Fatemeh Nazary
ViLLA-MMBench: A Unified Benchmark Suite for LLM-Augmented Multimodal Movie Recommendation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Recommending long-form video content demands joint modeling of visual, audio, and textual modalities, yet most benchmarks address only raw features or narrow fusion. We present ViLLA-MMBench, a reproducible, extensible benchmark for LLM-augmented multimodal movie recommendation. Built on MovieLens and MMTF-14K, it aligns dense item embeddings from three modalities: audio (block-level, i-vector), visual (CNN, AVF), and text. Missing or sparse metadata is automatically enriched using state-of-the-art LLMs (e.g., OpenAI Ada), generating high-quality synopses for thousands of movies. All text (raw or augmented) is embedded with configurable encoders (Ada, LLaMA-2, Sentence-T5), producing multiple ready-to-use sets. The pipeline supports interchangeable early-, mid-, and late-fusion (concatenation, PCA, CCA, rank-aggregation) and multiple backbones (MF, VAECF, VBPR, AMR, VMF) for ablation. Experiments are fully declarative via a single YAML file. Evaluation spans accuracy (Recall, nDCG) and beyond-accuracy metrics: cold-start rate, coverage, novelty, diversity, fairness. Results show LLM-based augmentation and strong text embeddings boost cold-start and coverage, especially when fused with audio-visual features. Systematic benchmarking reveals universal versus backbone- or metric-specific combinations. Open-source code, embeddings, and configs enable reproducible, fair multimodal RS research and advance principled generative AI integration in large-scale recommendation. Code: https://recsys-lab.github.io/ViLLA-MMBench
RAG-VisualRec: An Open Resource for Vision- and Text-Enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Recommendation
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of developing multimodal recommender systems for the movie domain, where limited metadata (e.g., title, genre) often hinders the generation of robust recommendations. We introduce a resource that combines LLM-generated plot descriptions with trailer-derived visual embeddings in a unified pipeline supporting both Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and collaborative filtering. Central to our approach is a data augmentation step that transforms sparse metadata into richer textual signals, alongside fusion strategies (e.g., PCA, CCA) that integrate visual cues. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that CCA-based fusion significantly boosts recall compared to unimodal baselines, while an LLM-driven re-ranking step further improves NDCG, particularly in scenarios with limited textual data. By releasing this framework, we invite further exploration of multi-modal recommendation techniques tailored to cold-start, novelty-focused, and domain-specific settings. All code, data, and detailed documentation are publicly available at: https://github.com/RecSys-lab/RAG-VisualRec
Stealthy LLM-Driven Data Poisoning Attacks Against Embedding-Based Retrieval-Augmented Recommender Systems
May 08, 2025Abstract:We present a systematic study of provider-side data poisoning in retrieval-augmented recommender systems (RAG-based). By modifying only a small fraction of tokens within item descriptions -- for instance, adding emotional keywords or borrowing phrases from semantically related items -- an attacker can significantly promote or demote targeted items. We formalize these attacks under token-edit and semantic-similarity constraints, and we examine their effectiveness in both promotion (long-tail items) and demotion (short-head items) scenarios. Our experiments on MovieLens, using two large language model (LLM) retrieval modules, show that even subtle attacks shift final rankings and item exposures while eluding naive detection. The results underscore the vulnerability of RAG-based pipelines to small-scale metadata rewrites and emphasize the need for robust textual consistency checks and provenance tracking to thwart stealthy provider-side poisoning.
Poison-RAG: Adversarial Data Poisoning Attacks on Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Recommender Systems
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:This study presents Poison-RAG, a framework for adversarial data poisoning attacks targeting retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-based recommender systems. Poison-RAG manipulates item metadata, such as tags and descriptions, to influence recommendation outcomes. Using item metadata generated through a large language model (LLM) and embeddings derived via the OpenAI API, we explore the impact of adversarial poisoning attacks on provider-side, where attacks are designed to promote long-tail items and demote popular ones. Two attack strategies are proposed: local modifications, which personalize tags for each item using BERT embeddings, and global modifications, applying uniform tags across the dataset. Experiments conducted on the MovieLens dataset in a black-box setting reveal that local strategies improve manipulation effectiveness by up to 50\%, while global strategies risk boosting already popular items. Results indicate that popular items are more susceptible to attacks, whereas long-tail items are harder to manipulate. Approximately 70\% of items lack tags, presenting a cold-start challenge; data augmentation and synthesis are proposed as potential defense mechanisms to enhance RAG-based systems' resilience. The findings emphasize the need for robust metadata management to safeguard recommendation frameworks. Code and data are available at https://github.com/atenanaz/Poison-RAG.
XAI4LLM. Let Machine Learning Models and LLMs Collaborate for Enhanced In-Context Learning in Healthcare
May 10, 2024Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into healthcare diagnostics offers a promising avenue for clinical decision-making. This study outlines the development of a novel method for zero-shot/few-shot in-context learning (ICL) by integrating medical domain knowledge using a multi-layered structured prompt. We also explore the efficacy of two communication styles between the user and LLMs: the Numerical Conversational (NC) style, which processes data incrementally, and the Natural Language Single-Turn (NL-ST) style, which employs long narrative prompts. Our study systematically evaluates the diagnostic accuracy and risk factors, including gender bias and false negative rates, using a dataset of 920 patient records in various few-shot scenarios. Results indicate that traditional clinical machine learning (ML) models generally outperform LLMs in zero-shot and few-shot settings. However, the performance gap narrows significantly when employing few-shot examples alongside effective explainable AI (XAI) methods as sources of domain knowledge. Moreover, with sufficient time and an increased number of examples, the conversational style (NC) nearly matches the performance of ML models. Most notably, LLMs demonstrate comparable or superior cost-sensitive accuracy relative to ML models. This research confirms that, with appropriate domain knowledge and tailored communication strategies, LLMs can significantly enhance diagnostic processes. The findings highlight the importance of optimizing the number of training examples and communication styles to improve accuracy and reduce biases in LLM applications.
ChatGPT-HealthPrompt. Harnessing the Power of XAI in Prompt-Based Healthcare Decision Support using ChatGPT
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:This study presents an innovative approach to the application of large language models (LLMs) in clinical decision-making, focusing on OpenAI's ChatGPT. Our approach introduces the use of contextual prompts-strategically designed to include task description, feature description, and crucially, integration of domain knowledge-for high-quality binary classification tasks even in data-scarce scenarios. The novelty of our work lies in the utilization of domain knowledge, obtained from high-performing interpretable ML models, and its seamless incorporation into prompt design. By viewing these ML models as medical experts, we extract key insights on feature importance to aid in decision-making processes. This interplay of domain knowledge and AI holds significant promise in creating a more insightful diagnostic tool. Additionally, our research explores the dynamics of zero-shot and few-shot prompt learning based on LLMs. By comparing the performance of OpenAI's ChatGPT with traditional supervised ML models in different data conditions, we aim to provide insights into the effectiveness of prompt engineering strategies under varied data availability. In essence, this paper bridges the gap between AI and healthcare, proposing a novel methodology for LLMs application in clinical decision support systems. It highlights the transformative potential of effective prompt design, domain knowledge integration, and flexible learning approaches in enhancing automated decision-making.
Machine-learned Adversarial Attacks against Fault Prediction Systems in Smart Electrical Grids
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:In smart electrical grids, fault detection tasks may have a high impact on society due to their economic and critical implications. In the recent years, numerous smart grid applications, such as defect detection and load forecasting, have embraced data-driven methodologies. The purpose of this study is to investigate the challenges associated with the security of machine learning (ML) applications in the smart grid scenario. Indeed, the robustness and security of these data-driven algorithms have not been extensively studied in relation to all power grid applications. We demonstrate first that the deep neural network method used in the smart grid is susceptible to adversarial perturbation. Then, we highlight how studies on fault localization and type classification illustrate the weaknesses of present ML algorithms in smart grids to various adversarial attacks
A Review of Modern Fashion Recommender Systems
Feb 06, 2022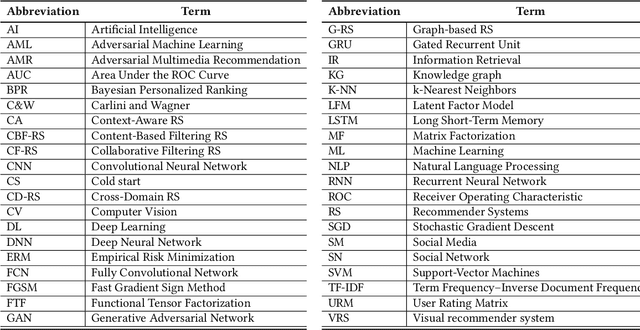

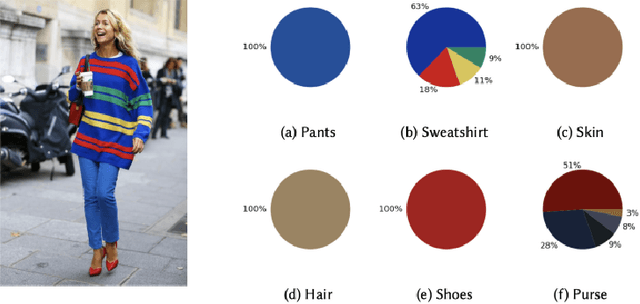
Abstract:The textile and apparel industries have grown tremendously over the last years. Customers no longer have to visit many stores, stand in long queues, or try on garments in dressing rooms as millions of products are now available in online catalogs. However, given the plethora of options available, an effective recommendation system is necessary to properly sort, order, and communicate relevant product material or information to users. Effective fashion RS can have a noticeable impact on billions of customers' shopping experiences and increase sales and revenues on the provider-side. The goal of this survey is to provide a review of recommender systems that operate in the specific vertical domain of garment and fashion products. We have identified the most pressing challenges in fashion RS research and created a taxonomy that categorizes the literature according to the objective they are trying to accomplish (e.g., item or outfit recommendation, size recommendation, explainability, among others) and type of side-information (users, items, context). We have also identified the most important evaluation goals and perspectives (outfit generation, outfit recommendation, pairing recommendation, and fill-in-the-blank outfit compatibility prediction) and the most commonly used datasets and evaluation metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge