Eun Kyoung Choe
Taking a Language Detour: How International Migrants Speaking a Minority Language Seek COVID-Related Information in Their Host Countries
Sep 07, 2022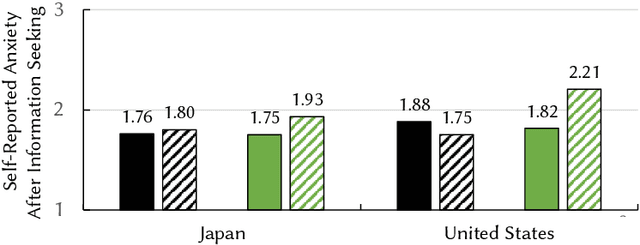
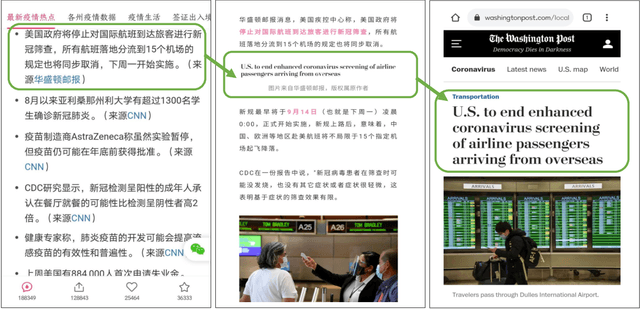
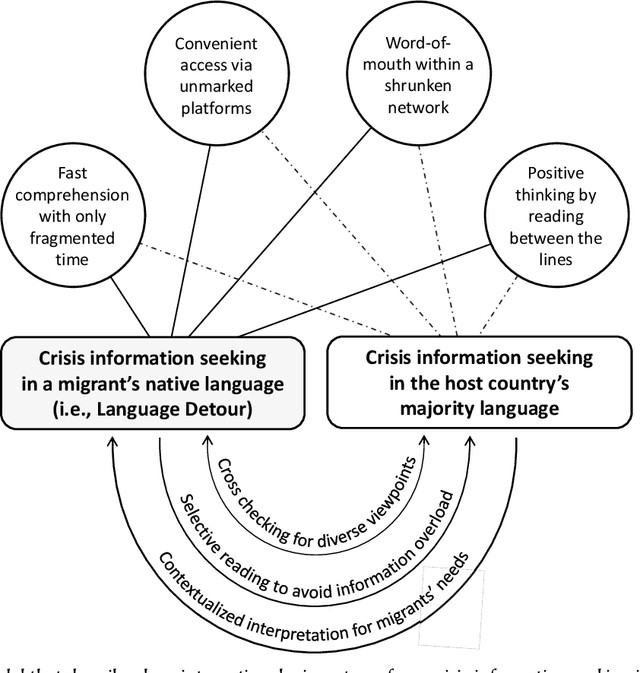
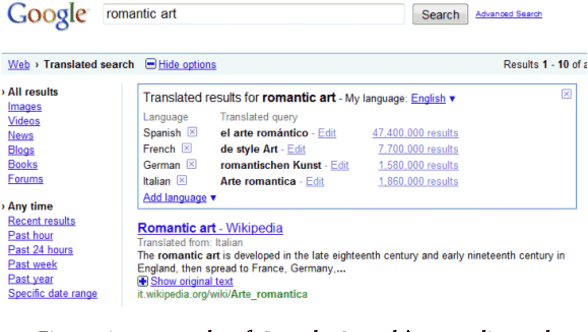
Abstract:Information seeking is crucial for people's self-care and wellbeing in times of public crises. Extensive research has investigated empirical understandings as well as technical solutions to facilitate information seeking by domestic citizens of affected regions. However, limited knowledge is established to support international migrants who need to survive a crisis in their host countries. The current paper presents an interview study with two cohorts of Chinese migrants living in Japan (N=14) and the United States (N=14). Participants reflected on their information seeking experiences during the COVID pandemic. The reflection was supplemented by two weeks of self-tracking where participants maintained records of their COVIDrelated information seeking practice. Our data indicated that participants often took language detours, or visits to Mandarin resources for information about the COVID outbreak in their host countries. They also made strategic use of the Mandarin information to perform selective reading, cross-checking, and contextualized interpretation of COVID-related information in Japanese or English. While such practices enhanced participants' perceived effectiveness of COVID-related information gathering and sensemaking, they disadvantaged people through sometimes incognizant ways. Further, participants lacked the awareness or preference to review migrant-oriented information that was issued by the host country's public authorities despite its availability. Building upon these findings, we discussed solutions to improve international migrants' COVID-related information seeking in their non-native language and cultural environment. We advocated inclusive crisis infrastructures that would engage people with diverse levels of local language fluency, information literacy, and experience in leveraging public services.
MyMove: Facilitating Older Adults to Collect In-Situ Activity Labels on a Smartwatch with Speech
Apr 01, 2022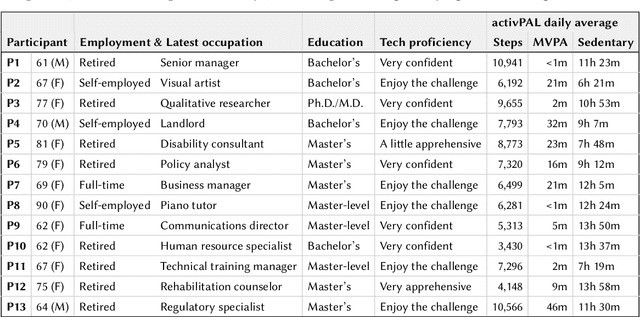

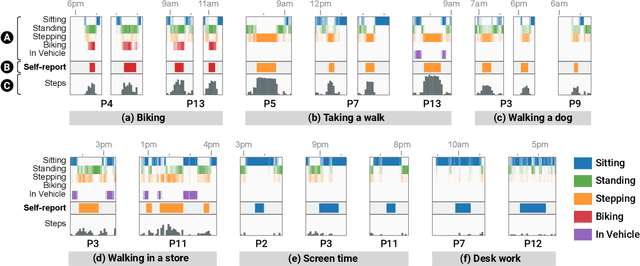
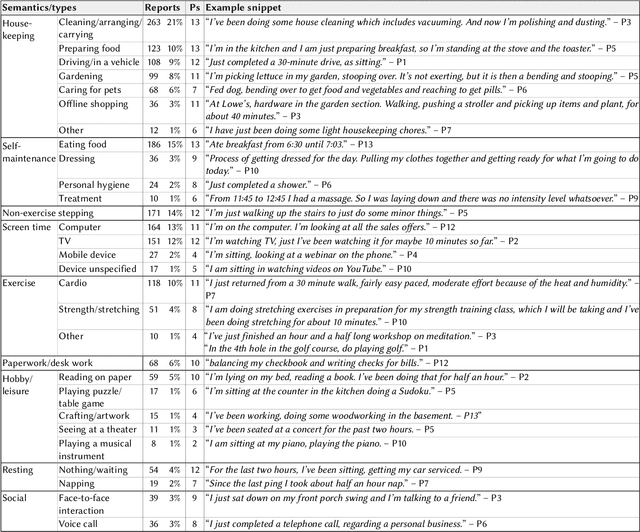
Abstract:Current activity tracking technologies are largely trained on younger adults' data, which can lead to solutions that are not well-suited for older adults. To build activity trackers for older adults, it is crucial to collect training data with them. To this end, we examine the feasibility and challenges with older adults in collecting activity labels by leveraging speech. Specifically, we built MyMove, a speech-based smartwatch app to facilitate the in-situ labeling with a low capture burden. We conducted a 7-day deployment study, where 13 older adults collected their activity labels and smartwatch sensor data, while wearing a thigh-worn activity monitor. Participants were highly engaged, capturing 1,224 verbal reports in total. We extracted 1,885 activities with corresponding effort level and timespan, and examined the usefulness of these reports as activity labels. We discuss the implications of our approach and the collected dataset in supporting older adults through personalized activity tracking technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge