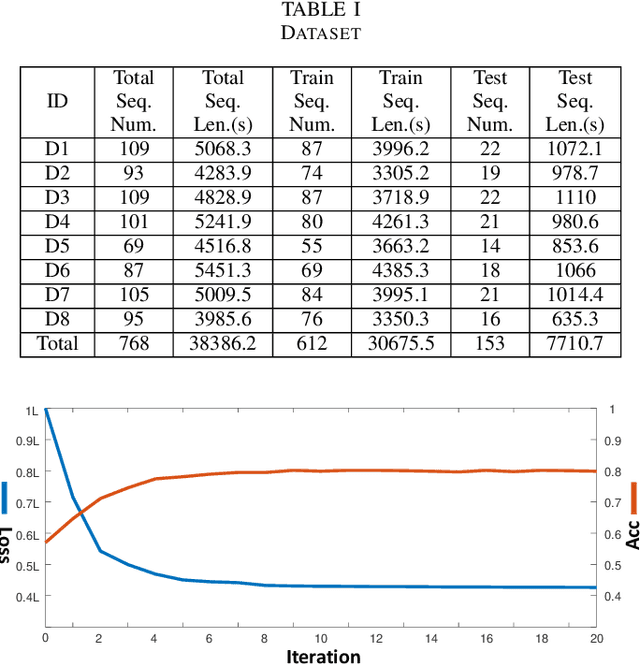
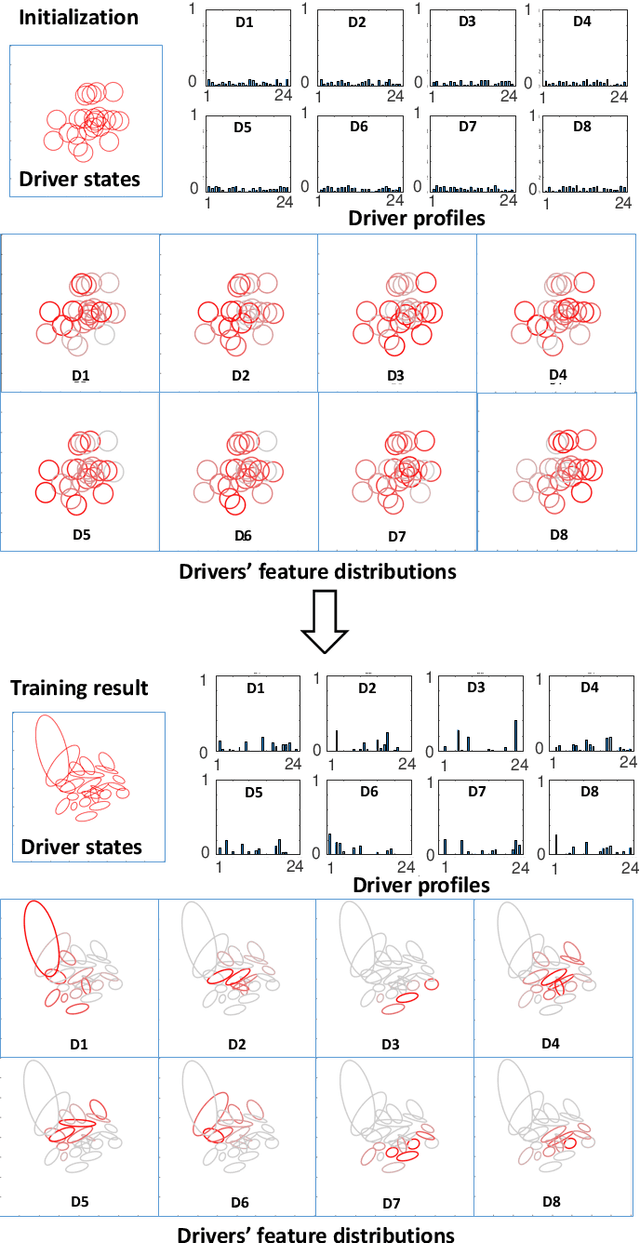
Abstract:Intra-driver and inter-driver heterogeneity has been confirmed to exist in human driving behaviors by many studies. In this study, a joint model of the two types of heterogeneity in car-following behavior is proposed as an approach of driver profiling and identification. It is assumed that all drivers share a pool of driver states; under each state a car-following data sequence obeys a specific probability distribution in feature space; each driver has his/her own probability distribution over the states, called driver profile, which characterize the intradriver heterogeneity, while the difference between the driver profile of different drivers depict the inter-driver heterogeneity. Thus, the driver profile can be used to distinguish a driver from others. Based on the assumption, a stochastic car-following model is proposed to take both intra-driver and inter-driver heterogeneity into consideration, and a method is proposed to jointly learn parameters in behavioral feature extractor, driver states and driver profiles. Experiments demonstrate the performance of the proposed method in driver identification on naturalistic car-following data: accuracy of 82.3% is achieved in an 8-driver experiment using 10 car-following sequences of duration 15 seconds for online inference. The potential of fast registration of new drivers are demonstrated and discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge